[TOC]
# 原型与继承
## 原型与原型链

- `prototype`: 每个函数都有一个 prototype(原型)属性,这个属性是一个指针,指向一个对象,而这个对象的用途是包含可以由特定类型的所有实例共享的属性和方法,如果使用这个函数生成了实例,那么称这个对象为所有实例的原型。
- `__proto__`: 每个对象都拥有`__proto__`属性,该属性用于实现原型链,当访问一个对象的属性时,如果该对象内部不存在这个属性,就通过原型链找直到找到或者到终点 null。
- `constructor`:每个原型都有一个 constructor 属性指向关联的构造函数
## Object() 与 Function()
所有的对象都是由 Object() 构造函数构造的,所有的函数声明 / 函数表达式都是 Function() 构造函数的实例,而 Object() 构造函数本身又是 Function() 构造函数的实例,其原型关系如下:
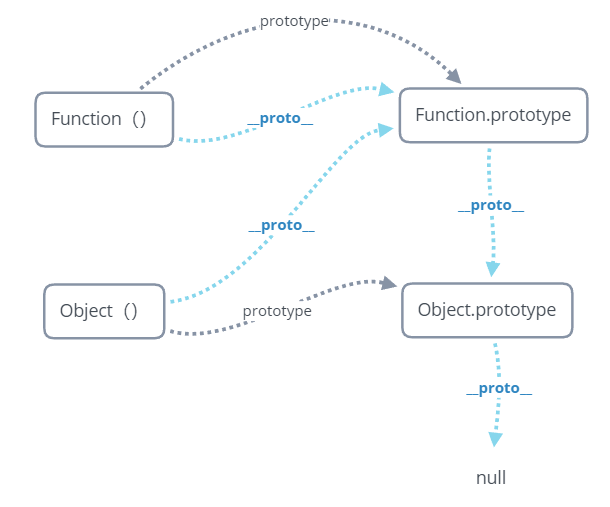
需要注意的是 Function() 的`__proto__ `属性直接指向的是其原型对象。
我们可以用下面的代码来验证这张图:在 node 环境及浏览器环境下都是一样的结果
```js
console.log(Object.__proto__ === Function.prototype) // true
console.log(Function.__proto__ === Function.prototype) // true
console.log(Function.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__ === null) // true
```
## 继承
首先要理解构造函数 new 时执行了哪些操作
1. 创建一个新对象,并做原型绑定(该对象的 \_\_proto\_\_ 属性指向构造函数的 prototype 属性指向的对象)
2. 将 this 绑定到这个新对象上
3. 执行构造函数中的代码(为这个新对象添加属性)
4. 返回新对象(一般情况下,构造函数不返回值,但是用户可以选择主动返回对象,来覆盖正常的对象创建步骤)
模拟实现 new
```js
function _new (fn, ...args) {
const obj = {}
obj.__proto__ = fn.prototype
fn.apply(obj, args)
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]' ? obj : {}
}
```
### 借用构造函数
在构造函数中使用 Parent.call(this) 的方法继承父类属性。
原理: 将子类的 this 使用父类的构造函数跑一遍
缺点: Parent 原型链上的属性和方法并不会被子类继承(子类连接不到父类)
``` javaScript
function Parent () {
this.name = 'parent'
}
Parent.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log('say Hello')
}
function Child () {
Parent.call(this) //函数名.call 调用这个函数但是更改其 this
this.type = 'child'
}
let p1 = new Parent()
let c1 = new Child()
p1.sayHello() // 'say Hello'
c1.sayHello() // error c1.sayHello is not a function
```
### 原型链实现继承
原理:把子类的 prototype(原型对象)直接设置为父类的实例
缺点:因为子类只进行一次原型更改,所以子类的所有实例保存的是同一个父类的值。 当子类对象上进行值修改时,如果是修改的原始类型的值,那么会在实例上新建这样一个值; 但如果是引用类型的话,他就会去修改子类上唯一一个父类实例里面的这个引用类型,这会影响所有子类实例(一句话:子类修改原型上的引用类型会影响父类)
``` javaScript
function Parent () {
this.name = 'parent'
this.arr = [1,2,3]
}
function Child () {
this.type = 'child'
}
Child.prototype = new Parent() // 拥有了这个 Parent 实例上的属性和方法
```
通过下面这个例子来观察该方法的缺点
```
function Parent () {
this.names = ['kevin', 'daisy'];
}
function Child () {
}
Child.prototype = new Parent()
var child1 = new Child()
child1.names.push('yayu')
console.log(child1.names) // ["kevin", "daisy", "yayu"]
var child2 = new Child()
console.log(child2.names) // ["kevin", "daisy", "yayu"]
```
### 组合继承方式(上面两种方法的配合)
组合构造函数中使用 call 继承和原型链继承。
原理: 子类构造函数中使用 Parent.call(this) 的方式可以继承写在父类构造函数中 this 上绑定的各属性和方法; 使用 Child.prototype = new Parent() 的方式可以继承挂载在父类原型上的各属性和方法
缺点: 父类构造函数在子类构造函数中执行了一次,在子类绑定原型时又执行了一次
``` js
function Parent () {
this.name = 'parent'
this.arr = [1,2,3]
}
function Child () {
Parent.call(this) // 继承 Parent 构造函数上的属性和方法
this.type = 'child'
}
Child.prototype = new Parent(); // 继承 Parent 的父类原型上的属性和方法
```
### 组合继承方式优化
使用 Object.create() 方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象(参数)来提供新创建的对象的 \_\_proto\_\_
``` js
function Parent () {
this.name = 'parent'
this.arr = [1,2,3]
}
function Child() {
Parent.call(this)
this.type = 'child'
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype) // 提供__proto__
Child.prototype.constructor = Child
