`pytest-bdd`和`behave`是 Python 的两个流行的 BDD 测试框架,两者都可以用来编写用户故事和可执行的测试用例,
具体选择哪一个则需要根据实际的项目状况来看。
先简单看一下两者的功能:
**pytest-bdd**
1. 基于`pytest`测试框架,可以与`pytest`的其他功能(例如 fixtures)一起使用。
2. 提供了一种紧凑的步骤定义方式,可以通过装饰器定义并重复使用步骤。
3. 支持参数化的测试,这样可以用同一组步骤进行多组数据的测试。
**behave**
1. 基于 Python 的`unittest`测试框架。
2. `behave`的步骤文件更加接近纯文本形式,对非编程人员更友好。
3. 支持使用`environment.py`文件来定义在整个 test suite 运行前后需要进行的操作。
## hehave
以下是`behave`的一些优点和特性:
1. **适用于非技术团队成员**:使用 Gherkin 语言,可以撰写更接近自然语言的测试场景描述,使得产品经理、商业分析师等非技术团队成员也能够理解、修改或编写测试场景。
2. **环境控制**:`behave`提供了在测试运行前后设置和清理环境的功能,例如数据库初始化或数据清理等,只需要在`environment.py`文件里定义相应的函数即可。
3. **可读性强和可维护性高**:`behave`强调的是实现从用户角度去描述系统行为的测试,这使得测试和实际用户需求更加贴合,增加了测试的可读性。而且将测试用例编写为人类可读的语言,可以提高代码的可维护性。
4. **创造可共享的步骤**:可以为常用的操作创建可重用的步骤,这样就能写出更加简洁、易于维护的测试代码。
5. **对标/兼容 Cucumber**:`behave`的 Gherkin 语言实现与宽广使用的 Cucumber 测试框架非常接近,这一点在迁移到或从 Cucumber 环境中迁出时会很有用。
6. **与其他 Python 测试框架相容**:`behave`可与`unittest`、`doctest`、`nose`、`py.test`等 Python 测试工具完美集成。
综上所述,`behave`提供了一种高度可读、可共享、适合大规模测试及非技术团队成员的 BDD 测试工具。
## pytest-bdd 与 behave的比较
`behave`和`pytest-bdd`都是 Python 下常用的为支持 BDD(行为驱动开发)流程而设计的测试框架,它们都采用`.feature`文件来描述行为,并使用相似的 Gherkin 语言语法进行描述。它们的`.feature`文件的格式大致上是相同的,但是在实际的使用和处理上可能会有一些细微差别。
以下是`behave`和`pytest-bdd`来处理`.feature`文件的一些细节差异:
* **Scenario 参数化**:`behave`使用`Scenario Outline`语法来实现参数化场景,而`pytest-bdd`使用`Scenarios`来实现参数化场景。在`behave`中,你必须定义 Examples 表格并在其中提供参数值, 而在`pytest-bdd`中,你可以简单地用`Scenarios`读取一个外部`.feature`文件。
* **装饰器参数**:在`pytest-bdd`中,步骤装饰器(例如`@given`、`@when`和`@then`)可以接受一个可选的解析器,用于从步骤文本中捕获值。这样,分析器可以为已经定义的步骤参数提供多个场景。
其他大部分方面,`behave`和`pytest-bdd`都是非常相似的,例如都支持`Given`、`When`和`Then`这样的基本步骤,都允许在`Background`段落中定义在每个场景前都要运行的步骤,仍然允许你创建可重用的步骤定义。
综上,`behave`和`pytest-bdd`处理`.feature`文件的方式非常相似,虽然在某些特性和实现上有些许差别。选哪个更多取决于个人或团队需求。
## pytest-bdd 与 behave的实例比较
接下来以一个具体的加法运算器为实例,初步演示两者使用上的差异。
首先, 两者的规格文件基本相同, 这里的文件名是 :calculator.feature,内容如下:
```
Feature: Addition
Scenario: Add two numbers
Given I have a calculator
When I enter "1" and "2"
Then the result should be "3"
```
规格很简单, 就是验证加法, 1+2 =3。
主要的差别是两者在测试代码上的差异。
使用pytest-bdd编写的测试代码的文件名是 test_calculator.py, 内容如下:
```
import sys
import os
import pytest
#sys.path.append('D:/devworkspace/python-ency/chp3/tests/bdd/util')
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))), 'util'))
from calculator import Calculator
from pytest_bdd import scenario, given, when, then, parsers
@scenario('../features/calculator.feature','Add two numbers')
def test_add():
print(sys.path.append(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__))+'util'))
pass
@pytest.fixture
@given("I have a calculator")
def calculator():
return Calculator()
@when(parsers.parse('I enter "{a}" and "{b}"'))
def enter_numbers(calculator, a, b):
calculator.a = int(a)
calculator.b = int(b)
@then(parsers.parse('the result should be "{result}"'))
def verify_result(calculator, result):
assert calculator.add(calculator.a, calculator.b) == int(result)
```
* pytest-bdd要求测试场景的函数和名称需要以test_开头, 步骤函数没有特定的要求,关于 pytest-bdd的更多命名的规范可以参考: [ 基于pytest-bdd的项目目录结构和命名规范](https://blog.csdn.net/oscar999/article/details/134452435)
