#动态索引
下一个需要解决的问题是如何在保持不可变好处的同时更新倒排索引。答案是,使用多个索引。
不是重写整个倒排索引,而是增加额外的索引反映最近的变化。每个倒排索引都可以按顺序查询,从最老的开始,最后把结果聚合。
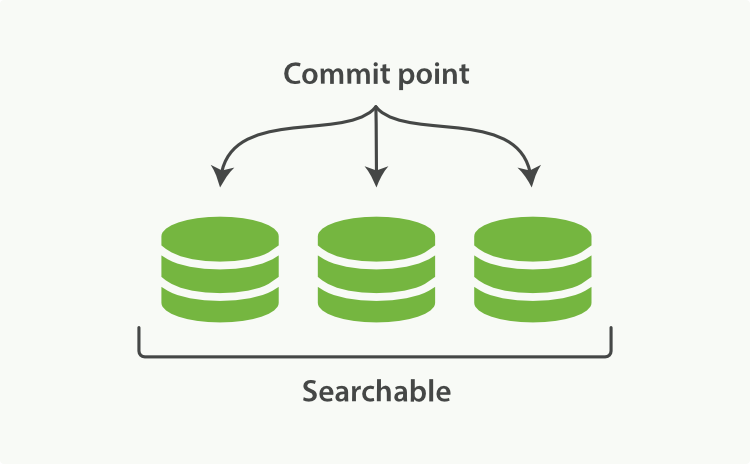
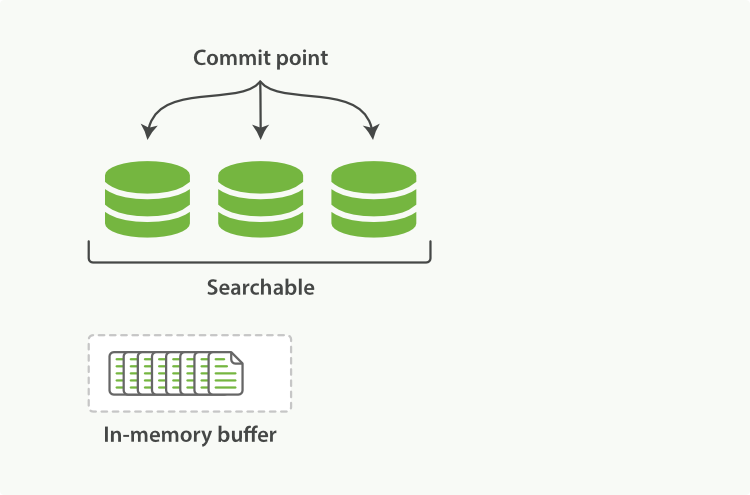
Elasticsearch底层依赖的Lucene,引入了`per-segment search`的概念。一个段(segment)是有完整功能的倒排索引,但是现在Lucene中的索引指的是段的集合,再加上提交点(commit point,包括所有段的文件),如**图1**所示。新的文档,在被写入磁盘的段之前,首先写入内存区的索引缓存,如**图2、图3**所示。
**图1:一个提交点和三个索引的Lucene**
>索引vs分片
>为了避免混淆,需要说明,Lucene索引是Elasticsearch中的分片,Elasticsearch中的索引是分片的集合。当Elasticsearch搜索索引时,它发送查询请求给该索引下的所有分片,然后过滤这些结果,聚合成全局的结果。
一个`per-segment search`如下工作:
1. 新的文档首先写入内存区的索引缓存。
2. 不时,这些buffer被提交:
* 一个新的段——额外的倒排索引——写入磁盘。
* 新的提交点写入磁盘,包括新段的名称。
* 磁盘是fsync’ed(文件同步)——所有写操作等待文件系统缓存同步到磁盘,确保它们可以被物理写入。
3. 新段被打开,它包含的文档可以被检索
4. 内存的缓存被清除,等待接受新的文档。
**图2:内存缓存区有即将提交文档的Lucene索引**
**图3:提交后,新的段加到了提交点,缓存被清空**
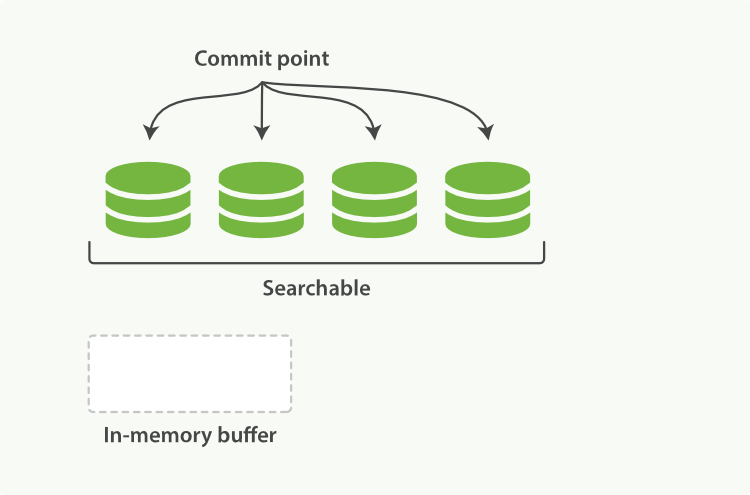
当一个请求被接受,所有段依次查询。所有段上的Term统计信息被聚合,确保每个term和文档的相关性被正确计算。通过这种方式,新的文档以较小的代价加入索引。
##删除和更新
段是不可变的,所以文档既不能从旧的段中移除,旧的段也不能更新以反映文档最新的版本。相反,每一个提交点包括一个.del文件,包含了段上已经被删除的文档。
当一个文档被删除,它实际上只是在.del文件中被标记为删除,依然可以匹配查询,但是最终返回之前会被从结果中删除。
文档的更新操作是类似的:当一个文档被更新,旧版本的文档被标记为删除,新版本的文档在新的段中索引。也许该文档的不同版本都会匹配一个查询,但是更老版本会从结果中删除。
在[合并段](075_Inside_a_shard/60_Segment_merging.md)这节,我们会展示删除的文件是如何从文件系统中清除的。
- Introduction
- 入门
- 是什么
- 安装
- API
- 文档
- 索引
- 搜索
- 聚合
- 小结
- 分布式
- 结语
- 分布式集群
- 空集群
- 集群健康
- 添加索引
- 故障转移
- 横向扩展
- 更多扩展
- 应对故障
- 数据
- 文档
- 索引
- 获取
- 存在
- 更新
- 创建
- 删除
- 版本控制
- 局部更新
- Mget
- 批量
- 结语
- 分布式增删改查
- 路由
- 分片交互
- 新建、索引和删除
- 检索
- 局部更新
- 批量请求
- 批量格式
- 搜索
- 空搜索
- 多索引和多类型
- 分页
- 查询字符串
- 映射和分析
- 数据类型差异
- 确切值对决全文
- 倒排索引
- 分析
- 映射
- 复合类型
- 结构化查询
- 请求体查询
- 结构化查询
- 查询与过滤
- 重要的查询子句
- 过滤查询
- 验证查询
- 结语
- 排序
- 排序
- 字符串排序
- 相关性
- 字段数据
- 分布式搜索
- 查询阶段