```
这种方式也叫寄生组合式继承,相比于之前的组合继承方式,其减少了一次父类构造函数的调用,如果不使用 Object.create() 方法,有时候也会这么封装:
```js
function object (o) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = o
return new F()
}
function prototype (child, parent) {
var prototype = object(parent.prototype)
prototype.constructor = child
child.prototype = prototype
}
// 当我们使用的时候:
prototype(Child, Parent)
```
### ES6 实现继承
ES6 的 Class 相当于构造函数的语法糖,extends 也是语法糖,其本质还是通过原型链实现继承
``` js
// Extends 关键字配合 Class 实现继承
class People { // 定义一个类 People
constructor(name) { // constructor 函数,必须存在,接收实例化参数
this.name = name
}
getName() {
console.log(this.name) // 类的属性
}
}
class Student extends People { // Student 类继承 People 类
constructor(name, grade) { // 声明 constructor 方法
super(name) // 执行父类的构造函数 相当于 People.prototype.constructor.call(this)
this.grade = grade
}
getGrade() { // Student 类的属性
console.log(this.grade)
}
}
let s = new Student('Tom', 6) // 实例化 Student 类
s.getName() // 调用继承的属性,输出'Tom'
s.getGrade()
```
ES5 的继承实质是先创造子类的实例对象 this,然后再将父类的方法添加到 this 上面。ES6 的继承机制是先创造父类的实例对象 this(所以必须先调用 super 方法),然后再将子类的构造函数修改 this
ES5 的寄生组合式继承:
```js
function Parent (name) {
this.name = name
}
function Child (name, age) {
Parent.call(this, name)
this.age = age
}
Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype)
var child1 = new Child('kevin', '18')
console.log(child1)
```
对应的 ES6 的 class:
```js
class Parent {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name) // 调用父类的 constructor(name)
this.age = age
}
}
let child1 = new Child('kevin', '18')
console.log(child1)
```
对应的原型链示意图为:
<img src="https://box.kancloud.cn/b37f76b440aeb6b0bec9f8a7315fac55_584x497.png" />
- 序言 & 更新日志
- H5
- Canvas
- 序言
- Part1-直线、矩形、多边形
- Part2-曲线图形
- Part3-线条操作
- Part4-文本操作
- Part5-图像操作
- Part6-变形操作
- Part7-像素操作
- Part8-渐变与阴影
- Part9-路径与状态
- Part10-物理动画
- Part11-边界检测
- Part12-碰撞检测
- Part13-用户交互
- Part14-高级动画
- CSS
- SCSS
- codePen
- 速查表
- 面试题
- 《CSS Secrets》
- SVG
- 移动端适配
- 滤镜(filter)的使用
- JS
- 基础概念
- 作用域、作用域链、闭包
- this
- 原型与继承
- 数组、字符串、Map、Set方法整理
- 垃圾回收机制
- DOM
- BOM
- 事件循环
- 严格模式
- 正则表达式
- ES6部分
- 设计模式
- AJAX
- 模块化
- 读冴羽博客笔记
- 第一部分总结-深入JS系列
- 第二部分总结-专题系列
- 第三部分总结-ES6系列
- 网络请求中的数据类型
- 事件
- 表单
- 函数式编程
- Tips
- JS-Coding
- Framework
- Vue
- 书写规范
- 基础
- vue-router & vuex
- 深入浅出 Vue
- 响应式原理及其他
- new Vue 发生了什么
- 组件化
- 编译流程
- Vue Router
- Vuex
- 前端路由的简单实现
- React
- 基础
- 书写规范
- Redux & react-router
- immutable.js
- CSS 管理
- React 16新特性-Fiber 与 Hook
- 《深入浅出React和Redux》笔记
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- react-transition-group
- Vue 与 React 的对比
- 工程化与架构
- Hybird
- React Native
- 新手上路
- 内置组件
- 常用插件
- 问题记录
- Echarts
- 基础
- Electron
- 序言
- 配置 Electron 开发环境 & 基础概念
- React + TypeScript 仿 Antd
- TypeScript 基础
- 样式设计
- 组件测试
- 图标解决方案
- Algorithm
- 排序算法及常见问题
- 剑指 offer
- 动态规划
- DataStruct
- 概述
- 树
- 链表
- Network
- Performance
- Webpack
- PWA
- Browser
- Safety
- 微信小程序
- mpvue 课程实战记录
- 服务器
- 操作系统基础知识
- Linux
- Nginx
- redis
- node.js
- 基础及原生模块
- express框架
- node.js操作数据库
- 《深入浅出 node.js》笔记
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- 数据库
- SQL
- 面试题收集
- 智力题
- 面试题精选1
- 面试题精选2
- 问答篇
- Other
- markdown 书写
- Git
- LaTex 常用命令
