# 第05章 布尔索引
```py
In[1]: import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
```
## 1\. 计算布尔值统计信息
```py
# 读取movie,设定行索引是movie_title
In[2]: pd.options.display.max_columns = 50
In[3]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
movie.head()
Out[3]:
```
```py
# 判断电影时长是否超过两小时
In[4]: movie_2_hours = movie['duration'] > 120
movie_2_hours.head(10)
Out[4]: movie_title
Avatar True
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End True
Spectre True
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
John Carter True
Spider-Man 3 True
Tangled False
Avengers: Age of Ultron True
Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince True
Name: duration, dtype: bool
```
```py
# 有多少时长超过两小时的电影
In[5]: movie_2_hours.sum()
Out[5]: 1039
```
```py
# 超过两小时的电影的比例
In[6]: movie_2_hours.mean()
Out[6]: 0.21135069161920261
```
```py
# 用describe()输出一些该布尔Series信息
In[7]: movie_2_hours.describe()
Out[7]: count 4916
unique 2
top False
freq 3877
Name: duration, dtype: object
```
```py
# 实际上,dureation这列是有缺失值的,要想获得真正的超过两小时的电影的比例,需要先删掉缺失值
In[8]: movie['duration'].dropna().gt(120).mean()
Out[8]: 0.21199755152009794
```
### 原理
```py
# 统计False和True值的比例
In[9]: movie_2_hours.value_counts(normalize=True)
Out[9]: False 0.788649
True 0.211351
Name: duration, dtype: float64
```
### 更多
```py
# 比较同一个DataFrame中的两列
In[10]: actors = movie[['actor_1_facebook_likes', 'actor_2_facebook_likes']].dropna()
(actors['actor_1_facebook_likes'] > actors['actor_2_facebook_likes']).mean()
Out[10]: 0.97776871303283708
```
## 2\. 构建多个布尔条件
```py
In[11]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
movie.head()
Out[11]:
```
```py
# 创建多个布尔条件
In[12]: criteria1 = movie.imdb_score > 8
criteria2 = movie.content_rating == 'PG-13'
criteria3 = (movie.title_year < 2000) | (movie.title_year >= 2010)
criteria2.head()
Out[12]: movie_title
Avatar True
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End True
Spectre True
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
Name: content_rating, dtype: bool
```
```py
# 将这些布尔条件合并成一个
In[13]: criteria_final = criteria1 & criteria2 & criteria3
criteria_final.head()
Out[13]: movie_title
Avatar False
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End False
Spectre False
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
Name: content_rating, dtype: bool
```
### 更多
```py
# 在Pandas中,位运算符(&, |, ~)的优先级高于比较运算符,因此如过前面的条件3不加括号,就会报错
In[14]: movie.title_year < 2000 | movie.title_year > 2009
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py in na_op(x, y)
882 try:
--> 883 result = op(x, y)
884 except TypeError:
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py in <lambda>(x, y)
