[TOC]
# 1. 需求
:-: 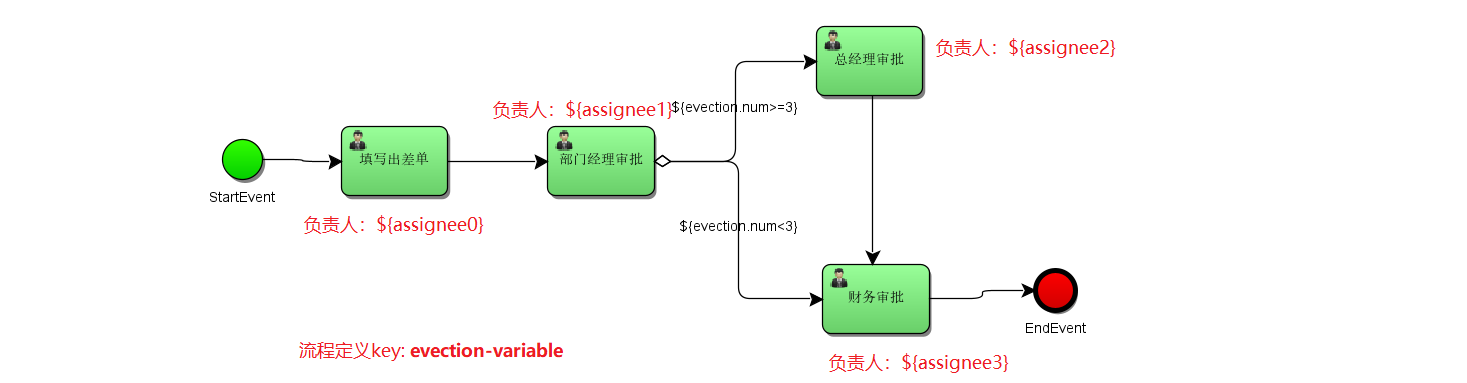
文件:`evection-variable.bpmn`
员工创建出差申请单,由部门经理审核,部门经理审核通过后出差少于3天则由财务直接审批,3天及以上先由总经理审核,总经理审核通过再由财务审批。
# 2. 设置global变量
**1. 定义一个实体类**
```java
/**
* Java实体类存储到流程变量中,必须实现序列化接口 Serializable
*/
@Data
public class Evection implements Serializable {
/**
* 为了防止由于新增字段无法反序列化,每个实体类需要生成 serialVersionUID
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 327322158719400704L;
/** 主键Id **/
private Long id;
/** 出差单的名字 **/
private String evectionName;
/** 出差天数 **/
private Double num;
/** 开始时间 **/
private Date beginDate;
/** 出差结束时间 **/
private Date endDate;
/** 目的地 **/
private String destination;
/** 出差原因 **/
private String reson;
}
```
**2. 可以在以下地方设置global变量**
>[info]1. 启动流程时设置global变量
(1)启动流程程序。
```java
/**
* ===========设置global变量位置1:启动流程时设置global变量===========
* 在启动流程时设置流程变量,变量的作用域是整个流程实例
*/
@Test
public void startProcessSetVariable() {
//获取流程引擎
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取RunTimeService
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//流程定义Key
String key = "evection-variable";
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<>();
Evection evection = new Evection();
//设置出差日期为2天
evection.setNum(2d);
variables.put("evection", evection);
variables.put("assignee0", "李四");
variables.put("assignee1", "王经理");
variables.put("assignee2", "杨总经理");
variables.put("assignee3", "张财务");
//启动流程并设置变量
runtimeService.startProcessInstanceByKey(key, variables);
}
```
(2)查看数据库已经存在流程变量了。
```sql
# 该表存储当前流程实例的变量,当流程实例被完成时,这些变量也就被删除了
mysql> select * from act_ru_variable;
+-------+------+--------------+-----------+---------------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+-------+----------+--------+
| ID_ | REV_ | TYPE_ | NAME_ | EXECUTION_ID_ | PROC_INST_ID_ | TASK_ID_ | BYTEARRAY_ID_ | DOUBLE_ | LONG_ | TEXT_ | TEXT2_ |
+-------+------+--------------+-----------+---------------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+-------+----------+--------+
| 20002 | 1 | string | assignee3 | 20001 | 20001 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 张财务 | NULL |
| 20004 | 1 | serializable | evection | 20001 | 20001 | NULL | 20003 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 20006 | 1 | string | assignee0 | 20001 | 20001 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 李四 | NULL |
| 20007 | 1 | string | assignee2 | 20001 | 20001 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 杨总经理 | NULL |
| 20008 | 1 | string | assignee1 | 20001 | 20001 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 王经理 | NULL |
+-------+------+--------------+-----------+---------------+---------------+----------+---------------+---------+-------+----------+--------+
```
(3)完成个人任务。
:-: 
```java
/**
* 完成个人任务
*/
@Test
public void completTask() {
//流程定义Key
String key = "evection-variable";
//任务负责人
String assingee = "李四";
//String assingee = "王经理";
//String assingee = "杨总经理";
//String assingee = "张财务";
//获取流程引擎
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取taskservice
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//查询任务
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assingee)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
//根据任务id来完成任务
taskService.complete(task.getId());
System.out.println(assingee + "完成了他的任务!");
} else {
System.out.println(assingee + "没有要完成的任务!");
}
}
```
依次的更换负责人,控制台输出如下:
```
李四完成了他的任务!
