jar包:执行SpringBoot主类的main方法,启动ioc容器,创建嵌入式的Servlet容器;
war包:启动服务器,**服务器启动SpringBoot应用**【SpringBootServletInitializer】,启动ioc容器;
servlet3.0(Spring注解版):
8.2.4 Shared libraries / runtimes pluggability:
规则:
1)、服务器启动(web应用启动)会创建当前web应用里面每一个jar包里面ServletContainerInitializer实例:
2)、ServletContainerInitializer的实现放在jar包的META-INF/services文件夹下,有一个名为javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer的文件,内容就是ServletContainerInitializer的实现类的全类名
3)、还可以使用@HandlesTypes,在应用启动的时候加载我们感兴趣的类;
流程:
1)、启动Tomcat
2)、org\springframework\spring-web\4.3.14.RELEASE\spring-web-4.3.14.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\services\javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer:
Spring的web模块里面有这个文件:**org.springframework.web.SpringServletContainerInitializer**
3)、SpringServletContainerInitializer将@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class)标注的所有这个类型的类都传入到onStartup方法的Set<Class<?>>;为这些WebApplicationInitializer类型的类创建实例;
4)、每一个WebApplicationInitializer都调用自己的onStartup;
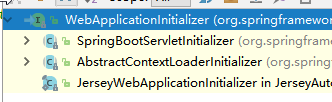
5)、相当于我们的SpringBootServletInitializer的类会被创建对象,并执行onStartup方法
6)、SpringBootServletInitializer实例执行onStartup的时候会createRootApplicationContext;创建容器
```java
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext(
ServletContext servletContext) {
//1、创建SpringApplicationBuilder
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = createSpringApplicationBuilder();
StandardServletEnvironment environment = new StandardServletEnvironment();
environment.initPropertySources(servletContext, null);
builder.environment(environment);
builder.main(getClass());
ApplicationContext parent = getExistingRootWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
if (parent != null) {
this.logger.info("Root context already created (using as parent).");
servletContext.setAttribute(
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, null);
builder.initializers(new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(parent));
}
builder.initializers(
new ServletContextApplicationContextInitializer(servletContext));
builder.contextClass(AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext.class);
//调用configure方法,子类重写了这个方法,将SpringBoot的主程序类传入了进来
builder = configure(builder);
//使用builder创建一个Spring应用
SpringApplication application = builder.build();
if (application.getSources().isEmpty() && AnnotationUtils
.findAnnotation(getClass(), Configuration.class) != null) {
application.getSources().add(getClass());
}
Assert.state(!application.getSources().isEmpty(),
"No SpringApplication sources have been defined. Either override the "
+ "configure method or add an @Configuration annotation");
// Ensure error pages are registered
if (this.registerErrorPageFilter) {
application.getSources().add(ErrorPageFilterConfiguration.class);
}
//启动Spring应用
return run(application);
}
```
7)、Spring的应用就启动并且创建IOC容器
```java
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
listeners.finished(context, null);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
```
**==启动Servlet容器,再启动SpringBoot应用==**
- Spring Boot 入门
- Spring Boot 简介
- 微服务
- 环境准备
- MAVEN设置
- IDEA设置
- Spring Boot HelloWorld
- 创建一个maven工程;(jar)
- 导入spring boot相关的依赖
- 编写一个主程序;启动Spring Boot应用
- 编写相关的Controller、Service
- 运行主程序测试
- 简化部署
- Hello World探究
- POM文件
- 父项目
- 启动器
- 主程序类,主入口类
- 使用Spring Initializer
- IDEA使用 Spring Initializer
- STS使用 Spring Starter Project快速创建项目
- 配置文件
- 配置文件
- YAML语法
- 基本语法
- 值的写法
- 普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
- 对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对)
- 数组(List、Set)
- 配置文件值注入
- 其他问题
- properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
- @Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
- 配置文件注入值数据校验
- @PropertySource&@ImportResource&@Bean
- 配置文件占位符
- 随机数
- 占位符获取之前配置的值
- Profile
- 多Profile文件
- yml支持多文档块方式
- 激活指定profile
- 配置文件加载位置
- 外部配置加载顺序
- 自动配置原理
- 自动配置原理
- 细节
- @Conditional派生注解(Spring注解版原生的@Conditional作用)
- 日志
- 日志框架
- SLF4j使用
- 如何在系统中使用SLF4j
- 遗留问题
- SpringBoot日志关系
- 日志使用
- 默认配置
- 指定配置
- 切换日志框架
- Web开发
- 简介
- SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则
- 模板引擎
- 引入thymeleaf
- Thymeleaf使用
- 语法规则
- SpringMVC自动配置
- Spring MVC auto-configuration
- 扩展SpringMVC
- 全面接管SpringMVC
- 如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置
- RestfulCRUD
- 默认访问首页
- 国际化
- 登陆
- 拦截器进行登陆检查
- CRUD-员工列表
- thymeleaf公共页面元素抽取
- CRUD-员工添加
- CRUD-员工修改
- CRUD-员工删除
- 错误处理机制
- SpringBoot默认的错误处理机制
- 如果定制错误响应
- 如何定制错误的页面
- 如何定制错误的json数据
- 将我们的定制数据携带出去
- 配置嵌入式Servlet容器
- 如何定制和修改Servlet容器的相关配置
- 注册Servlet三大组件【Servlet、Filter、Listener】
- 替换为其他嵌入式Servlet容器
- 嵌入式Servlet容器自动配置原理
- 嵌入式Servlet容器启动原理
- 使用外置的Servlet容器
- 步骤
- 原理
- Docker
- 简介
- 核心概念
- 安装Docker
- 安装linux虚拟机
- 在linux虚拟机上安装docker
- Docker常用命令&操作
- 镜像操作
- 容器操作
- 安装MySQL示例
- SpringBoot与数据访问
- JDBC
- 整合Druid数据源
- 整合MyBatis
- 注解版
- 配置文件版
- 整合SpringData JPA
- SpringData简介
- 整合SpringData JPA
- 启动配置原理
- 创建SpringApplication对象
- 运行run方法
- 事件监听机制
- 自定义starter