130 names('rand_'), op('&')),
--> 131 ror_=bool_method(lambda x, y: operator.or_(y, x),
132 names('ror_'), op('|')),
TypeError: ufunc 'bitwise_or' not supported for the input types, and the inputs could not be safely coerced to any supported types according to the casting rule ''safe''
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py in na_op(x, y)
900 y = bool(y)
--> 901 result = lib.scalar_binop(x, y, op)
902 except:
pandas/_libs/lib.pyx in pandas._libs.lib.scalar_binop (pandas/_libs/lib.c:15035)()
ValueError: Buffer dtype mismatch, expected 'Python object' but got 'double'
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-14-1e7ee3f1401c> in <module>()
----> 1 movie.title_year < 2000 | movie.title_year > 2009
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py in wrapper(self, other)
933 is_integer_dtype(np.asarray(other)) else fill_bool)
934 return filler(self._constructor(
--> 935 na_op(self.values, other),
936 index=self.index)).__finalize__(self)
937
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/ops.py in na_op(x, y)
903 raise TypeError("cannot compare a dtyped [{0}] array with "
904 "a scalar of type [{1}]".format(
--> 905 x.dtype, type(y).__name__))
906
907 return result
TypeError: cannot compare a dtyped [float64] array with a scalar of type [bool]
```
## 3\. 用布尔索引过滤
```py
# 读取movie数据集,创建布尔条件
In[15]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
crit_a1 = movie.imdb_score > 8
crit_a2 = movie.content_rating == 'PG-13'
crit_a3 = (movie.title_year < 2000) | (movie.title_year > 2009)
final_crit_a = crit_a1 & crit_a2 & crit_a3
# 创建第二个布尔条件
In[16]: crit_b1 = movie.imdb_score < 5
crit_b2 = movie.content_rating == 'R'
crit_b3 = (movie.title_year >= 2000) & (movie.title_year <= 2010)
final_crit_b = crit_b1 & crit_b2 & crit_b3
# 将这两个条件用或运算合并起来
In[17]: final_crit_all = final_crit_a | final_crit_b
final_crit_all.head()
Out[17]: movie_title
Avatar False
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End False
Spectre False
The Dark Knight Rises True
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens False
dtype: bool
```
```py
# 用最终的布尔条件过滤数据
In[18]: movie[final_crit_all].head()
Out[18]:
```
```py
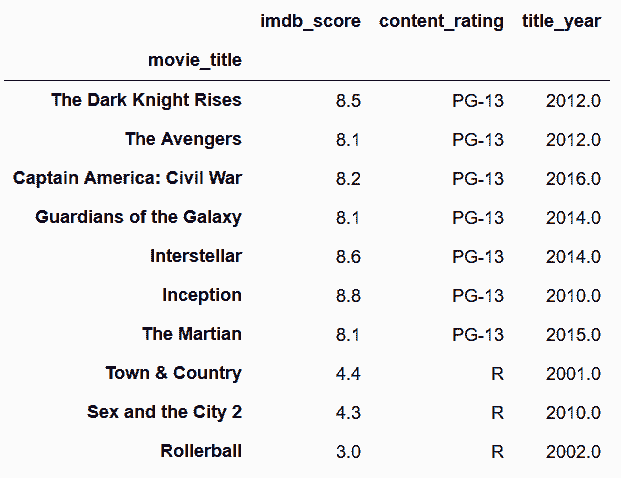
# 使用loc,对指定的列做过滤操作,可以清楚地看到过滤是否起作用
In[19]: cols = ['imdb_score', 'content_rating', 'title_year']
movie_filtered = movie.loc[final_crit_all, cols]
movie_filtered.head(10)
Out[19]:
```
### 更多
```py
# 用一个长布尔表达式代替前面由短表达式生成的布尔条件
In[21]: final_crit_a2 = (movie.imdb_score > 8) & \
(movie.content_rating == 'PG-13') & \
((movie.title_year < 2000) | (movie.title_year > 2009))
final_crit_a2.equals(final_crit_a)
Out[21]:
```

## 4\. 用标签索引代替布尔索引
```py