使用behave编写的测试代码的文件名同样是 test_calculator.py, 内容如下:
```
import sys
import os
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)))), 'util'))
from behave import given, when, then
from calculator import Calculator
@given('I have a calculator')
def step_impl(context):
context.calc = Calculator()
@when('I enter "{num1}" and "{num2}"')
def step_impl(context, num1, num2):
context.result = context.calc.add(int(num1), int(num2))
@then('the result should be "{expected_result}"')
def step_impl(context, expected_result):
assert context.result == int(expected_result)
```
简单对比一下两者的测试代码区别:
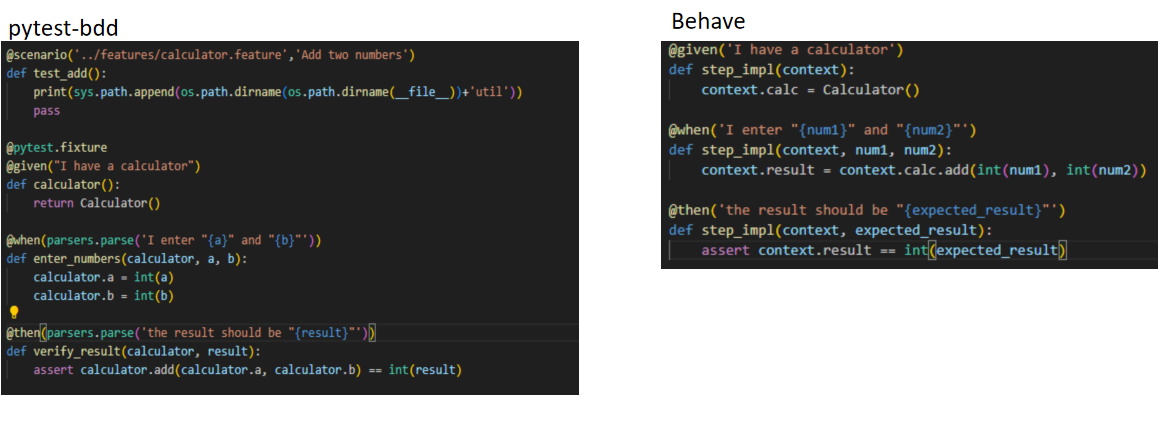
1. Beave 的写法相比更加简洁
2. pytest-bdd 可以手动关联测试场景,看上去灵活度更高
## 总结
这两个框架都有其优点和特性,选择哪一个主要取决于特定需求。
* 如果你已经在使用`pytest`,并且希望以最少的学习曲线使用 BDD,那么`pytest-bdd`可能是更好的选择。
* 另一方面,如果你希望编写的测试代码更接近自然语言,并且适合非技术团队成员阅读和修改,那么`behave`可能是更好的选择。
*****
这是一个使用 pytest-bdd 编写的简单计算器示例。该示例包含以下功能:
- 支持加法、减法、乘法和除法操作。
- 支持连续计算。
- 支持清空操作。
## 安装 pytest-bdd
依赖于 `pytest-bdd` 模块,可以使用以下命令进行安装:
```
pip install pytest-bdd
```
## 编写特性文件
创建一个名为 `calculator.feature` 的特性文件,编写以下内容:
```gherkin
Feature: Calculator
Scenario: Addition operation
Given I have entered 50 into the calculator
And I have entered 70 into the calculator
When I press add
Then the result should be 120 on the screen
Scenario: Subtraction operation
Given I have entered 70 into the calculator
And I have entered 50 into the calculator
When I press subtract
Then the result should be 20 on the screen
Scenario: Multiplication operation
Given I have entered 10 into the calculator
And I have entered 5 into the calculator
When I press multiply
Then the result should be 50 on the screen
Scenario: Division operation
Given I have entered 50 into the calculator
And I have entered 5 into the calculator
When I press divide
Then the result should be 10 on the screen
Scenario: Multiple operations
Given I have entered 5 into the calculator
And I have entered 10 into the calculator
When I press multiply
And I have entered 2 into the calculator
When I press add
And I have entered 5 into the calculator
When I press subtract
Then the result should be 20 on the screen
Scenario: Clear operation
Given I have entered 5 into the calculator
And I have entered 10 into the calculator
When I press clear
Then the result should be 0 on the screen
```
## 编写步骤实现
创建一个名为 `test_calculator.py` 的文件,编写以下内容:
```python
import pytest
from calculator import Calculator
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def calculator():
return Calculator()
@given("I have entered <x> into the calculator")
def step_impl(calculator, x):
calculator.enter(int(x))
@when("I press add")
def step_impl(calculator):
calculator.add()
@when("I press subtract")
def step_impl(calculator):
calculator.subtract()
@when("I press multiply")
def step_impl(calculator):
calculator.multiply()
@when("I press divide")
def step_impl(calculator):
calculator.divide()
@when("I press clear")
def step_impl(calculator):
calculator.clear()
