### 1.3 堆排序
堆结构:
算法中的堆结构指的是用数组实现的`完全二叉树结构`,其模拟过程如下(数组元素从下标0开始):
~~~
# 对于下标i的元素
左孩子节点的下标为:2 * i + 1
右孩子节点的下标为:2 * (i + 1)
# 对于下标i的元素
其父亲节点的下标为:(i - 1) / 2
~~~
堆结构分为:
* 大根堆:每颗完全二叉树都满足最大元素在根节点。
* 小根堆:每颗完全二叉树都满足最小元素在根节点,Java中PriorityQueue优先级队列结构就是小根堆结构。
与堆结构相关的有两个关键的操作:
1. heapInsert():从最后一个元素开始调整堆结构,O(lgn)的时间复杂度。
2. heapify():从根元素往下调整堆结构,O(lgn)的时间复杂度。
代码实现:
#### heapInsert
~~~
/**
* Adjust the heap from bottom to top.
* @param arr
* @param index
*/
private void heapInsert(int[] arr, int index) {
while (arr[index] > arr[(index - 1) / 2]) {
swap(arr, index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
~~~
#### heapify
~~~
/**
* Adjust the heap from root to bottom
* @param arr
* @param index
* @param heapSize
*/
private void heapify(int[] arr, int index, int heapSize) {
int left = 2 * index + 1;
while (left < heapSize) {
int largestIndex = (left + 1 < heapSize) && arr[left + 1] > arr[left] ? left + 1 : left;
largestIndex = arr[largestIndex] > arr[index] ? largestIndex : index;
if (largestIndex == index) {
break;
}
swap(arr, largestIndex, index);
index = largestIndex;
left = 2 * index + 1;
}
}
~~~
该过程从根元素到叶子节点维护堆结构,只需每次判断的时候找到左右节点的更大的一个值即可;heapify过程用在从堆中弹出一个元素的时候(根节点元素),用堆中的最后一个元素替换第一元素,然后再重新维护堆的过程。
#### heapSort
~~~
/**
* heap sort
* @param arr
*/
public static void heapSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
// 维护根结构的的方式
// for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// heapInsert(arr, i);
// }
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i++) {
heapify(arr, i, arr.length - 1);
}
int heapSize = arr.length;
// 将最大值交换到堆结构的最后一个位置
swap(arr, 0, --heapSize);
while (heapSize > 0) {
heapify(arr, 0, heapSize);
swap(arr, 0, --heapSize);
}
}
~~~
整个堆排序的主要过程是逐个的将大根堆的根元素与堆的最后一个元素(用heapSize来指明)替换,然后再进行堆的维护,直到heapSize为0。
堆排序的时间复杂度为:O(nlgn)。
时间复杂度的推导:
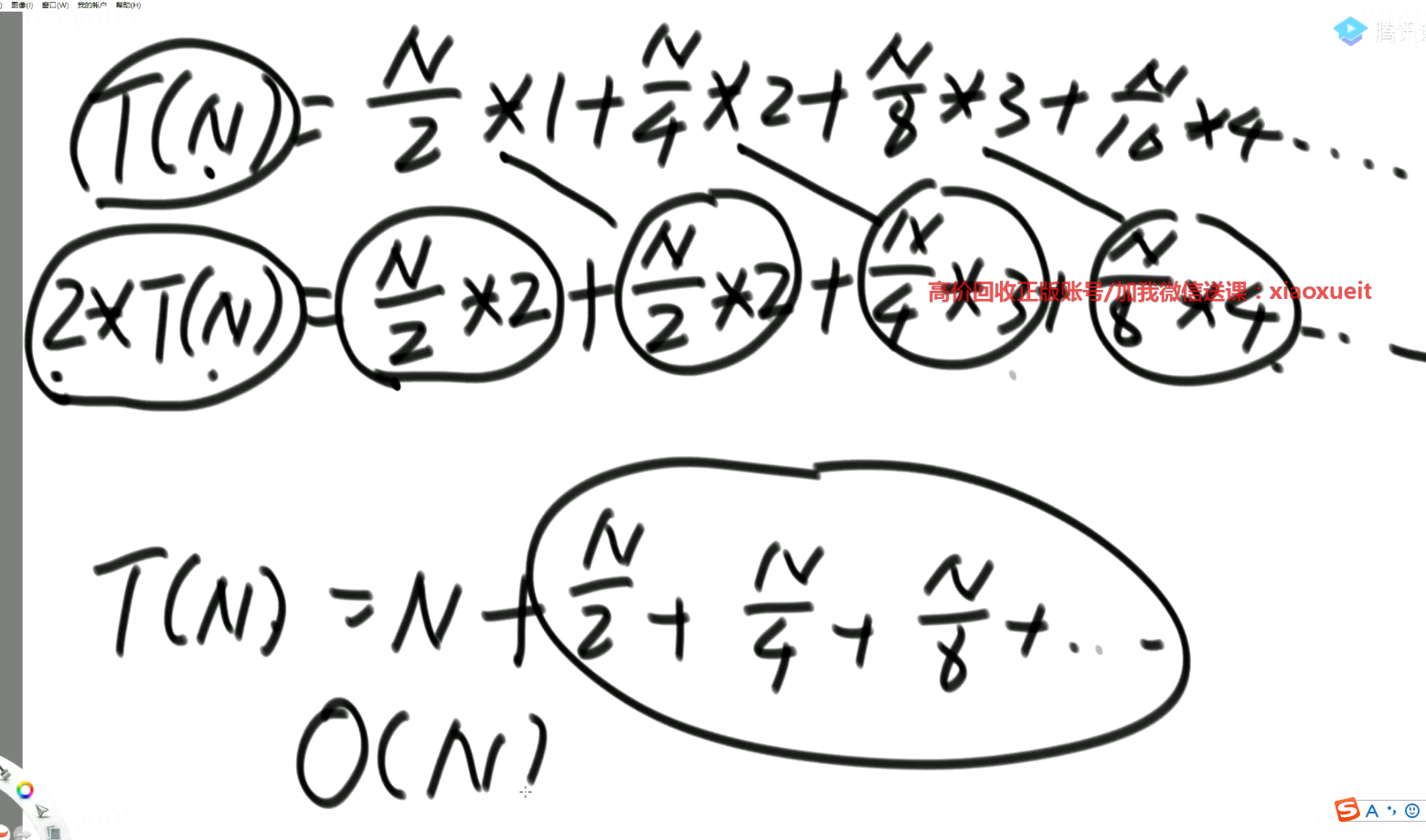
堆空间的额外空间复杂度为:O(1);
**总结:**
1. 堆结构就是用数组实现的完全二叉树结构。
2. 完全二叉树中如果每棵子树的最大值都在顶部就是大根堆。
3. 完全二叉树如果每棵子树的最小值都在顶部就是小根堆。
4. 堆结构两个主要的操作是heapInsert和heapify。
5. 优先级队列结构就是堆结构。
堆结构中重要的是heapInsert和heapify结构,并且经常在代码实现中重写堆结构而不用语言提供的堆结构。
使用系统的堆的结构时,如果存进去的是对象,则中途改变对象的内容,堆结构很可能不会继续维护正确的结构。因此可以自己手写一个堆来实现,使用一个HashMap来记录在堆上的位置:
`Code:`
~~~
public static class MyHeap<T> {
private ArrayList<T> heap;
private HashMap<T, Integer> indexMap;
private int heapSize;
private Comparator<? super T> comparator;