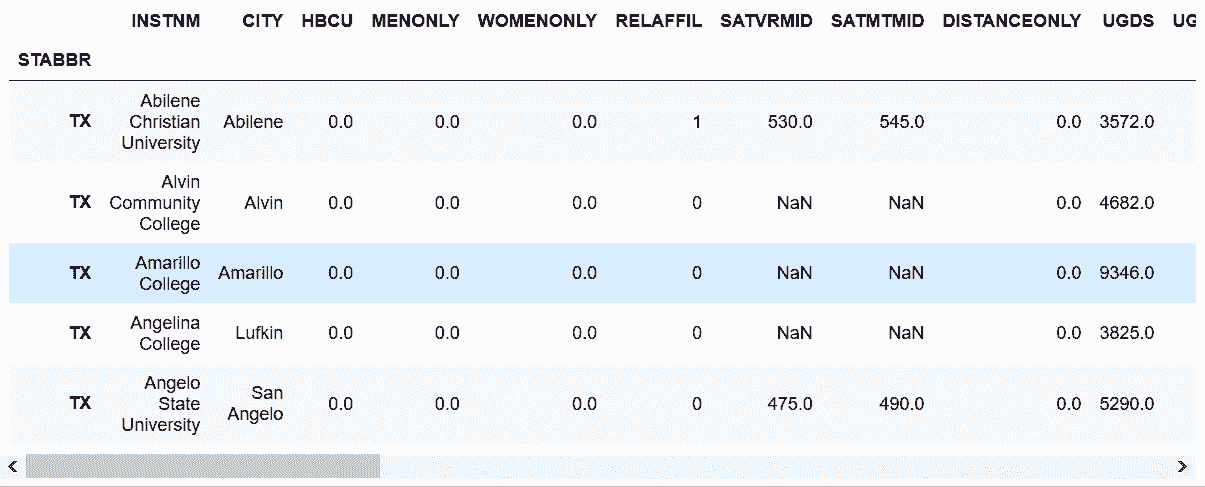
# 用布尔索引选取所有得克萨斯州的学校
>>> college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv')
>>> college[college['STABBR'] == 'TX'].head()
```
```py
# 用STABBR作为行索引,然后用loc选取
In[22]: college2 = college.set_index('STABBR')
college2.loc['TX'].head()
Out[22]:
```
```py
# 比较二者的速度
In[23]: %timeit college[college['STABBR'] == 'TX']
1.51 ms ± 51.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
In[24]: %timeit college2.loc['TX']
604 µs ± 23.9 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
```py
# 使用STABBR作为行索引所用的时间
In[25]: %timeit college2 = college.set_index('STABBR')
1.28 ms ± 47.5 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
### 更多
```py
# 使用布尔索引和标签选取多列
In[26]: states =['TX', 'CA', 'NY']
college[college['STABBR'].isin(states)]
college2.loc[states].head()
Out[26]:
```

## 5\. 用唯一和有序索引选取
```py
# 读取college数据集,使用STABBR作为行索引,检查行索引是否有序
In[27]: college = pd.read_csv('data/college.csv')
college2 = college.set_index('STABBR')
In[28]: college2.index.is_monotonic
Out[28]: False
```
```py
# 将college2排序,存储成另一个对象,查看其是否有序
In[29]: college3 = college2.sort_index()
college3.index.is_monotonic
Out[29]: True
```
```py
# 从这三个DataFrame选取得克萨斯州,比较速度
In[30]: %timeit college[college['STABBR'] == 'TX']
1.58 ms ± 63.8 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
In[31]: %timeit college2.loc['TX']
622 µs ± 18.1 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
In[32]: %timeit college3.loc['TX']
198 µs ± 5.8 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
```py
# 使用INSTNM作为行索引,检测行索引是否唯一
In[33]: college_unique = college.set_index('INSTNM')
college_unique.index.is_unique
Out[33]: True
```
```py
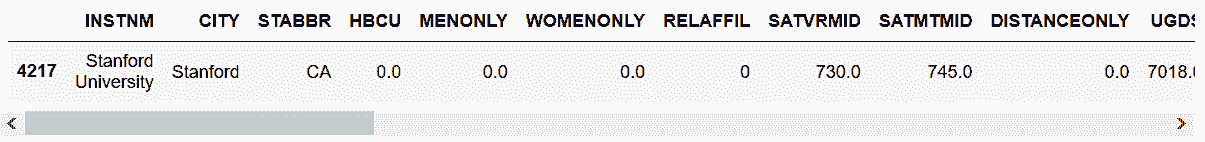
# 用布尔索引选取斯坦福大学
In[34]: college[college['INSTNM'] == 'Stanford University']
Out[34]:
```
```py
# 用行索引标签选取斯坦福大学
In[35]: college_unique.loc['Stanford University']
Out[35]:
CITY Stanford
STABBR CA
HBCU 0
MENONLY 0
WOMENONLY 0
RELAFFIL 0
SATVRMID 730
SATMTMID 745
DISTANCEONLY 0
UGDS 7018
UGDS_WHITE 0.3752
UGDS_BLACK 0.0591
UGDS_HISP 0.1607
UGDS_ASIAN 0.1979
UGDS_AIAN 0.0114
UGDS_NHPI 0.0038
UGDS_2MOR 0.1067
UGDS_NRA 0.0819
UGDS_UNKN 0.0031
PPTUG_EF 0
CURROPER 1
PCTPELL 0.1556
PCTFLOAN 0.1256
UG25ABV 0.0401
MD_EARN_WNE_P10 86000
GRAD_DEBT_MDN_SUPP 12782
Name: Stanford University, dtype: object
```
```py
# 比较两种方法的速度
In[36]: %timeit college[college['INSTNM'] == 'Stanford University']
1.44 ms ± 66 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
In[37]: %timeit college_unique.loc['Stanford University']
191 µs ± 5.31 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each)
```
### 更多
```py
# 使用CITY和STABBR两列作为行索引,并进行排序
In[38]: college.index = college['CITY'] + ', ' + college['STABBR']