@then("the result should be <y> on the screen")
def step_impl(calculator, y):
assert calculator.result == int(y)
```
## 编写计算器类
创建一个名为 `calculator.py` 的文件,编写以下内容:
```python
class Calculator:
def __init__(self):
self.result = 0
def enter(self, num):
self.result = num
def add(self):
num = int(input())
self.result += num
def subtract(self):
num = int(input())
self.result -= num
def multiply(self):
num = int(input())
self.result *= num
def divide(self):
num = int(input())
self.result /= num
def clear(self):
self.result = 0
```
## 运行测试
最后,使用以下命令运行测试:
```
pytest
```
测试结果:
```bash
collected 6 items
calculator.feature ...... [100%]
======================================================= 6 passed in 0.02s =======================================================
```
这意味着所有测试成功通过。
可以注意到,每个特性都经过了测试,且是使用自然语言编写的。这使得测试更易于阅读和理解。
## 目录结构
在使用`pytest-bdd`进行 BDD 测试时,测试文件的组织和目录结构通常如下:
~~~
Copy code/myproject
/features
/steps
__init__.py
test_steps.py
__init__.py
test.feature
/myproject
__init__.py
app.py
test_app.py
pytest.ini
~~~
这是一个基础的目录结构,每部分的说明如下:
1. `/myproject/features`目录:这是所有的`.feature`文件所在地。`.feature`文件采用 Gherkin 语法来描述需求和场景。通常,你可能会按照项目的不同模块或者功能来分别创建对应的`.feature`文件。
2. `/myproject/features/steps`目录:这是用 Python 所编写的步骤定义文件所在地。这些步骤定义将描述`.feature`文件中所给出的各个步骤应该如何执行。
3. `/myproject/myproject`目录:这里是项目的代码部分。
4. `test_app.py`文件:你的其他`pytest`测试可能会写在这里。
5. `pytest.ini`文件:这是`pytest`的配置文件。
可以根据实际情况调整上述目录结构,例如你可能需要创建更多的子目录或者文件,来适应你的项目结构。
##
## aa
* https://www.yii666.com/blog/621694.html
* http://www.cuketest.com/zh-cn/cucumber/pytest_bdd
* https://github.com/pytest-dev/pytest-bdd
* https://pytest-bdd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/
- 前言
- 1.入门篇
- Python介绍
- 安装与使用
- Python开发利器之VS Code
- 模块安装
- 命令行
- 一次Python无法安装模块的问题探索与解决之旅
- 命令运行
- Conda
- 下载地址
- 2.基础篇
- 基础语法
- 输入与输出
- with as的用法
- 注释
- Python命令行参数
- 编码
- 变量类型
- 列表遍历
- 运算符
- 表达式语句
- 条件
- 循环
- 日期和时间
- 函数
- 高级语法
- @符号-装饰器
- 模块和包
- name
- init.py
- 错误和异常
- 面向对象
- 3.专题篇
- 常用功能
- Python 字符串连接
- python web
- Python CGI编程
- Python OAuth2
- 认证 Flask-HTTPAuth
- 常用命令
- 内置函数
- dir()
- print(f)
- 标准模块
- sys
- pickle-数据序列化
- os
- IO(输入输出)
- 键盘输入
- 文件读写
- 测试
- Python测试框架之pytest快速入门
- pytest-bdd快速示例和问题解决
- 基于pytest-bdd的项目目录结构和命名规范
- python BDD 的相关概念
- Behave介绍和快速示例
- Python BDD之Behave测试报告
- Python BDD 框架比较之 pytest-bdd vs behave
- pytest进阶
- Flask + pytest测试
- 参考网址
- pytest-bdd进阶
- hehave进阶
- 测试路径
- python + selunium
- HTML 根据多层CSS 查找元素
- 等待执行
- 使用text 查找 span
- pytest如何在控制台输出
- 4.问题篇
- pip pip3 及区别
- TypeError: can only concatenate str (not "NoneType") to str
- 5.实战篇
- matplotlib-绘图包
- 导入类
- 命名规范
- 模块查找
- 6.进阶篇
- Flask
- Flask介绍
- Flask扩展模块
- Flask-Login
- 问题
- Jinja2
- Flask-RESTful
- Flask-JWT-Extended
- WSGI
- Flask-SQLAlchemy
- 部署
- Flask VS Django
- Flask Web
- Flask + Vue
- Flask实战
- Flask 标准目录结构
- Blueprints
- 参考
- FastAPI 测试
- https 证书 Caused by SSLError(SSLCertVerificationError(1, '[SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED] certificate verify failed: unable to get local issuer certificate