public MyHeap(Comparator<? super T> comparator) {
heap = new ArrayList<>();
indexMap = new HashMap<>();
heapSize = 0;
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
public int size() {
return heapSize;
}
/**
* 判断某个键是否存在
* @param key
* @return
*/
public boolean contains(T key) {
return indexMap.containsKey(key);
}
public void push(T value) {
heap.add(value);
indexMap.put(value, heapSize);
heapInsert(heapSize++);
}
public T pop() {
T ans = heap.get(0);
int end = heapSize - 1;
swap(0, end);
// 移除最后一个元素
heap.remove(end);
// 移除映射元素
indexMap.remove(ans);
// 重新调整堆结构
heapify(0, --heapSize);
return ans;
}
/**
* 从下往上调整堆结构
* @param index
*/
private void heapInsert(int index) {
while (comparator.compare(heap.get(index), heap.get((index - 1) / 2)) > 0) {
swap(index, (index - 1) / 2);
index = (index - 1) / 2;
}
}
/**
* 从上往下调整堆结构
* @param index
* @param heapSize
*/
private void heapify(int index, int heapSize) {
int left = index * 2 + 1;
while (left < heapSize) {
left = left + 1 < heapSize && comparator.compare(heap.get(left), heap.get(left + 1)) > 0 ? left : left + 1;
left = comparator.compare(heap.get(index), heap.get(left)) > 0 ? index : left;
if (left == index) {
break;
}
swap(left, index);
index = left;
left = index * 2 + 1;
}
}
private void swap(int index1, int index2) {
T t = heap.get(index1);
T t1 = heap.get(index2);
heap.set(index1, t1);
heap.set(index2, t);
indexMap.put(t, index2);
indexMap.put(t1, index1);
}
}
~~~
**堆排序**
* 先让整个数组都变成大根堆结构,建立堆的过程:
* 从上到下的方法heapify,时间复杂度为O(N\*logN);
* 从下到上的方法heapInsert,时间复杂度为O(N);
* 把堆的最大值和堆末尾的值交换,然后减少堆的大小后,再次调整堆,一直周而复始,时间复杂度为O(N \* logN);
* 堆的大小减小为0之后,排序成功。
系统实现的堆结构:默认是小根堆的实现。
~~~
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
~~~
> 题目:已知一个几乎有序的数组,如果把数组排好顺序之后,每个元素移动的距离一定不超过K,并且K相对于长度来说是比较小的。
>
> 请选择一个合适的排序策略,对这个数组进行排序。
`Code:`
思路:将前面k+1个元素放入小根堆中,然后弹出堆根,插入第k+2,一直执行这个过程。理由是每个元素移动的距离不超过K。
~~~
public void sortedArrDistanceLessK(int[] arr, int k) {
// 创建小根堆结构
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
int index = 0;
for (; index <= Math.min(arr.length, k); index++) {
heap.add(arr[index]);
}
int i = 0;
for (; index < arr.length; i++, index++) {
heap.add(arr[index]);
// 重新设置值,可以保证排好序
arr[i] = heap.poll();
}
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
arr[i++] = heap.poll();
}
}
~~~
时间复杂度为:O(N\*lgk);
**其他**
PriorityQueue不是线程安全的,线程安全的为PriorityBlockingQueue队列,其操作用可重入锁进行同步操作。