college = college.sort_index()
college.head()
Out[38]:
```

```py
# 选取所有Miami, FL的大学
In[39]: college.loc['Miami, FL'].head()
Out[39]:
```

```py
# 速度比较
In[40]: %%timeit
crit1 = college['CITY'] == 'Miami'
crit2 = college['STABBR'] == 'FL'
college[crit1 & crit2]
2.83 ms ± 82.4 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
In[41]: %timeit college.loc['Miami, FL']
226 µs ± 17.3 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
```py
# 判断这两个条件是否相同
In[42]: college[(college['CITY'] == 'Miami') & (college['STABBR'] == 'FL')].equals(college.loc['Miami, FL'])
Out[42]: True
```
## 6\. 观察股价
```py
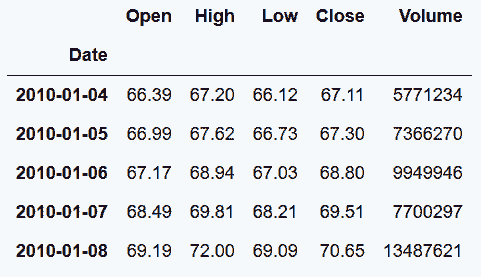
# 读取Schlumberger stock数据集,行索引设为Date列,并将其转变为DatetimeIndex
In[43]: slb = pd.read_csv('data/slb_stock.csv', index_col='Date', parse_dates=['Date'])
slb.head()
Out[43]:
```
```py
# 选取Close这列,用describe返回统计信息
In[44]: slb_close = slb['Close']
slb_summary = slb_close.describe(percentiles=[.1, .9])
slb_summary
Out[44]: count 1895.000000
mean 79.121905
std 11.767802
min 51.750000
10% 64.892000
50% 78.000000
90% 93.248000
max 117.950000
Name: Close, dtype: float64
```
```py
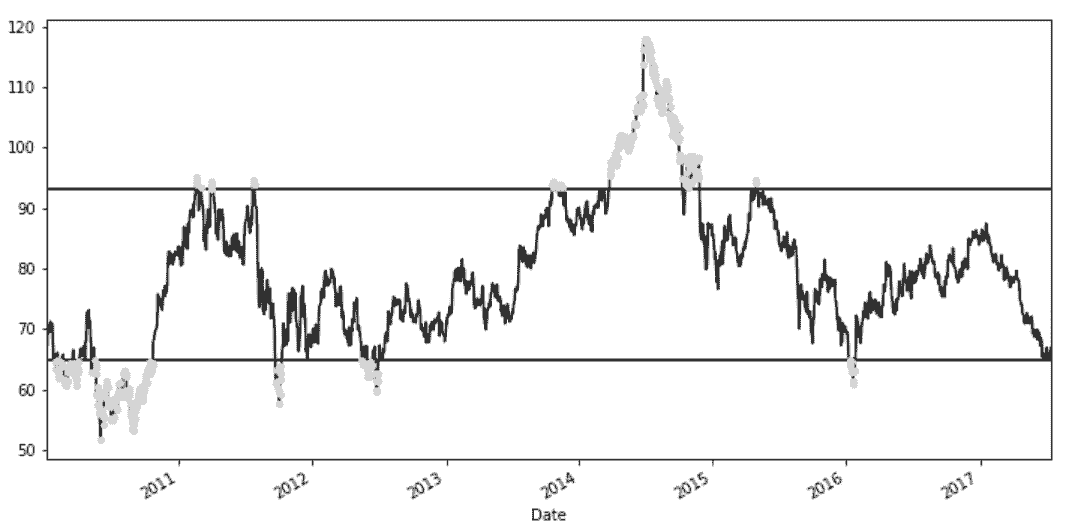
# 用布尔索引选取最高和最低10%的收盘价
In[45]: upper_10 = slb_summary.loc['90%']
lower_10 = slb_summary.loc['10%']
criteria = (slb_close < lower_10) | (slb_close > upper_10)
slb_top_bottom_10 = slb_close[criteria]
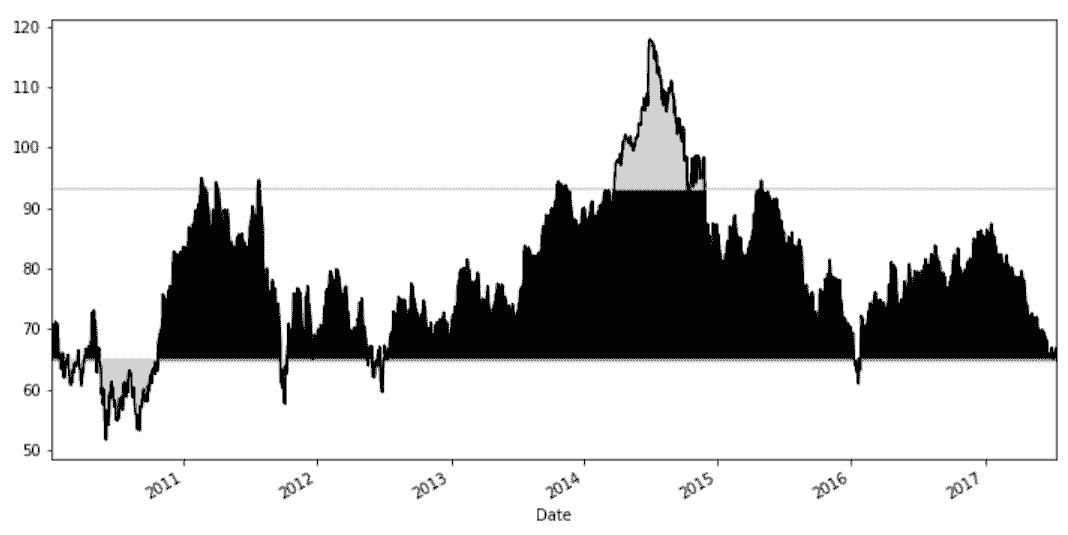
# 过滤出的数据使用灰色,所有的收盘价使用黑色,用matplotlib在十分之一和十分之九分位数位置画横线
In[46]: slb_close.plot(color='black', figsize=(12,6))
slb_top_bottom_10.plot(marker='o', style=' ', ms=4, color='lightgray')
xmin = criteria.index[0]
xmax = criteria.index[-1]
plt.hlines(y=[lower_10, upper_10], xmin=xmin, xmax=xmax,color='black')
Out[46]: <matplotlib.collections.LineCollection at 0x1174b3278>
```
### 更多
```py
# 使用fill_between可以在两条线之间填充颜色
In[47]: slb_close.plot(color='black', figsize=(12,6))
plt.hlines(y=[lower_10, upper_10],
xmin=xmin, xmax=xmax,color='lightgray')
plt.fill_between(x=criteria.index, y1=lower_10,
y2=slb_close.values, color='black')
plt.fill_between(x=criteria.index,y1=lower_10,
y2=slb_close.values, where=slb_close < lower_10,
color='lightgray')
plt.fill_between(x=criteria.index, y1=upper_10,
y2=slb_close.values, where=slb_close > upper_10,
color='lightgray')
Out[47]:
```
## 7\. 翻译SQL的WHERE语句
```py
# 读取employee数据集
In[48]: employee = pd.read_csv('data/employee.csv')
# 对各项做下了解
In[49]: employee.DEPARTMENT.value_counts().head()
Out[49]: Houston Police Department-HPD 638
Houston Fire Department (HFD) 384
Public Works & Engineering-PWE 343
Health & Human Services 110
Houston Airport System (HAS) 106
Name: DEPARTMENT, dtype: int64
