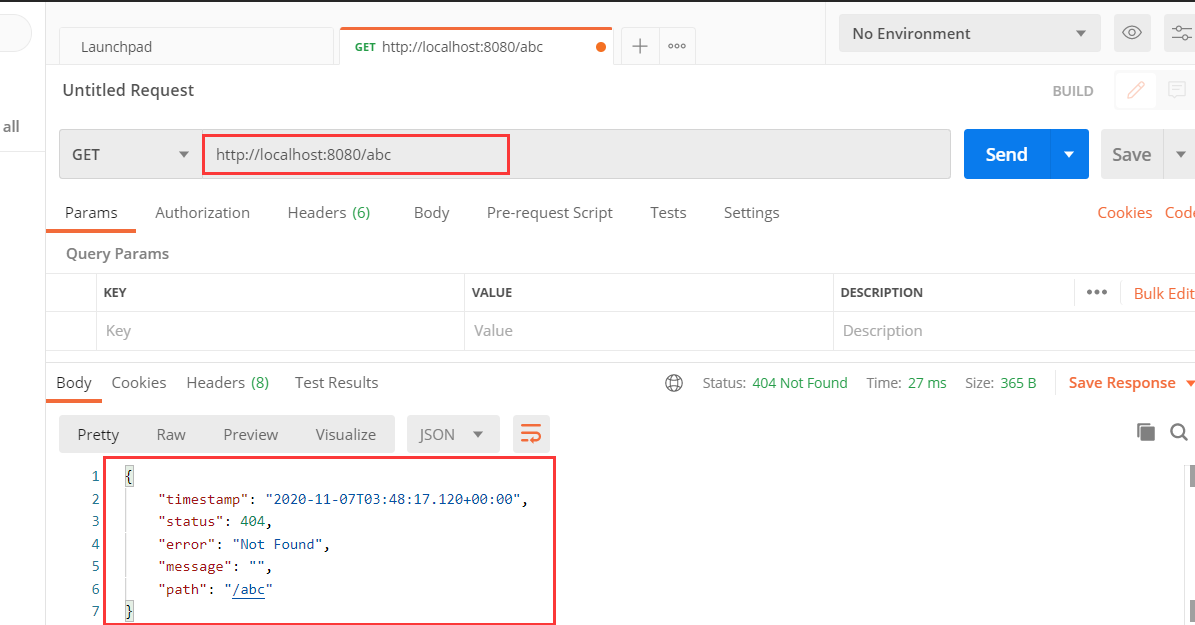
当我们使用浏览器访问一个不存在的地址时,SpringBoot 默认提供如下类似的404页面。

当如 Android、IOS 等非浏览器客户端访问时,比如使用 [Postman](https://www.postman.com/downloads/) 客户端软件模拟请求一个不存在的页面时响应的是json数据。
SpringBoot 的错误处理机制由 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 类管理,它的源码如下,它注册了下面4个错误处理组件。
```java
-----ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration-----
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorAttributes.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
// 组件1:DefaultErrorAttributes
public DefaultErrorAttributes errorAttributes() {
return new DefaultErrorAttributes();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorController.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
// 组件2:BasicErrorController
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes,
this.serverProperties.getError(), (List)errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
// 组件3:ErrorPageCustomizer
public ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean({DispatcherServlet.class})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({ErrorViewResolver.class})
组件4:DefaultErrorViewResolver
DefaultErrorViewResolver conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resourceProperties);
}
```
这4个组件的调用步骤如下:
1. 当系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误 ,调用ErrorPageCustomizer来定制错误的响应规则,它会获取系统默认的/error页面;
```java
-----ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration-----
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage =
new ErrorPage(this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().▲▲▲▲getPath()▲▲▲▲));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(new ErrorPage[]{errorPage});
}
->
-----ErrorProperties-----
public class ErrorProperties {
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
private boolean includeException;
```
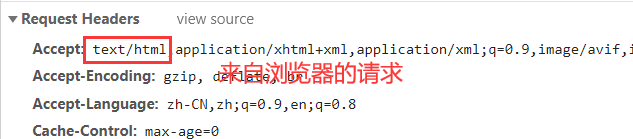
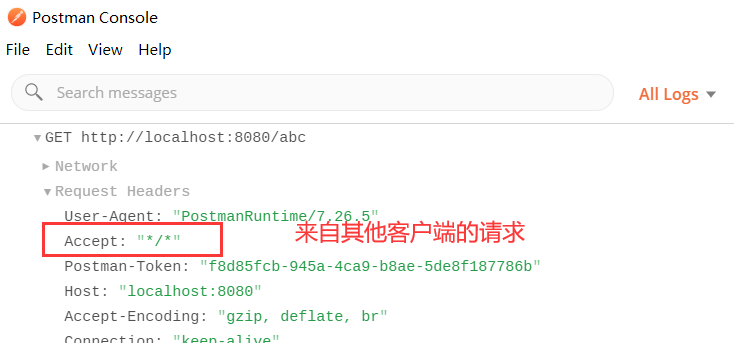
2. 接着调用BasicErrorController来处理这个/error页面,BasicErrorController
会根据请求的头部信息来判断是来自浏览器的请求,还是客户端的请求,决定应该响应一个页面,还是json数据。
```java
-----ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration-----
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {ErrorController.class},
search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT
)
public ▲▲▲▲BasicErrorController▲▲▲▲ basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
(List)errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
->
-----BasicErrorController-----
@Controller
// 如果没有找到server.error.path,则采用errorp.path,如果还是没有则最后采用/error错误配置
@RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"})
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
private final ErrorProperties errorProperties;
@RequestMapping(
produces = {"text/html"}
)
// 当是浏览器访问时,返回html
