# :-: Vue3 · 5 个常用的 API
Vue3之于Vue2最大的变化,当属`composition API`了,而除了引入`composition API`外,一些我们在Vue2上经常使用的东西到了Vue3时也发生了不小的变化,本文将介绍一些有Vue2到Vue3中几个比较重要且常用的知识点,欢迎感兴趣的同学阅读。
> 文中代码示例使用`setup语法糖 + ts`
# v-model
## 支持多个v-model
在`Vue3`中,可以通过参数来达到一个组件支持多个`v-model`的能力。
~~~
// 父组件
<template>
<child v-model="name" v-model:email="email" />
<p>姓名:{{ name }}</p>
<p>邮箱:{{ email }}</p>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import child from './child.vue'
import { ref } from 'vue'
const name = ref<string>('张三')
const email = ref<string>('666@qq.com')
</script>
~~~
~~~
// 子组件
<template>
<button @click="updateName">更新name</button>
<button @click="updateEmail">更新email</button>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
// 定义emit
const emits = defineEmits<{
(e: 'update:modelValue', value: string): void
(e: 'update:email', value: string): void
}>()
const updateName = () => {
emits('update:modelValue', '李四')
}
const updateEmail = () => {
emits('update:email', '123456@qq.com')
}
</script>
~~~
如果`v-model`没有使用参数,则其默认值为`modelValue`,如上面的第一个`v-model`,注意此时不再是像Vue2那样使用`$emit('input')`了,而是统一使用`update:xxx`的方式。
## 废弃`.sync`
在Vue2中,由于一个组件只支持一个`v-model`,当我们还有另外的值也想要实现双向绑定更新时,往往用`.sync`修饰符来实现,而在Vue3中该修饰符已被废弃,因为`v-model`可以支持多个,所以`.sync`也就没有存在的必要了。
# watch
## 不同数据类型的监听
基础数据类型的监听:
~~~
const name = ref<string>('张三')
watch(name, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch===', newValue, oldValue)
})
~~~
复杂数据类型的监听:
~~~
interface UserInfo {
name: string age: number
}
const userInfo = reactive<UserInfo>({
name: '张三',
age: 10
})
// 监听整个对象
watch(userInfo, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch userInfo', newValue, oldValue)
})
// 监听某个属性
watch(() => userInfo.name, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log('watch name', newValue, oldValue)
})
~~~
## 支持监听多个源
在`Vue3`里,`watch`多了一个特性,可以传入一个数组同时侦听多个数据,这比起`Vue2`确实优雅多了,以往在`Vue2`中为了实现同时监听多个数据,往往需要借助computed,现在在Vue3里我们可以少一些不必要的代码了。
~~~
const name = ref<string>('张三')
const userInfo = reactive({
age: 18
})
// 同时监听name和userInfo的age属性
watch([name, () => userInfo.age], ([newName, newAge], [oldName, oldAge]) => {
//
})
~~~
# watchEffect
## watchEffect与watch的区别
相比`Vue2`,`Vue3多`了`watchEffect`这个API,`watchEffect`传入一个函数参数,该函数会立即执行,同时会响应式的最终函数内的依赖变量,并在依赖发生改变时重新运行改函数。
~~~
const name = ref<string>('张三')
const age = ref<number>(18)
watchEffect(() => {
console.log(`${name.value}:${age.value}`) // 张三:18
})
setTimeout(() => {
name.value = '李四' // 李四:18
}, 3000)
setTimeout(() => {
age.value = 20 // 李四:20
}, 5000)
~~~
***和watch的区别:***
* 运行时机不同,`watchEffect`会立即执行,相当于设置了`immediate: true`的`watch`。
* `watchEffect`无法获取改变前后的值。
* 与`watch`显示的指定依赖源不同,`watchEffect`会自动收集依赖源。
## 用`watchEffect`还是`watch`?
建议在大部分时间里使用`watch`,避免一些不必要的重复触发。
# $attrs
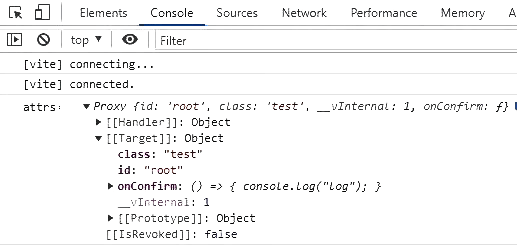
Vue3中,`$attrs`包含父组件中除props和自定义事件外的所有属性集合。
不同于`Vue2`,`$attrs`包含了父组件的事件,因此`$listenners`则被移除了。
~~~
// 父组件
<template>
<child id="root" class="test" name="张三" @confirm="getData" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
const getData = () => {
console.log('log')
}
</script>
// 子组件
<template>
<div>
<span>hello:{{ props.name }}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
export default {
inheritAttrs: false
}
</script>
<script lang="ts" setup>
const props = defineProps(['name'])
const attrs = useAttrs()
console.log('attrs', attrs)
</script>
~~~
:-: 
使用`v-bind`即可实现组件属性及事件透传:
~~~
// 父组件
<template>
<child closeable @close="onClose" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
const onClose = () => {
console.log('close')
}
</script>
// 子组件
<template>
<div>
<el-tag v-bind="attrs">标签</el-tag>
</div>
</template>
~~~
# 使用`ref`访问子组件
在`Vue2`中,使用`ref`即可访问子组件里的任意数据及方法,但在`Vue3`中则必须使用`defineExpose`暴露子组件内的方法或属性才能被父组件所调用。
~~~
// 父组件
<template>
<child ref="childRef" />
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue'
const childRef = ref()
onMounted(() => { childRef.value.getData()})
</script>
// 子组件
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { defineExpose } from 'vue'
const getData = () => {
console.log('getData')
}
const name = ref('张三')
defineExpose({
getData,
name
})
</script>
~~~
