# C 编程,第 4 部分:字符串和结构体
> 原文:[Processes, Part 1: Introduction](https://github.com/angrave/SystemProgramming/wiki/Processes%2C-Part-1%3A-Introduction)
> 校验:[_stund](https://github.com/hqiwen)
> 自豪地采用[谷歌翻译](https://translate.google.cn/)
## 字符串,结构和陷阱
## 那什么是字符串?

在 C 中,由于历史原因,我们有 [Null Terminated](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Null-terminated_string) 字符串而不是 [Length Prefixed](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/String_(computer_science)#Length-prefixed) 。对于平均日常编程而言,这意味着您需要记住空字符! C 中的字符串被定义为一串字节,直到您达到'\ 0'或空字节。
### 两个不同地方的字符串
每当你定义一个常量字符串(即`char* str = "constant"`形式的那个)时,该字符串存储在数据或代码 段中,**只读**意味着任何修改字符串的尝试都会导致段错误。
如果一个字符串在`malloc`的空间,可以将该字符串更改为他们想要的任何内容。
### 内穿管理不善
一个常见的问题是当你写下面的内容时
```c
char* hello_string = malloc(14);
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
// hello_string ----> | g | a | r | b | a | g | e | g | a | r | b | a | g | e |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
hello_string = "Hello Bhuvan!";
// (constant string in the text segment)
// hello_string ----> [ "H" , "e" , "l" , "l" , "o" , " " , "B" , "h" , "u" , "v" , "a" , "n" , "!" , "\0" ]
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
// memory_leak -----> | g | a | r | b | a | g | e | g | a | r | b | a | g | e |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
hello_string[9] = 't'; //segfault!!分段错误
```
我们做了什么?我们为 14 个字节分配了空间,重新分配指针并成功实现了分段错误!记得要记录你的指针在做什么。您可能想要做的是使用`string.h`功能`strcpy`。
```c
strcpy(hello_string, "Hello Bhuvan!");
```
### 记住 NULL 字节!
忘记 NULL 终止字符串对字符串有很大的影响!界限检查很重要,它是之前在 wikibook 中提到的重要bug的一部分。
### 我在哪里可以找到所有这些功能的深入和分配 - 综合解释?
[就在这里!](https://linux.die.net/man/3/string)
### 字符串信息/比较:`strlen` `strcmp`
`int strlen(const char *s)`返回不包括空字节的字符串的长度
`int strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2)`返回一个确定字符串的字典顺序的整数。如果 s1 在字典中的 s2 之前到达,则返回-1。如果两个字符串相等,则为 0.否则为 1。
对于大多数这些函数,他们希望字符串是可读的而不是 NULL,但是当你将它们传递给 NULL 时会有未定义的行为。
### 字符串更改:`strcpy` `strcat` `strdup`
`char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)`将`src`处的字符串复制到`dest`。 **假设 dest 有足够的空间用于 src**
`char *strcat(char *dest, const char *src)`将`src`的字符串连接到目的地的末尾。 **此函数假定目的地末尾有足够的`src`空间,包括 NULL 字节**
`char *strdup(const char *dest)`返回字符串的`malloc`编辑副本。
### 字符串搜索:`strchr` `strstr`
`char *strchr(const char *haystack, int needle)`返回指向`haystack`中第一次出现`needle`的指针。如果没有找到,则返回`NULL`。
`char *strstr(const char *haystack, const char *needle)`与上面相同,但这次是一个字符串!
### 字符串切分:`strtok`
一个危险但有用的函数 strtok 需要一个字符串并将其切分。这意味着它会将字符串转换为单独的字符串。这个函数有很多规格,所以请阅读手册,下面是一个人为的例子。
```c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char* upped = strdup("strtok,is,tricky,!!");
char* start = strtok(upped, ",");
do{
printf("%s\n", start);
}while((start = strtok(NULL, ",")));
return 0;
}
```
**输出**
```c
strtok
is
tricky
!!
```
当我像这样更改`upped`时会发生什么?
```c
char* upped = strdup("strtok,is,tricky,,,!!");
```
### 内存移动:`memcpy`和`memmove`
为什么`memcpy`和`memmove`都在`<string.h>`中?因为字符串本质上是原始内存,在它们的末尾有一个空字节!