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model =
// 获取模型数据
Collections.unmodifiableMap(▲▲▲▲this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))▲▲▲▲);
response.setStatus(status.value());
// 去哪个页面作为错误页面
ModelAndView modelAndView = ▲▲▲▲this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model)▲▲▲▲;
return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
// 当是非浏览器访问时,返回json数据
@RequestMapping
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity(status);
} else {
Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity(body, status);
}
}
```
3. 接着DefaultErrorViewResolver起作用;
当是浏览器访问时,响应的是html,DefaultErrorViewResolver解析应该响应哪个页面;
```java
-----ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration----- @Bean @ConditionalOnBean( {
DispatcherServlet.class
}
) @ConditionalOnMissingBean( {
ErrorViewResolver.class
}
) ▲▲▲▲DefaultErrorViewResolver▲▲▲▲ conventionErrorViewResolver() {
return new DefaultErrorViewResolver(this.applicationContext, this.resourceProperties);
}
->-----DefaultErrorViewResolver-----
// 解析出是客户端错误,还是服务端错误,客户端错误为4xx,服务端错误为5xx,将它们存入Map中
static {
Map<Series,
String>views=new EnumMap(Series.class);
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx");
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx");
SERIES_VIEWS=Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
// 返回对应的视图
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView=this.resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView==null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
// 根据不同的状态码SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series())解析出对应的视图
modelAndView=this.resolve((String)SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
// 将对应的视图拼接为error/viewName,比如如果是404状态码,则为error/404.html
String errorViewName="error/"+viewName;
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider=this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName, this.applicationContext);
// 如果模板引擎可用,而且解析的错误页面可用,则用;如果不能用则用this.resolveResource(errorViewName, model)提供的错误页面
return provider !=null ? new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model): this.resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
// 到静态资源目录下寻找可用的error页面
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
String[] var3=this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations();
int var4=var3.length;
for(int var5=0;
var5 < var4;
++var5) {
String location=var3[var5];
try {
Resource resource=this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource=resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
// 当静态资源目录下存在templates/error/404.html则用,不存在也是返回null
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new DefaultErrorViewResolver.HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception var8) {}