In[50]: employee.GENDER.value_counts()
Out[50]: Male 1397
Female 603
Name: GENDER, dtype: int64
In[51]: employee.BASE_SALARY.describe().astype(int)
Out[51]: count 1886
mean 55767
std 21693
min 24960
25% 40170
50% 54461
75% 66614
max 275000
Name: BASE_SALARY, dtype: int64
```
```py
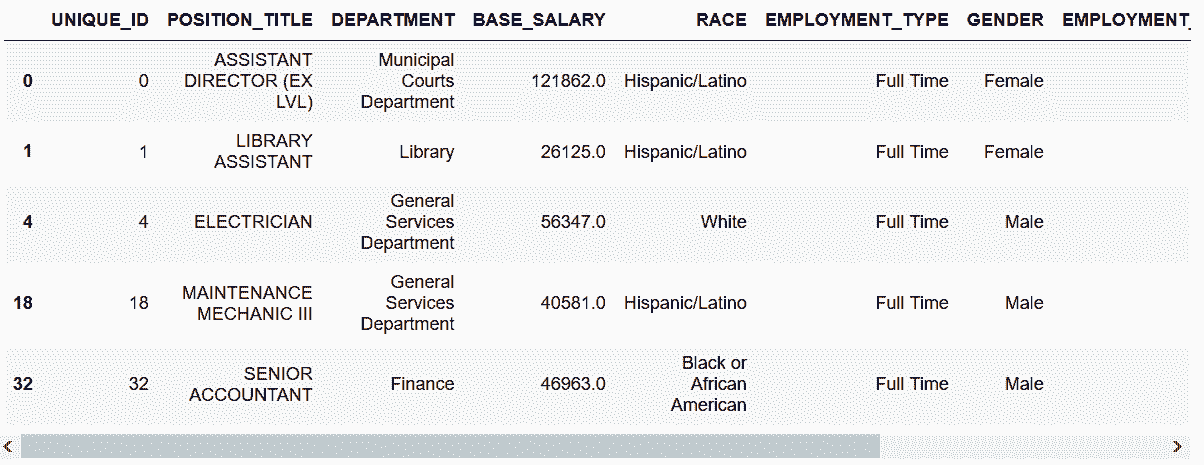
# 创建布尔条件,并从'UNIQUE_ID', 'DEPARTMENT', 'GENDER', 'BASE_SALARY'四列选取
In[52]: depts = ['Houston Police Department-HPD',
'Houston Fire Department (HFD)']
criteria_dept = employee.DEPARTMENT.isin(depts)
criteria_gender = employee.GENDER == 'Female'
criteria_sal = (employee.BASE_SALARY >= 80000) & \
(employee.BASE_SALARY <= 120000)
In[53]: criteria_final = criteria_dept & criteria_gender & criteria_sal
In[54]: select_columns = ['UNIQUE_ID', 'DEPARTMENT', 'GENDER', 'BASE_SALARY']
employee.loc[criteria_final, select_columns].head()
Out[54]:
```

### 更多
```py
# 使用between选取80000到120000之间的薪水
In[55]: criteria_sal = employee.BASE_SALARY.between(80000, 120000)
# 排除最常出现的5家单位
In[56]: top_5_depts = employee.DEPARTMENT.value_counts().index[:5]
criteria = ~employee.DEPARTMENT.isin(top_5_depts)
employee[criteria].head()
Out[56]:
```
功能一样的SQL语句是:
```py
SELECT
*
FROM
EMPLOYEE
WHERE
DEPARTMENT not in
(
SELECT
DEPARTMENT
FROM (
SELECT
DEPARTMENT,
COUNT(1) as CT
FROM
EMPLOYEE
GROUP BY
DEPARTMENT
ORDER BY
CT DESC
LIMIT 5
)
);
```
## 8\. 确定股票收益的正态值
```py
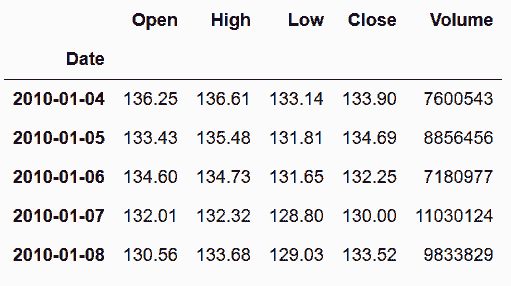
# 加载亚马逊的股票数据,使用Data作为行索引
In[57]: amzn = pd.read_csv('data/amzn_stock.csv', index_col='Date', parse_dates=['Date'])
amzn.head()
Out[57]:
```
```py
# 选取Close收盘价,用pct_change()计算每日回报率
In[58]: amzn_daily_return = amzn.Close.pct_change()
amzn_daily_return.head()
Out[58]: Date
2010-01-04 NaN
2010-01-05 0.005900
2010-01-06 -0.018116
2010-01-07 -0.017013
2010-01-08 0.027077
Name: Close, dtype: float64
```
```py
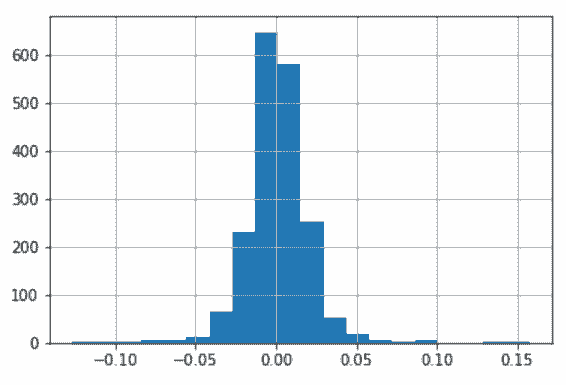
# 去掉缺失值,画一张柱状图,查看分布情况
In[59]: amzn_daily_return = amzn_daily_return.dropna()
amzn_daily_return.hist(bins=20)
Out[59]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x1174b3128>
```
```py
# 计算平均值和标准差
In[60]: mean = amzn_daily_return.mean()
std = amzn_daily_return.std()
# 计算每个数据的z-score的绝对值:z-score是远离平均值的标准差值得个数
In[61]: abs_z_score = amzn_daily_return.sub(mean).abs().div(std)
# 计算位于1,2,3个标准差之内的收益率的比例
In[62]: pcts = [abs_z_score.lt(i).mean() for i in range(1,4)]
print('{:.3f} fall within 1 standard deviation. '
'{:.3f} within 2 and {:.3f} within 3'.format(*pcts))
0.787 fall within 1 standard deviation. 0.956 within 2 and 0.985 within 3
```
### 更多
```py
# 将上面的方法整合成一个函数
In[63]: def test_return_normality(stock_data):
close = stock_data['Close']
daily_return = close.pct_change().dropna()
