# 快速排序
## 示意图
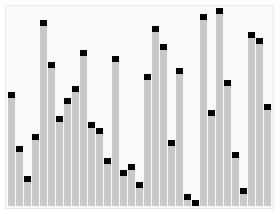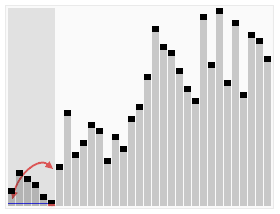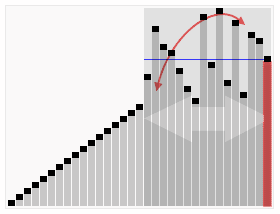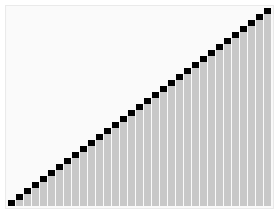
## 运作步骤
1. 挑选基准值:从数列中挑出一个元素,称为“基准”(pivot)
2. 分割:重新排序数列,所有比基准值小的元素摆放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的元素摆在基准后面(与基准值相等的数可以到任何一边)。在这个分割结束之后,对基准值的排序就已经完成
3. 递归排序子序列:递归地将小于基准值元素的子序列和大于基准值元素的子序列排序。
## 算法分析
* 最坏时间复杂度 O(n^2)
* 最优时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
* 平均时间复杂度 O(nlogn)
## 实现
```Python
def quick_sort(list):
'''Python中的快速排序算法简单实现
:param list: 需要排序的数字列表
:return: 排序结果
'''
if len(list) <= 1:
return list
less, greater, pivot = [], [], list.pop()
for item in list:
if item < pivot:
less.append(item)
else:
greater.append(item)
list.append(pivot)
return quick_sort(less) + [pivot] + quick_sort(greater)
def quick_sort_in_place(list):
'''Python中的快速排序算法原地排序版本实现
:param list: 需要排序的数字列表
:return: 排序结果
'''
def partition(list, start, end):
pivot = list[end]
for j in range(start, end):
if list[j] < pivot:
list[start], list[j] = list[j], list[start]
start += 1
list[start], list[end] = list[end], list[start]
return start
def sort(list, start, end):
if start >= end:
return
p = partition(list, start, end)
sort(list, start, p - 1)
sort(list, p + 1, end)
sort(list, 0, len(list) - 1)
return list
```
## 测试
```
$ python quick_sort.py
快速排序>>>
请输入需要排序的数字,用英文半角逗号隔开,直接回车则使用默认数据:
需要排序的数字为:
8,-5,10,6,-23,15,45,20,16
quick_sort排序结果:
-23,-5,6,8,10,15,16,20,45
quick_sort_in_place排序结果:
-23,-5,6,8,10,15,16,20,45
```
# 代码库地址
[https://github.com/liuzhen153/play-algorithm-python](https://github.com/liuzhen153/play-algorithm-python)
