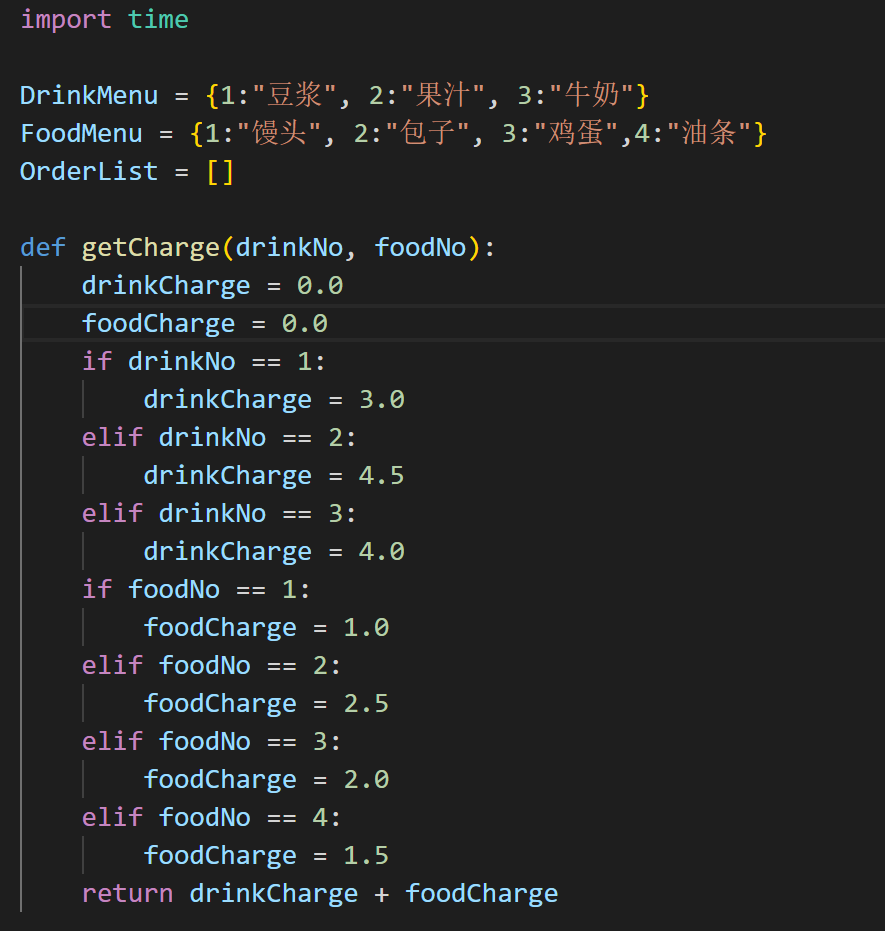
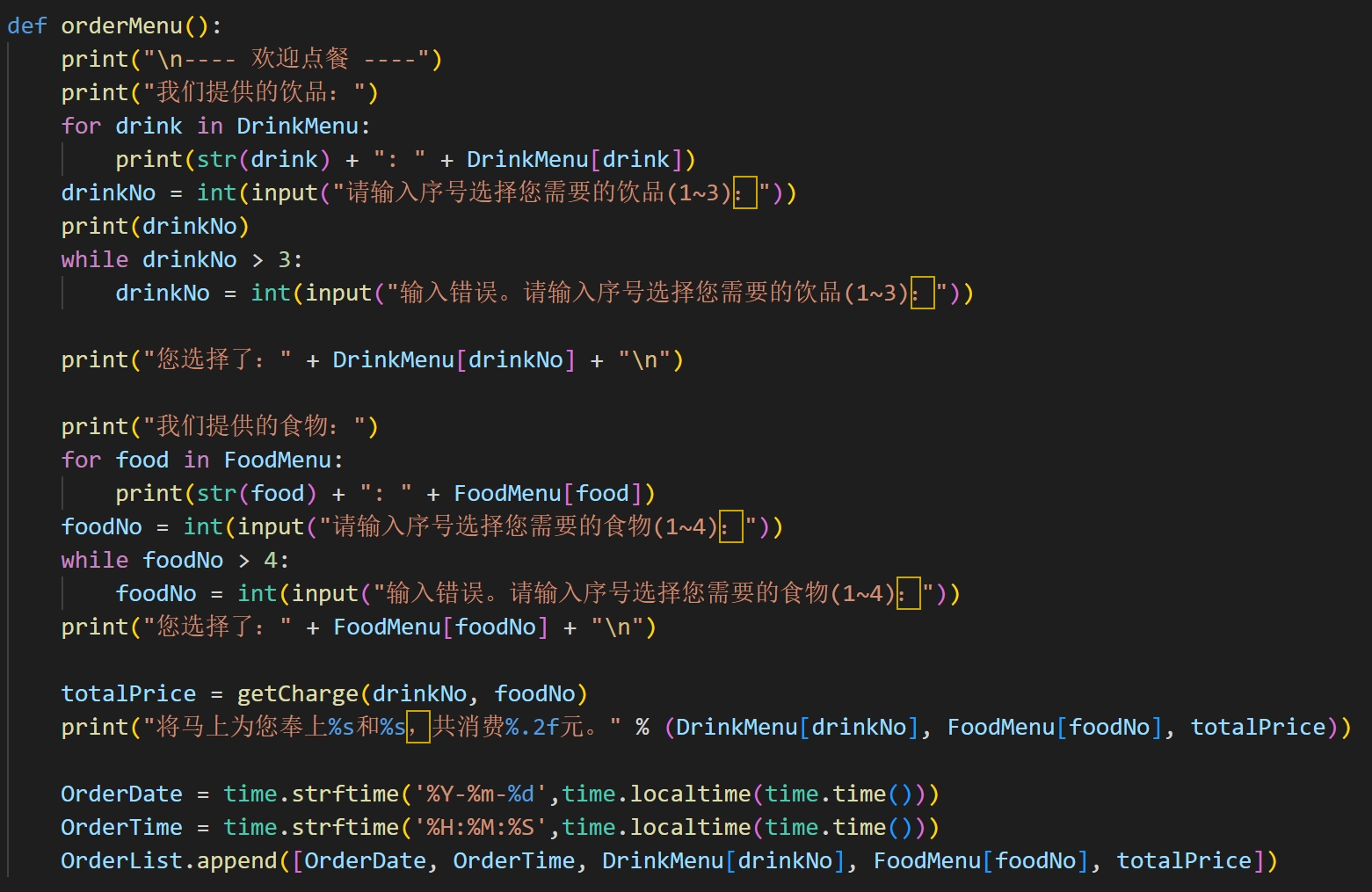
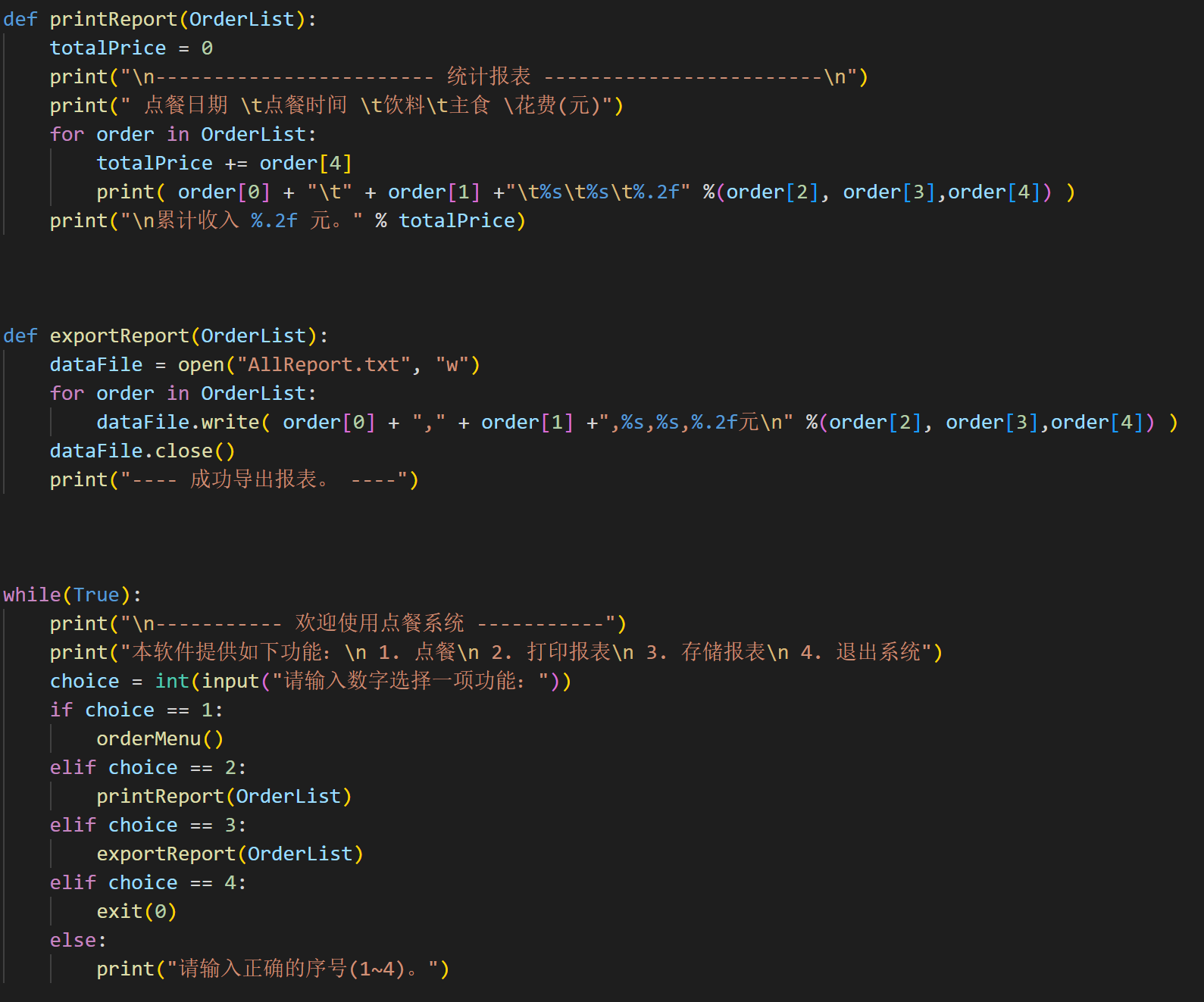
## 3.1推导式练习
给定一个包含5个英语单词的列表,请构造1个字典以列表的元素为键,以每个键对应的单词字母个数为值。
~~~
en_list = ["apple", "banana", "peach", "pineapple", "watermelon"]
~~~
~~~
en_dict = {word: len(word) for word in en_list}
en_dict
~~~
## 3.4 练习:for循环和控制台打印
```
# 假设有三名学生
students = ["小明", "小红", "小刚"]
# 每位学生的分数
scores = [90, 85, 78]
# 开始打印报告卡
print("学生分数报告卡:")
# 对于每一个学生,进行一次循环
for i in range(len(students)):
# 获取学生的名字和分数
student_name = students[i]
score = scores[i]
# 打印学生的名字和分数
print(f"{student_name}的分数是:{score}分")
# 结束打印报告卡
print("报告卡打印完毕!")