daily_return.hist(bins=20)
mean = daily_return.mean()
std = daily_return.std()
abs_z_score = abs(daily_return - mean) / std
pcts = [abs_z_score.lt(i).mean() for i in range(1,4)]
print('{:.3f} fall within 1 standard deviation. '
'{:.3f} within 2 and {:.3f} within 3'.format(*pcts))
In[64]: slb = pd.read_csv('data/slb_stock.csv',
index_col='Date', parse_dates=['Date'])
test_return_normality(slb)
0.742 fall within 1 standard deviation. 0.946 within 2 and 0.986 within 3
```
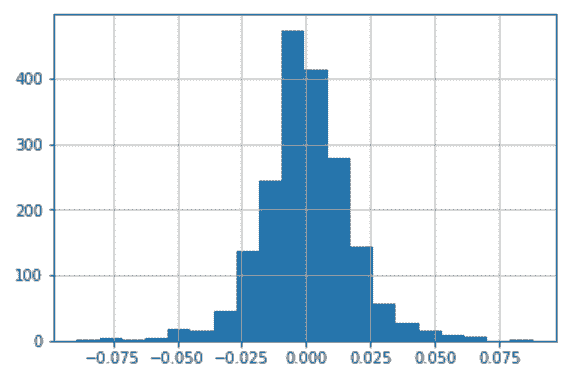
## 9\. 使用查询方法提高布尔索引的可读性
```py
# 读取employee数据,确定选取的部门和列
In[65]: employee = pd.read_csv('data/employee.csv')
depts = ['Houston Police Department-HPD', 'Houston Fire Department (HFD)']
select_columns = ['UNIQUE_ID', 'DEPARTMENT', 'GENDER', 'BASE_SALARY']
# 创建查询字符串,并执行query方法
In[66]: qs = "DEPARTMENT in @depts " \
"and GENDER == 'Female' " \
"and 80000 <= BASE_SALARY <= 120000"
emp_filtered = employee.query(qs)
emp_filtered[select_columns].head()
Out[66]:
```
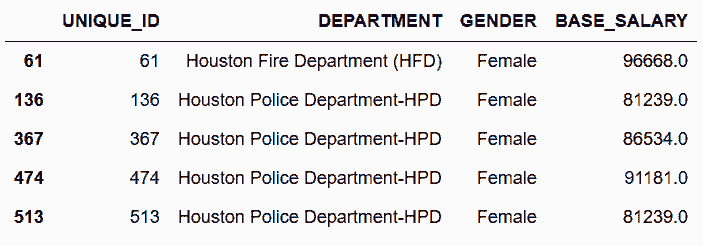
### 更多
```py
# 若要不使用部门列表,也可以使用下面的方法
In[67]: top10_depts = employee.DEPARTMENT.value_counts().index[:10].tolist()
qs = "DEPARTMENT not in @top10_depts and GENDER == 'Female'"
employee_filtered2 = employee.query(qs)
employee_filtered2[['DEPARTMENT', 'GENDER']].head()
Out[67]:
```

## 10\. 用where方法保留Series
```py
# 读取movie数据集,movie_title作为行索引,actor_1_facebook_likes列删除缺失值
In[68]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
fb_likes = movie['actor_1_facebook_likes'].dropna()
fb_likes.head()
Out[68]: movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 40000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 27000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
```
```py
# 使用describe获得对数据的认知
In[69]: fb_likes.describe(percentiles=[.1, .25, .5, .75, .9]).astype(int)
Out[69]: count 4909
mean 6494
std 15106
min 0
10% 240
25% 607
50% 982
75% 11000
90% 18000
max 640000
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: int64
```
```py
# 作用和前面相同(这里是作者代码弄乱了)
In[70]: fb_likes.describe(percentiles=[.1,.25,.5,.75,.9])
Out[70]: count 4909.000000
mean 6494.488491
std 15106.986884
min 0.000000
10% 240.000000
25% 607.000000
50% 982.000000
75% 11000.000000
90% 18000.000000
max 640000.000000
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
```
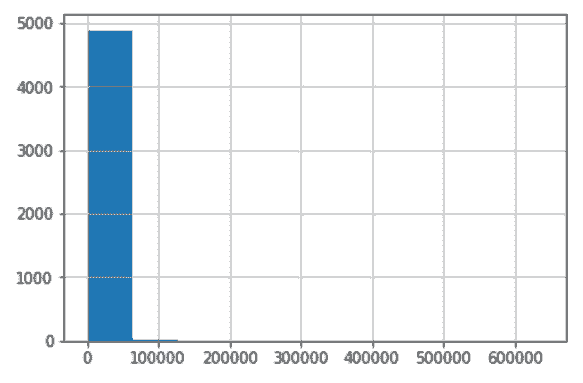
```py
# 画一张柱状图
In[71]: fb_likes.hist()
Out[71]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x10f9fbe80>
```
```py
# 检测小于20000个喜欢的的比例
In[72]: criteria_high = fb_likes < 20000
criteria_high.mean().round(2)
Out[71]: 0.91000000000000003
```
```py
# where条件可以返回一个同样大小的Series,但是所有False会被替换成缺失值
In[73]: fb_likes.where(criteria_high).head()
