## 视图view的基本属性
下面是视图在代码中常用的设置方法说明。
* setLayoutParams:设置该视图的布局参数。参数对象的构造函数可以设置视图的宽度和高度。参数对象的setMargins方法可以设置该视图与周围视图之间的空白距离。
* setMinimumWidth:设置该视图的最小宽度。
* setMinimumHeight:设置该视图的最小高度。
* setBackgroundColor:设置该视图的背景颜色。
* setBackgroundDrawable:设置该视图的背景图片。
* setBackgroundResource:设置该视图的背景资源id。
* setPadding:设置该视图边缘与内部内容之间的空白距离。
* setVisibility:设置该视图的可视类型。
### margin和padding的区别
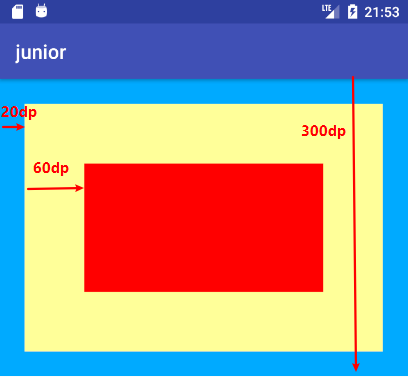
margin和padding看字面意思都是空白距离,那么它们到底有什么区别呢?
* (1)margin是指当前视图与周围视图的距离。**外边距**
* (2)padding是指当前视图与内部视图的距离。**内边距**
示例
~~~
<!-- 最外层的布局背景为蓝色 -->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00aaff"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="5dp">
<!-- 中间层的布局背景为黄色 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:background="#ffff99"
android:padding="60dp">
<!-- 最内层的视图背景为红色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ff0000" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
~~~
如图所示
### 线性布局
线性布局的常见属性说明如下:
* orientation:指定线性布局的方向。
horizontal表示水平布局,vertical表示垂直布局。如果不指定该属性,就默认是horizontal。
* gravity:指定布局内部视图与本线性布局的对齐方式。
* layout_gravity:指定该视图与上级视图的对齐方式,
* layout_weight:指定当前视图的宽或高占上级线性布局的权重。
示例如下
~~~
<!-- 最外层的布局背景为橙色,它的下级布局在水平方向上依次排列 -->
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#ffff99"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:padding="5dp">
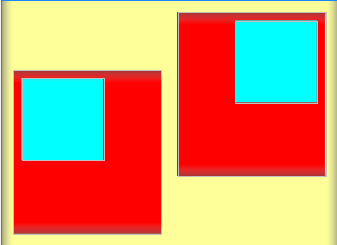
<!-- 第一个子布局背景为红色,它与上级布局靠下对齐,它的下级视图则靠左对齐 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:gravity="left"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 内层视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff" />
</LinearLayout>
<!-- 第二个子布局背景为红色,它与上级布局靠上对齐,它的下级视图则靠右对齐 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:gravity="right"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- 内层视图的宽度和高度都是100dp,且背景色为青色 -->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
~~~
### 滚动视图
手机屏幕的显示空间有限,常常需要上下滑动或左右滑动才能拉出其余页面内容,可惜Android的布局节点都不支持自行滚动,这时就要借助ScrollView滚动视图实现了。
与线性布局类似,滚动视图也分为垂直方向和水平方向两类,其中垂直滚动的视图名是ScrollView,水平滚动的视图名是HorizontalScrollView。
* (1)垂直方向滚动时,layout_width要设置为match_parent,layout_height要设置为wrap_content。
* (2)水平方向滚动时,layout_width要设置为wrap_content,layout_height要设置为match_parent。
* (3)滚动视图节点下面必须且只能挂着一个子布局节点,否则会在运行时报错`Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: ScrollView can host only one direct child`。
示例
~~~
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<!-- HorizontalScrollView是水平方向的滚动视图,当前高度为200dp -->
<HorizontalScrollView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="200dp">
<!-- 水平方向的线性视图,两个子视图的颜色分别为青色和黄色 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<View
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#aaffff" />
<View
android:layout_width="400dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff00" />
</LinearLayout>
</HorizontalScrollView>
<!-- ScrollView是垂直方向的滚动视图,当前高度为自适应 -->
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!-- 垂直方向的线性视图,两个子视图的颜色分别为绿色和橙色 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="400dp"
android:background="#00ff00" />
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="400dp"
android:background="#ffffaa" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
~~~
>[info]注意:有时ScrollView的实际内容不够,又想让它充满屏幕,怎么办呢?如果把layout_height属性赋值为match_parent,那么结果还是不会充满,正确的做法是再增加一行fillViewport的属性设置(该属性为true表示允许填满视图窗口),举例如下:
```
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fillViewport="true"
```