`void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n)`将从`str`开始的`n`字节移动到`dest`。 **注意**当内存区域重叠时,存在未定义的行为。这是我的机器示例中的经典作品之一,因为很多时候 valgrind 将无法拾取它,因为它看起来像是在你的机器上运行。当自动编程器命中时,失败。考虑更安全的版本。
`void *memmove(void *dest, const void *src, size_t n)`执行与上面相同的操作,但如果内存区域重叠,则可以保证所有字节都将被正确复制。
## 那么什么是`struct`结构体?
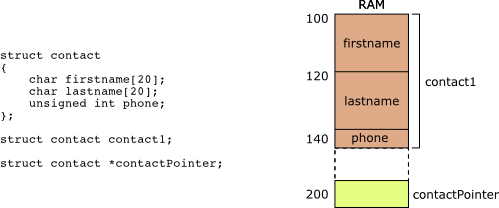
在低层次上,结构体只是一块连续的内存,仅此而已。就像数组一样,struct 有足够的空间来保留其所有成员。但与数组不同,它可以存储不同的类型。考虑上面声明的 contact 结构
```c
struct contact {
char firstname[20];
char lastname[20];
unsigned int phone;
};
struct contact bhuvan;
```
**简短的写法**
```c
/* a lot of times we will do the following typdef
so we can just write contact contact1 */
typedef struct contact contact;
contact bhuvan;
/* You can also declare the struct like this to get
it done in one statement */
typedef struct optional_name {
...
} contact;
```
如果在没有任何优化和重新排序的情况下编译代码,您可以期望每个变量的地址看起来像这样。
```c
&bhuvan // 0x100
&bhuvan.firstname // 0x100 = 0x100+0x00
&bhuvan.lastname // 0x114 = 0x100+0x14
&bhuvan.phone // 0x128 = 0x100+0x28
```
因为你所有的编译器都说'嘿保留这么多空间,我将去计算你想写的任何变量的偏移'。
### 这些偏移是什么意思?
偏移量是变量开始的位置。联系变量从`0x128`个字节开始,并继续为 sizeof(int)字节,但并非总是如此。 **偏移不会确定**变量的结束位置。考虑一下你在很多内核代码中看到的以下 hack。
```c
typedef struct {
int length;
char c_str[0];
} string;
const char* to_convert = "bhuvan";
int length = strlen(to_convert);
// Let's convert to a c string
string* bhuvan_name;
bhuvan_name = malloc(sizeof(string) + length+1);
/*
Currently, our memory looks like this with junk in those black spaces
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
bhuvan_name = | | | | | | | | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
*/
bhuvan_name->length = length;
/*
This writes the following values to the first four bytes
The rest is still garbage
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
bhuvan_name = | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | | | | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
*/
strcpy(bhuvan_name->c_str, to_convert);
/*
Now our string is filled in correctly at the end of the struct
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ____
bhuvan_name = | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | b | h | u | v | a | n | \0 |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾‾
*/
strcmp(bhuvan_name->c_str, "bhuvan") == 0 //The strings are equal!