Out[73]: movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End NaN
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises NaN
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
```
```py
# 第二个参数other,可以让你控制替换值
In[74]: fb_likes.where(criteria_high, other=20000).head()
Out[74]: movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 20000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 20000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 131.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
```
```py
# 通过where条件,设定上下限的值
In[75]: criteria_low = fb_likes > 300
fb_likes_cap = fb_likes.where(criteria_high, other=20000)\
.where(criteria_low, 300)
fb_likes_cap.head()
Out[75]: movie_title
Avatar 1000.0
Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End 20000.0
Spectre 11000.0
The Dark Knight Rises 20000.0
Star Wars: Episode VII - The Force Awakens 300.0
Name: actor_1_facebook_likes, dtype: float64
```
```py
# 原始Series和修改过的Series的长度是一样的
In[76]: len(fb_likes), len(fb_likes_cap)
Out[76]: (4909, 4909)
```
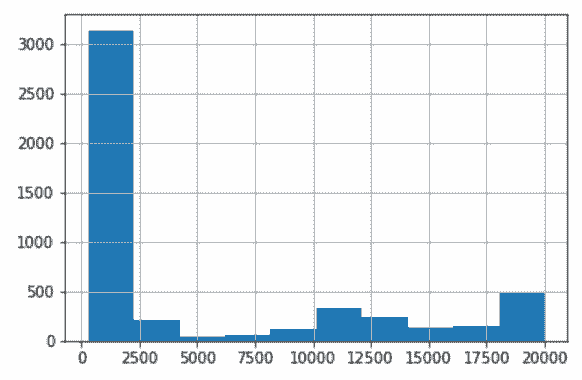
```py
# 再做一张柱状图,效果好多了
In[77]: fb_likes_cap.hist()
Out[77]: <matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x10eeea8d0>
```
```py
In[78]: fb_likes_cap2 = fb_likes.clip(lower=300, upper=20000)
fb_likes_cap2.equals(fb_likes_cap)
Out[78]: True
```
## 11\. 对DataFrame的行做mask
```py
# 读取movie,根据条件进行筛选
In[79]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
c1 = movie['title_year'] >= 2010
c2 = movie['title_year'].isnull()
criteria = c1 | c2
# 使用mask方法,使所有满足条件的数据消失
In[80]: movie.mask(criteria).head()
Out[80]:
```
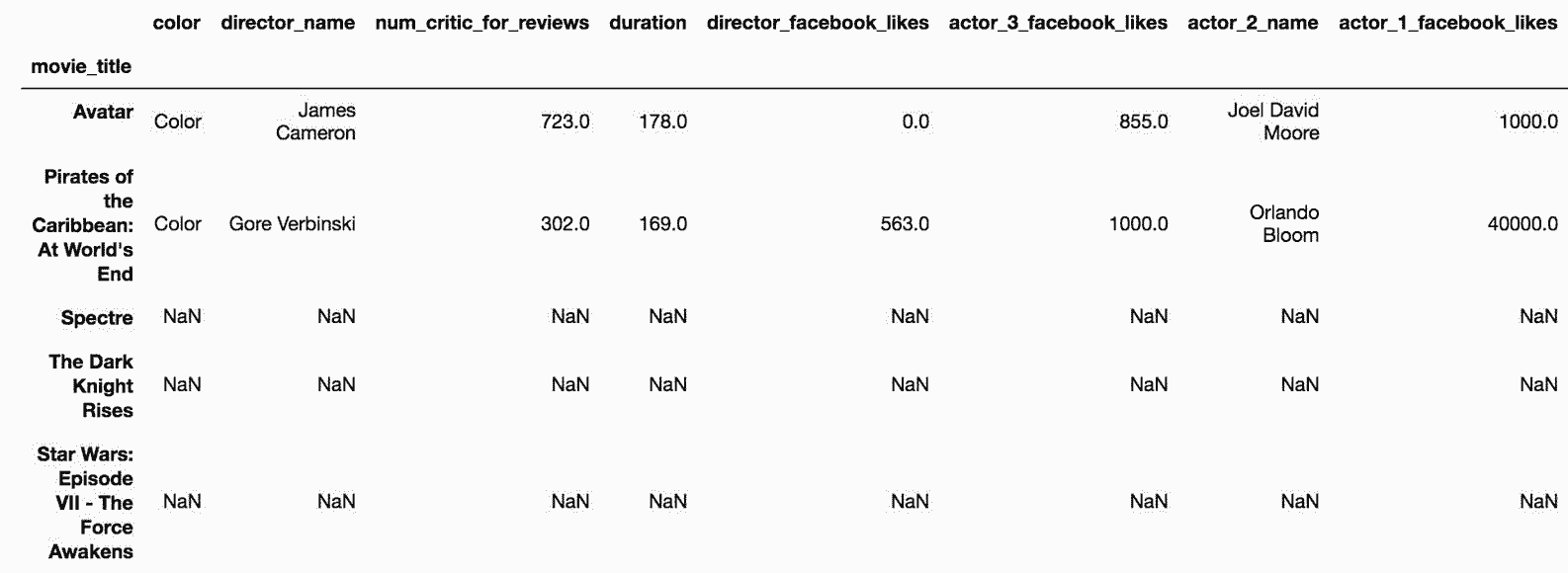
```py
# 去除缺失值
In[81]: movie_mask = movie.mask(criteria).dropna(how='all')
movie_mask.head()
Out[81]:
```

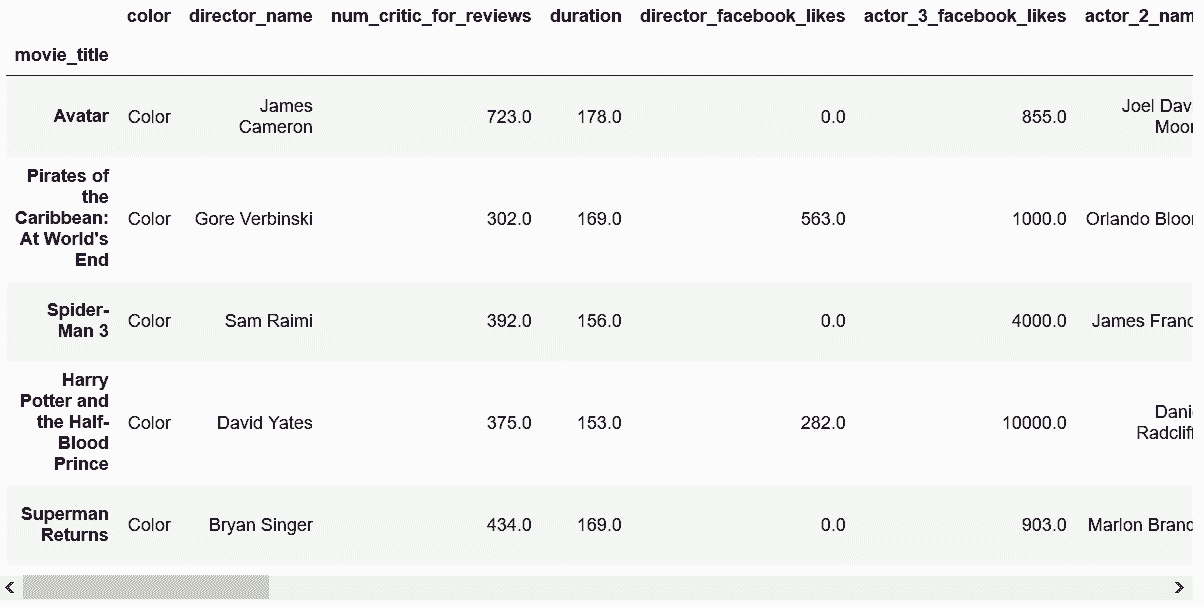
```py
# 用布尔索引选取title_year小于2010的电影
In[82]: movie_boolean = movie[movie['title_year'] < 2010]
movie_boolean.head()
Out[82]:
```
```py
# 判断这两种方法是否相同
In[83]: movie_mask.equals(movie_boolean)
Out[83]: False
```
```py
# 判断二者的形状是否相同
In[84]: movie_mask.shape == movie_boolean.shape
Out[84]: True
```
```py
# mask方法产生了许多缺失值,缺失值是float类型,所以之前是整数型的列都变成了浮点型
In[85]: movie_mask.dtypes == movie_boolean.dtypes
Out[85]:
color True
director_name True
num_critic_for_reviews True
duration True
director_facebook_likes True
actor_3_facebook_likes True
actor_2_name True
actor_1_facebook_likes True
gross True
genres True
actor_1_name True
num_voted_users False
cast_total_facebook_likes False
actor_3_name True
facenumber_in_poster True
plot_keywords True
movie_imdb_link True
num_user_for_reviews True
language True
country True
content_rating True
budget True