王经理完成了他的任务!
杨总经理没有要完成的任务!
张财务完成了他的任务!
```
可以看到总经理没有任务,因为出差的天数我们设置为2天,所以直接到财务审批了。
>[info]2. 其他设置global变量的位置,这里就不测试了
```java
public class TestVariables {
/**
* ===========设置global变量位置2:当前任务完成时设置global变量===========
* 1) 在完成任务时设置流程变量,该流程变量只有在该任务完成后其它结点才可使用该变量,
* 它的作用域是整个流程实例,如果设置的流程变量的key在流程实例中已存在相同的名字
* 则后设置的变量替换前边设置的变量。
* 2) 通过当前任务设置流程变量,需要指定当前任务id,如果当前执行的任务id不存在则抛出异常。
*/
@Test
public void completTaskSetVariable() {
//流程定义key
String key = "evection-variable";
//任务负责人
String assingee = "张三";
//获取processEngine
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//创建TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//创建变量集合
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Evection evection = new Evection();
//设置出差天数
evection.setNum(2d);
//定义流程变量
map.put("evection", evection);
//获取任务
Task task = taskService.createTaskQuery()
.processDefinitionKey(key)
.taskAssignee(assingee)
.singleResult();
if (task != null) {
//完成任务后设置流程变量
taskService.complete(task.getId(), map);
System.out.println("任务执行完成!");
} else {
System.out.println("没有任务要完成!");
}
}
/**
* ===========设置global变量位置3:在当前流程实例设置global变量===========
* 通过流程实例id设置全局变量,该流程实例必须未执行完成。
*/
@Test
public void setGlobalVariableByExecutionId() {
//当前流程实例执行id,通常设置为当前执行的流程实例
String executionId = "2601";
// 获取processEngine
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取RuntimeService
RuntimeService runtimeService = processEngine.getRuntimeService();
//创建出差pojo对象
Evection evection = new Evection();
//设置天数
evection.setNum(3d);
//通过流程实例 id设置流程变量
runtimeService.setVariable(executionId, "evection", evection);
//一次设置多个值
//runtimeService.setVariables(executionId, variables)
}
/**
* ===========设置global变量位置4:通过当前任务设置global变量===========
* 任务id必须是当前待办任务id,即该id在表act_ru_task中存在。如果该任务已结束,会报错。
*/
@Test
public void setGlobalVariableByTaskId() {
//当前待办任务id
String taskId = "1404";
//获取processEngine
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Evection evection = new Evection();
evection.setNum(3d);
//通过任务设置流程变量
taskService.setVariable(taskId, "evection", evection);
//一次设置多个值
//taskService.setVariables(taskId, variables)
}
}
```
```sql
# 历史变量可以到表act_hi_varinst中查看
mysql> select * from act_hi_varinst;
+-------+---------------+---------------+----------+-----------+--------------+------+---------------+---------+-------+--
| ID_ | PROC_INST_ID_ | EXECUTION_ID_ | TASK_ID_ | NAME_ | VAR_TYPE_ | REV_ | BYTEARRAY_ID_ | DOUBLE_ | LONG_
+-------+---------------+---------------+----------+-----------+--------------+------+---------------+---------+-------+--
| 45002 | 45001 | 45001 | NULL | assignee3 | string | 0 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 张财务 | NULL | 20
| 45004 | 45001 | 45001 | NULL | evection | serializable | 0 | 45005 | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2
| 45006 | 45001 | 45001 | NULL | assignee0 | string | 0 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 李四 | NULL | 20
| 45007 | 45001 | 45001 | NULL | assignee2 | string | 0 | NULL | NULL | NULL | 杨总经理 | NULL | 2