```
### 但并非所有结构都是完美的
结构体可能需要一些称为[填充](http://www.catb.org/esr/structure-packing/)(教程)的东西。 **我们不希望你在这个课程中打包结构,只知道它在那里这是因为在早期(甚至现在)当你需要从内存中的地址时你必须在 32 位或 64 位块中进行。这也意味着您只能请求多次来获得相应的地址。意思是
```c
struct picture{
int height;
pixel** data;
int width;
char* enconding;
}
// You think picture looks like this
height data width encoding
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
picture = | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
```
在概念上可能看起来像这样
```c
struct picture{
int height;
char slop1[4];
pixel** data;
int width;
char slop2[4];
char* enconding;
}
height slop1 data width slop2 encoding
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
picture = | | | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
```
(这是在 64 位系统上)并非总是如此,因为有时您的处理器支持未对齐的访问。这是什么意思?那么您可以设置两个属性选项
```c
struct __attribute__((packed, aligned(4))) picture{
int height;
pixel** data;
int width;
char* enconding;
}
// Will look like this
height data width encoding
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
picture = | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
```
但现在每次我想访问`data`或`encoding`时,我都要进行两次内存访问。您可以做的另一件事是重新排序结构,尽管这并不总是可行的
```c
struct picture{
int height;
int width;
pixel** data;
char* enconding;
}
// You think picture looks like this
height width data encoding
___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___
picture = | | | | |
‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾ ‾‾‾
```
- UIUC CS241 系统编程中文讲义
- 0. 简介
- #Informal 词汇表
- #Piazza:何时以及如何寻求帮助
- 编程技巧,第 1 部分
- 系统编程短篇小说和歌曲
- 1.学习 C
- C 编程,第 1 部分:简介
- C 编程,第 2 部分:文本输入和输出
- C 编程,第 3 部分:常见问题
- C 编程,第 4 部分:字符串和结构
- C 编程,第 5 部分:调试
- C 编程,复习题
- 2.进程
- 进程,第 1 部分:简介
- 分叉,第 1 部分:简介
- 分叉,第 2 部分:Fork,Exec,等等
- 进程控制,第 1 部分:使用信号等待宏
- 进程复习题
- 3.内存和分配器
- 内存,第 1 部分:堆内存简介
- 内存,第 2 部分:实现内存分配器
- 内存,第 3 部分:粉碎堆栈示例
- 内存复习题
- 4.介绍 Pthreads
- Pthreads,第 1 部分:简介
- Pthreads,第 2 部分:实践中的用法
- Pthreads,第 3 部分:并行问题(奖金)
- Pthread 复习题
- 5.同步
- 同步,第 1 部分:互斥锁
- 同步,第 2 部分:计算信号量
- 同步,第 3 部分:使用互斥锁和信号量
- 同步,第 4 部分:临界区问题
- 同步,第 5 部分:条件变量
- 同步,第 6 部分:实现障碍
- 同步,第 7 部分:读者编写器问题
- 同步,第 8 部分:环形缓冲区示例
- 同步复习题
- 6.死锁
- 死锁,第 1 部分:资源分配图
- 死锁,第 2 部分:死锁条件
- 死锁,第 3 部分:餐饮哲学家
- 死锁复习题
- 7.进程间通信&amp;调度
- 虚拟内存,第 1 部分:虚拟内存简介
- 管道,第 1 部分:管道介绍
- 管道,第 2 部分:管道编程秘密
- 文件,第 1 部分:使用文件
- 调度,第 1 部分:调度过程
- 调度,第 2 部分:调度过程:算法
- IPC 复习题
- 8.网络
- POSIX,第 1 部分:错误处理
- 网络,第 1 部分:简介
- 网络,第 2 部分:使用 getaddrinfo
- 网络,第 3 部分:构建一个简单的 TCP 客户端
- 网络,第 4 部分:构建一个简单的 TCP 服务器
- 网络,第 5 部分:关闭端口,重用端口和其他技巧
- 网络,第 6 部分:创建 UDP 服务器
- 网络,第 7 部分:非阻塞 I O,select()和 epoll
- RPC,第 1 部分:远程过程调用简介
- 网络复习题
- 9.文件系统
- 文件系统,第 1 部分:简介
- 文件系统,第 2 部分:文件是 inode(其他一切只是数据...)
- 文件系统,第 3 部分:权限
- 文件系统,第 4 部分:使用目录
- 文件系统,第 5 部分:虚拟文件系统
- 文件系统,第 6 部分:内存映射文件和共享内存
- 文件系统,第 7 部分:可扩展且可靠的文件系统
- 文件系统,第 8 部分:从 Android 设备中删除预装的恶意软件
- 文件系统,第 9 部分:磁盘块示例
- 文件系统复习题
- 10.信号
- 过程控制,第 1 部分:使用信号等待宏
- 信号,第 2 部分:待处理的信号和信号掩码
- 信号,第 3 部分:提高信号
- 信号,第 4 部分:信号
- 信号复习题
- 考试练习题
- 考试主题
- C 编程:复习题
- 多线程编程:复习题
- 同步概念:复习题
- 记忆:复习题
- 管道:复习题
- 文件系统:复习题
- 网络:复习题
- 信号:复习题
- 系统编程笑话
