案例代码:https://gitee.com/flymini/codes02/tree/master/collection_/com-learn-collection02
****
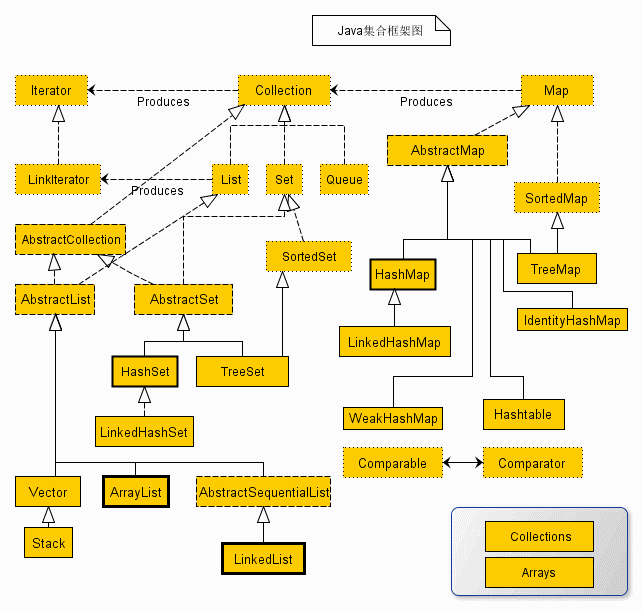
迭代器有 Iterator 和 ListIterator(上图中的 LinkIterator 是写错了,Java 中没有 LinkIterator 这个组件)。
<br/>
**1. Iterator**
List 和 Set 都有这个迭代器,可以通过该迭代器去遍历集合中的元素。该迭代器提供的方法一共就下面三个。
```java
//判断集合中是否还存在元素,如果有返回true
boolean hasNext()
//返回集合中的元素
Object next()
//删除集合中的元素
void remove()
```
```java
@Test
public void testIterator() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.addAll(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
//获取迭代器
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Integer integer = iterator.next();
if (integer.intValue() == 3) {
iterator.remove();
}
}
System.out.println(list);
//[1, 2, 4, 5]
}
```
<br/>
**2. ListIterator**
继承 Iterator 接口,提供了专门操作 List 的方法。ListIterator 在 Iterator 的基础上增加了以下几个方法.
```java
//判断集合中是否还存在元素,如果有返回true
boolean hasPrevious()
//返回集合中的元素
Object previous()
//在某一个元素前插入一个新元素
void add(Object o)
```
```java
@Test
public void testListIterator() {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.addAll(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
//获取迭代器
ListIterator<Integer> iterator = list.listIterator(list.size() - 1);
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
Integer integer = iterator.previous();
if (integer.intValue() == 3) {
iterator.add(300); //在集合中等于3的元素前插入一个元素
}
System.out.print(integer.intValue() + " ");
}
//4 3 300 2 1
System.out.println(list);
//[1, 2, 300, 3, 4, 5]
}
```
<br/>
两个迭代器相比较,不难发现,ListIterator 增加了向前迭代的功能(Iterator只能向后迭代),ListIterator 还可以通过`add`方法向 List 集合中添加元素(Iterator 只能删除元素)。
- 网络通信
- 网络协议
- 端口和套接字
- TCP网络程序
- UDP网络程序
- 多线程聊天室
- 多线程
- 线程相关概念
- 线程实现方式
- 中断线程
- 线程生命周期
- 线程优先级
- 优先级规则
- 案例演示
- 线程同步机制
- 线程同步机制
- synchronized关键字
- ReentrantLock类
- Condition类
- 监视器概念
- volatile关键字
- final变量
- 死锁
- 线程局部变量
- 读/写锁
- 原子类
- 阻塞队列
- 工作规则
- 案例演示
- 常用阻塞队列
- 线程安全集合
- 高效的映射/集/队列
- 并发集视图
- 写数组的拷贝
- Arrays类的并行数组算法
- 同步包装器
- Callable与Future
- 执行器
- 线程池
- 预定执行
- 控制任务组
- Fork-Join框架
- 同步器
- 同步器
- 信号量
- CountDownLatch类
- CyclicBarrier类
- Exchanger类
- SynchronousQueue类
- 线程与Swing
- Swing与线程问题
- 两个原则
- Swing工作线程
- 单一线程规则
- 文件IO
- File类
- 文件输入输出
- ZIP压缩文件
- 集合
- 集合框架
- 集合接口
- 集合实现类
- 线程安全集合
- 集合算法
- 迭代器
- 集合排序
- JDBC
- JDBC是什么
- JDBC-ODBC桥
- JDBC驱动程序类型
- JDBC常用类与接口
- 数据库操作
- 连接数据库
- 增/删/改/查/预处理
- 事务
- 批处理
- commons-dbutils工具
- 安全问题
- Jedis
- 使用Jedis操作Redis数据库
- JSON转换
- 使用连接池
- 案例
- 单例破坏
- 单例定义
- 单例实现方式
- 懒汉式实现单例
- 饿汉式实现单例
- 单例破坏
- 类的单例破坏
- 枚举的单例破坏
- 克隆
- 克隆是什么
- 浅克隆
- 深克隆
- 注解
- 注解是什么
- 三大注解
- 内置注解
- 元注解
- 自定义注解
- NIO
- 相关概念
- BIO/NIO/AIO
- 多线程编程
- 线程同步
- 线程通信
- NIO
- NIO三大核心组件
- NIO网络编程
- NIO文件读写
- AIO
- Java8新特性
- Lambda表达式
- 方法引用
- 函数式接口
- 默认方法
- 什么是默认方法
- 默认方法语法格式
- 多个同名的默认方法问题
- 静态默认方法
- 默认方法实例
- Stream
- Stream是什么
- Stream示例
- Optional容器
- 新的日期时间API
- Base64
- SPI
- SPI是什么
- SPI与API的区别
- 常见场景
- 使用SPI需遵循的约定
- SPI使用步骤