- 取回阶段
- 搜索选项
- 扫描和滚屏
- 索引管理
- 创建删除
- 设置
- 配置分析器
- 自定义分析器
- 映射
- 根对象
- 元数据中的source字段
- 元数据中的all字段
- 元数据中的ID字段
- 动态映射
- 自定义动态映射
- 默认映射
- 重建索引
- 别名
- 深入分片
- 使文本可以被搜索
- 动态索引
- 近实时搜索
- 持久化变更
- 合并段
- 结构化搜索
- 查询准确值
- 组合过滤
- 查询多个准确值
- 包含,而不是相等
- 范围
- 处理 Null 值
- 缓存
- 过滤顺序
- 全文搜索
- 匹配查询
- 多词查询
- 组合查询
- 布尔匹配
- 增加子句
- 控制分析
- 关联失效
- 多字段搜索
- 多重查询字符串
- 单一查询字符串
- 最佳字段
- 最佳字段查询调优
- 多重匹配查询
- 最多字段查询
- 跨字段对象查询
- 以字段为中心查询
- 全字段查询
- 跨字段查询
- 精确查询
- 模糊匹配
- Phrase matching
- Slop
- Multi value fields
- Scoring
- Relevance
- Performance
- Shingles
- Partial_Matching
- Postcodes
- Prefix query
- Wildcard Regexp
- Match phrase prefix
- Index time
- Ngram intro
- Search as you type
- Compound words
- Relevance
- Scoring theory
- Practical scoring
- Query time boosting
- Query scoring
- Not quite not
- Ignoring TFIDF
- Function score query
- Popularity
- Boosting filtered subsets
- Random scoring
- Decay functions
- Pluggable similarities
- Conclusion
- Language intro
- Intro
- Using
- Configuring
- Language pitfalls
- One language per doc
- One language per field
- Mixed language fields
- Conclusion
- Identifying words
- Intro
- Standard analyzer
- Standard tokenizer
- ICU plugin
- ICU tokenizer
- Tidying text
- Token normalization
- Intro
- Lowercasing
- Removing diacritics
- Unicode world
- Case folding
- Character folding
- Sorting and collations
- Stemming
- Intro
- Algorithmic stemmers
- Dictionary stemmers
- Hunspell stemmer
- Choosing a stemmer
- Controlling stemming
- Stemming in situ
- Stopwords
- Intro
- Using stopwords
- Stopwords and performance
- Divide and conquer
- Phrase queries
- Common grams
- Relevance
- Synonyms
- Intro
- Using synonyms