```
# 3. 设置local变量
```java
public class TestVariables {
/**
* ===========设置local变量位置1:处理任务时设置local流程变量===========
* 任务办理时设置local流程变量,当前运行的流程实例只能在该任务结束前使用,
* 任务结束该变量无法在当前流程实例使用,可以通过查询历史任务查询。
*/
@Test
public void completTaskSetLocalVariable() {
//任务id
String taskId = "1404";
//获取processEngine
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
//定义流程变量
Map<String, Object> variables = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Evection evection = new Evection();
evection.setNum(3d);
variables.put("evection", evection);
//设置local变量,作用域为该任务
taskService.setVariablesLocal(taskId, variables);
//完成任务
taskService.complete(taskId);
}
/**
* ===========设置local变量位置2:通过当前任务设置local流程变量===========
* 任务id必须是当前待办任务id,即该id要在表act_ru_task中存在。
*/
@Test
public void setLocalVariableByTaskId() {
//当前待办任务id
String taskId = "1404";
//获取processEngine
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取TaskService
TaskService taskService = processEngine.getTaskService();
Evection evection = new Evection();
evection.setNum(3d);
//通过任务设置流程变量
taskService.setVariableLocal(taskId, "evection", evection);
//一次设置多个值
//taskService.setVariablesLocal(taskId, Map)
}
/**
* 查询历史任务信息,包括设置的local变量等
*/
@Test
public void findHistoryTask() {
//获取引擎
ProcessEngine processEngine = ProcessEngines.getDefaultProcessEngine();
//获取HistoryService
HistoryService historyService = processEngine.getHistoryService();
//创建历史任务查询对象
HistoricTaskInstanceQuery historicTaskInstanceQuery = historyService.createHistoricTaskInstanceQuery();
//流程定义key
historicTaskInstanceQuery.processDefinitionId("evection-variable:1:17503");
//查询所有内容
List<HistoricTaskInstance> list = historicTaskInstanceQuery.list();
// 查询结果包括 local变量
historicTaskInstanceQuery.includeTaskLocalVariables();
for (HistoricTaskInstance historicTaskInstance : list) {
System.out.println("任务id:" + historicTaskInstance.getId());
System.out.println("任务名称:" + historicTaskInstance.getName());
System.out.println("任务负责人:" + historicTaskInstance.getAssignee());
System.out.println("任务local变量:"+ historicTaskInstance.getTaskLocalVariables());
System.out.println();
}
}
}
```
# 4. 注意事项
1、 如果UEL表达式中流程变量名不存在则报错。
2、 如果UEL表达式中流程变量值为空NULL,流程不按UEL表达式去执行,而流程结束 。
3、 如果UEL表达式都不符合条件,流程结束。
4、 如果连线不设置条件,会走flow序号小的那条线。
- Activiti流程引擎
- 工作流介绍
- Activiti是什么
- Activiti流程处理步骤
- Activiti环境搭建
- 搭建步骤
- 表结构介绍
- ActivitiAPI结构
- 认识流程符号
- 流程设计器的使用
- 流程处理步骤
- 乱码问题
- 流程实例
- 流程实例是什么
- 业务标识
- 查询流程实例
- 挂起/激活流程实例
- 个人任务
- 分配任务负责人
- 查询待办任务
- 办理权限
- 流程变量
- 流程变量类型
- 流程变量作用域
- 使用流程变量控制流程
- 组任务
- 设置任务候选人
- 组任务办理流程
- 网关
- 4种网关类型
- 排他网关
- 并行网关
- 包含网关
- 事件网关
- Spring整合Activiti
- SpringBoot整合Activiti
- Flowable流程引擎
- Flowable是什么
- Flowable与Activiti
- Flowable环境搭建
- FlowableAPI
- 流程引擎API与服务
- 流程处理步骤
- 流程部署
- 流程部署方式
- 流程定义版本
- 删除已部署的流程
- 下载资源
- 流程实例
- 什么是流程实例
- 业务标识
- 查询流程实例
- 挂起/激活流程实例
- 分配任务负责人
- 固定分配
- UEL表达式分配
- 监听器分配
- 办理权限
- 流程变量
- 流程变量类型
- 流程变量作用域
- 流程变量控制流程
- 组任务
- 设置任务候选人
- 组任务办理流程
- 网关
- 排他网关
- 并行网关
- 包含网关
- 事件网关
- 历史查询
- 查询历史
- Spring整合Flowable
- 配置文件整合
- 配置类整合
- SpringBoot整合Flowable