}
return null;
}
```
4. 最终由DefaultErrorAttributes来配置页面的共享信息
```java
-----DefaultErrorAttributes-----
errorAttributes.put("status", 999); // 状态码
errorAttributes.put("error", "None"); // 错误提示
errorAttributes.put("exception", error.getClass().getName()); // 异常对象
errorAttributes.put("message", message); // 消息
errorAttributes.put("errors", result.getAllErrors()); // jsr303数据校验错误提示
errorAttributes.put("trace", stackTrace.toString());
errorAttributes.put("path", path);
errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date());
```
- Mybatis
- mybatis是什么
- mybatis优缺点
- 环境搭建
- 使用步骤
- 传参方式
- 无需传参
- 一个参数
- 多个参数
- 增/删/改
- 查询
- 单表查询
- 一对一查询
- 一对多查询
- 动态SQL
- 注解操作
- Spring
- Spring什么
- Spring优点
- Spring组成
- 第一个Spring程序
- 两大核心技术
- IoC控制反转
- IoC思想
- IoC容器使用步骤
- 属性注入
- IoC注入方式
- 模拟IoC实现
- AOP
- AOP概念
- AOP原理
- AOP关键术语
- AOP编程过程
- 切入点规则
- 5种增强方式
- Spring注解开发
- 注解开发的优势
- Bean注解开发
- AOP注解开发
- 完全注解开发
- 模拟Spring注解开发
- 自动装配
- 配置文件拆分
- SpringBean
- Bean常用属性
- Bean的作用域
- Bean的生命周期
- Spring整合MyBatis
- 整合步骤
- SqlSessionTemplate
- 业务层添加事务
- 事务的作用
- 配置文件事务
- 注解事务
- 事务参数
- SpringMVC
- SpringMVC是什么
- 环境搭建
- 请求流程
- 核心组件
- 前后端交互
- 简单交互演示
- 常用注解
- 后端数据传递至前端
- ServletAPI
- 访问静态资源
- 异常处理
- HandlerExceptionResolver
- 局部异常
- 全局异常
- 转发与重定向
- 转发演示
- 重定向演示
- 转发与重定向的区别
- 获取表单数据
- 表单标签
- REST风格的URL
- 异步处理
- 异步请求
- JSON数据处理
- 中文乱码处理
- 日期处理
- 上传文件
- 拦截器
- 视图解析器
- 视图类型
- 多视图解析器
- 自定义pdf视图
- JSR303数据验证
- JSR303是什么
- 常用约束
- 使用步骤
- SpringMVC整合Mybatis
- 整合步骤
- Mybatis分页插件
- SpringBoot
- SpringBoot是什么
- 环境搭建
- SpringBoot启动分析
- SpringBoot启动类
- 启动过程
- SpringBoot配置文件
- 配置文件类型
- 更改配置文件
- 读取配置文件
- 占位符
- 配置优先级
- 自定义IoC容器
- 定义方式
- 引入Spring配置文件
- @Configuration
- SpringBoot自动配置
- 自动配置原理
- 条件注解
- 自动配置报告
- 自定义自动配置
- 关闭自动配置
- 接管自动配置
- 多环境配置
- CommandLineRunner
- SpringBoot与Web开发
- 引入模板引擎
- Thymeleaf模板
- Freemarker模板
- 静态资源访问
- webjars
- 静态资源位置
- ico图标
- 指定首页
- 更换Web服务器
- 国际化
- 拦截器
- 错误处理机制
- 错误处理机制原理
- 定制错误页面
- 定制错误数据
- 上传文件
- 注册servlet三大组件
- 注册Servlet
- 注册过滤器
- 注册监听器
- 外部Tomcat与jsp模板
- 前后端交互
- 传递json字符串
- 传递js对象
- 传递表单
- 下载功能
- Swagger2文档
- SpringBoot整合JDBC
- 整合步骤
- 核心API
- JdbcTemplate
- 增删改
- 查询
- NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
- 增删改
- 查询
- SpringBoot整合Mybatis
- 整合步骤
- 切换为Druid数据源
- 添加事务
- Mybatis分页插件
- 场景启动器
- 场景启动器是什么
- 自定义场景启动器
- SpringBoot与日志
- 日志框架
- slf4j日志
- slf4j日志实现
- 统一切换为slf4j
- 日志配置
- 日志文件
- 切换日志框架
- 切换日志场景启动器
- SpringBoot与缓存
- JSR107缓存技术
- Spring缓存抽象
- 缓存注解
- SpEL表达式
- 使用缓存
- 自定义key生成器
- 缓存工作原理与流程
- SpringBoot整合Redis
- 整合步骤
- 初步使用
- 序列化机制
- 缓存管理器
- SpringBoot与任务
- 异步任务
- 实现异步任务
- 注意事项与原理
- 自定义线程池
- 定时任务
- cron表达式
- 创建定时任务
- @Scheduled参数
- 动态时间
- 邮件任务
- Quartz定时任务
- Quartz是什么
- 创建定时任务
- 触发器与任务
- 任务的CURD
- 两种触发器
- 并发问题
- 持久化
- 任务持久化
- Quartz集群
- misfire策略
- 打包插件
- appassembler-maven-plugin
- appassembler与assembly配合