- Synonym formats
- Expand contract
- Analysis chain
- Multi word synonyms
- Symbol synonyms
- Fuzzy matching
- Intro
- Fuzziness
- Fuzzy query
- Fuzzy match query
- Scoring fuzziness
- Phonetic matching
- Aggregations
- overview
- circuit breaker fd settings
- filtering
- facets
- docvalues
- eager
- breadth vs depth
- Conclusion
- concepts buckets
- basic example
- add metric
- nested bucket
- extra metrics
- bucket metric list
- histogram
- date histogram
- scope
- filtering
- sorting ordering
- approx intro
- cardinality
- percentiles
- sigterms intro
- sigterms
- fielddata
- analyzed vs not
- 地理坐标点
- 地理坐标点
- 通过地理坐标点过滤
- 地理坐标盒模型过滤器
- 地理距离过滤器
- 缓存地理位置过滤器
- 减少内存占用
- 按距离排序
- Geohashe
- Geohashe
- Geohashe映射
- Geohash单元过滤器
- 地理位置聚合
- 地理位置聚合
- 按距离聚合
- Geohash单元聚合器
- 范围(边界)聚合器
- 地理形状
- 地理形状
- 映射地理形状
- 索引地理形状
- 查询地理形状
- 在查询中使用已索引的形状
- 地理形状的过滤与缓存
- 关系
- 关系
- 应用级别的Join操作
- 扁平化你的数据
- Top hits
- Concurrency
- Concurrency solutions
- 嵌套
- 嵌套对象
- 嵌套映射
- 嵌套查询
- 嵌套排序
- 嵌套集合
- Parent Child
- Parent child
- Indexing parent child
- Has child
- Has parent
- Children agg
- Grandparents
- Practical considerations
- Scaling
- Shard
- Overallocation
- Kagillion shards
- Capacity planning
- Replica shards
- Multiple indices
- Index per timeframe
- Index templates
- Retiring data
- Index per user
- Shared index
- Faking it
- One big user
- Scale is not infinite
- Cluster Admin
- Marvel
- Health
- Node stats
- Other stats
- Deployment
- hardware
- other
- config
- dont touch
- heap
- file descriptors
- conclusion
- cluster settings
- Post Deployment
- dynamic settings
- logging
- indexing perf
- rolling restart
- backup
- restore
- conclusion