```
## 3.6 列表练习:计算销售额
```
# 假设每天售出的商品和数量如下
sales = [
{"product": "苹果", "quantity": 10, "price": 5},
{"product": "香蕉", "quantity": 8, "price": 3},
{"product": "橙子", "quantity": 12, "price": 4},
]
# 计算总销售额
total_sales = 0
# 对于每一天的销售记录,进行一次循环
for sale in sales:
# 获取商品的数量和价格
quantity = sale["quantity"]
price = sale["price"]
# 计算当天的销售额
daily_sales = quantity * price
# 累加到总销售额
total_sales += daily_sales
# 打印当天的销售额
print(f"{sale['product']}的销售额是:{daily_sales}元")
# 打印总销售额
print("总销售额是:", total_sales, "元")
```
## 3.7 列表的切片的练习
```
# 食材列表
food_list = ["葱", "姜", "蒜", "料酒", "猪肝", "大闸蟹", "鸡丁", "花生米", "酱油", "淀粉"]
# 获取所需食材
selected_food1 = food_list[0:4]
selected_food2 = food_list[-4:]
select_list = selected_food1+selected_food2
# 打印选中的食材
print("您选中的食材是:")
for food in select_list:
print(food)
```
## 3.8列表组成字典
```
list_food=["腰子","辣子","和牛","大闸蟹","黑虎虾","西兰花"]
list_price=[68,0.5,128,60,40,12]
list = {}
for food,price in zip(list_food,list_price):
list[food] = price
list
```
## 3.8 zip函数练习
```
# 步骤 1: 创建一个包含客人名字和喜好的字典
guests = [
"老王",
"老马",
"老陈",
"李小宝",
"小林"
]
likes=[
"川菜",
"西式快餐",
"南通菜",
"东北菜",
"法餐"
]
feeds = [
"钵钵鸡",
"巨无霸汉堡",
"南通头菜",
"锅包肉",
"红酒鹅肝"
]
# 步骤 3: 使用 zip 函数将客人和他们的喜好配对,并打印出来
preferences = list(zip(guests, likes))
print("客人的喜好:")
for guest, preference in preferences:
print(f"{guest} 喜欢 {preference}")
# 步骤 4: 使用 zip 函数将客人和菜品配对,并创建一个新的字典
feeds_for_guests = list(zip(guests, gifts))
# 步骤 5: 打印新的字典,查看每个客人将收到的礼物
print("\n客人点的菜:")
for guest, feeds in feeds_for_guests:
print(f"{guest} 点了 {feeds}")
```
## 3.8 字典——练习
```
# 创建一个空的菜单字典
menu = {
"宫保鸡丁": 35.0,
"麻婆豆腐": 28.0,
"清蒸鱼": 45.0,
"炒时蔬": 20.0,
"米饭": 5.0
}
# 创建一个空的订单字典
order = {}
def add_to_order(dish_name):
"""将菜品添加到订单中"""
if dish_name in menu:
if dish_name in order:
order[dish_name] += 1
else:
order[dish_name] = 1
else:
print("该菜品不在菜单中。")
def remove_from_order(dish_name):
"""从订单中删除菜品"""
if dish_name in order:
if order[dish_name] > 1:
order[dish_name] -= 1
else:
del order[dish_name]
else:
print("订单中不存在该菜品。")
def calculate_total():
"""计算订单的总价"""
total = sum(menu[dish] * quantity for dish, quantity in order.items())
return total
def view_order():
"""查看订单详情"""
if order:
print("订单详情:")
for dish, quantity in order.items():
print(f"{dish}: {quantity} 份")
print(f"总价: {calculate_total()} 元")
else:
print("订单为空。")
# 示例使用
add_to_order("宫保鸡丁")
add_to_order("清蒸鱼")
add_to_order("炒时蔬")
view_order()
remove_from_order("清蒸鱼")
view_order()
print(f"最终订单总价: {calculate_total()} 元")
```
## 3.9 集合的练习
```
# 你的购物清单
your_list = {"烤鸭", "篮球鞋", "iphone15", "牛肉卷", "提拉米苏"}
# 朋友的购物清单
friend_list = {"烤鸭", "牛奶", "鸡蛋", "牛肉卷"}
# 使用并集操作合并清单
combined_list = your_list.union(friend_list)
print("合并后的购物清单:", combined_list)
# 使用交集操作找出共同想购买的物品
common_items = your_list.intersection(friend_list)
print("共同想购买的物品:", common_items)
```
## 项目2