title_year True
actor_2_facebook_likes True
imdb_score True
aspect_ratio True
movie_facebook_likes False
dtype: bool
```
```py
# Pandas有一个assert_frame_equal方法,可以判断两个Pandas对象是否一样,而不检测其数据类型
In[86]: from pandas.testing import assert_frame_equal
assert_frame_equal(movie_boolean, movie_mask, check_dtype=False)
```
### 更多
```py
# 比较mask和布尔索引的速度,两者相差了一个数量级
In[87]: %timeit movie.mask(criteria).dropna(how='all')
11.1 ms ± 48.3 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)
In[88]: %timeit movie[movie['title_year'] < 2010]
1.12 ms ± 36.7 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1000 loops each)
```
## 12\. 使用布尔值、整数、标签进行选取
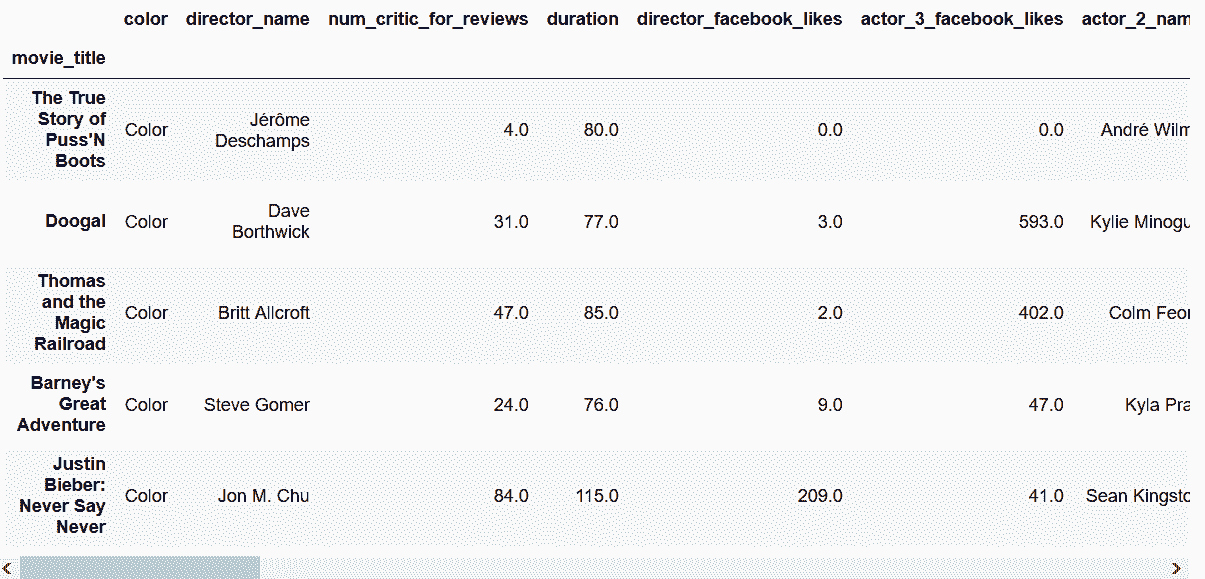
```py
# 读取movie,根据布尔条件选取
In[89]: movie = pd.read_csv('data/movie.csv', index_col='movie_title')
c1 = movie['content_rating'] == 'G'
c2 = movie['imdb_score'] < 4
criteria = c1 & c2
In[90]: movie_loc = movie.loc[criteria]
movie_loc.head()
Out[90]:
```
```py
# 检查loc条件和布尔条件创建出来的两个DataFrame是否一样
In[91]: movie_loc.equals(movie[criteria])
Out[91]: True
```
```py
# 尝试用.iloc使用布尔索引
In[92]: movie_iloc = movie.iloc[criteria]
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-92-24a12062c6c3> in <module>()
----> 1 movie_iloc = movie.iloc[criteria]
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/indexing.py in __getitem__(self, key)
1326 else:
1327 key = com._apply_if_callable(key, self.obj)
-> 1328 return self._getitem_axis(key, axis=0)
1329
1330 def _is_scalar_access(self, key):
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/indexing.py in _getitem_axis(self, key, axis)
1731
1732 if is_bool_indexer(key):
-> 1733 self._has_valid_type(key, axis)
1734 return self._getbool_axis(key, axis=axis)
1735
/Users/Ted/anaconda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/pandas/core/indexing.py in _has_valid_type(self, key, axis)
1588 "indexing on an integer type "
1589 "is not available")
-> 1590 raise ValueError("iLocation based boolean indexing cannot use "
1591 "an indexable as a mask")
1592 return True
ValueError: iLocation based boolean indexing cannot use an indexable as a mask
```
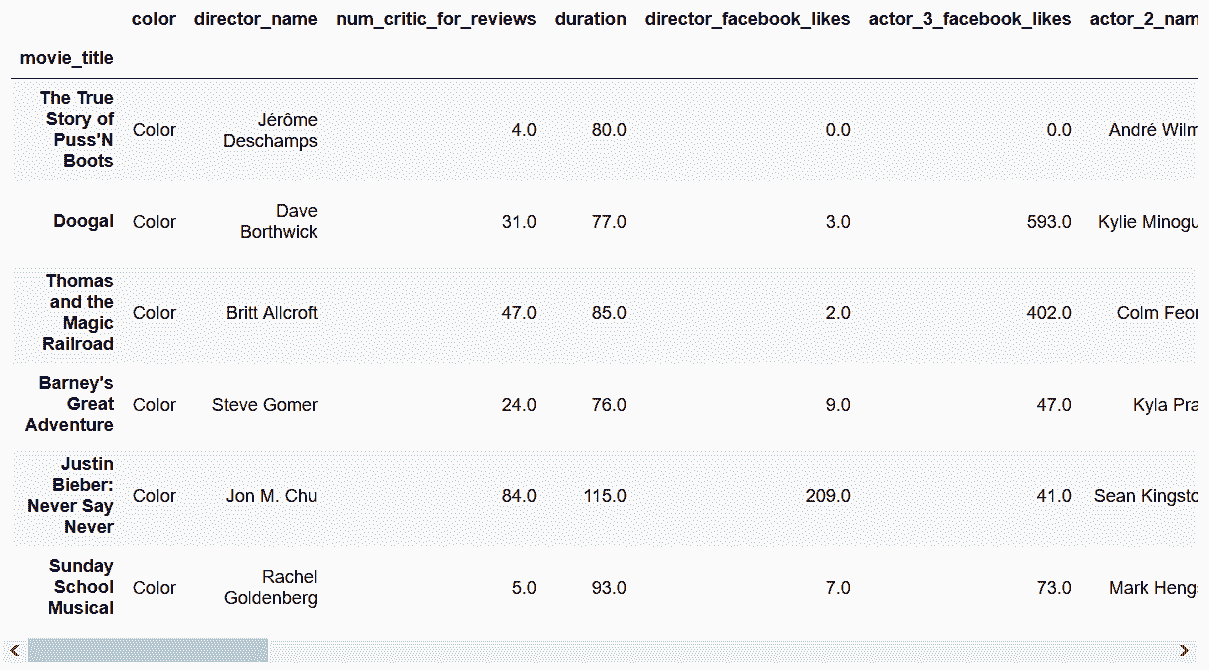
```py
# 但是,却可以使用布尔值得ndarray,用values可以取出array
In[93]: movie_iloc = movie.iloc[criteria.values]
In[94]: movie_iloc.equals(movie_loc)
Out[94]: True
In[95]: movie.loc[criteria.values]
Out[95]:
```
```py
# 布尔索引也可以用来选取列
In[96]: criteria_col = movie.dtypes == np.int64
criteria_col.head()
Out[96]: color False
director_name False
num_critic_for_reviews False
duration False
director_facebook_likes False
dtype: bool
```
```py
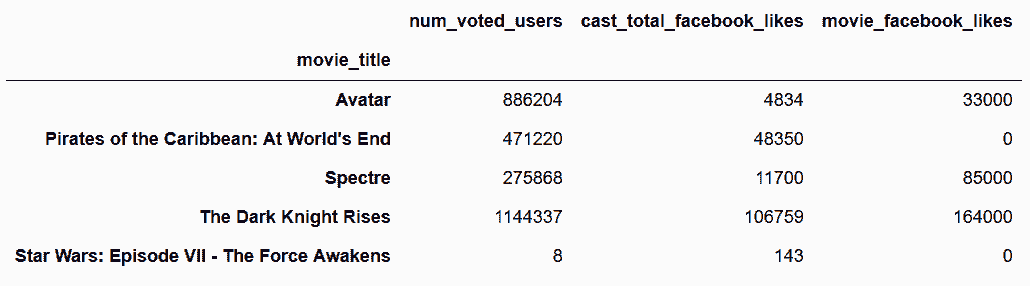
In[97]: movie.loc[:, criteria_col].head()
Out[97]:
```
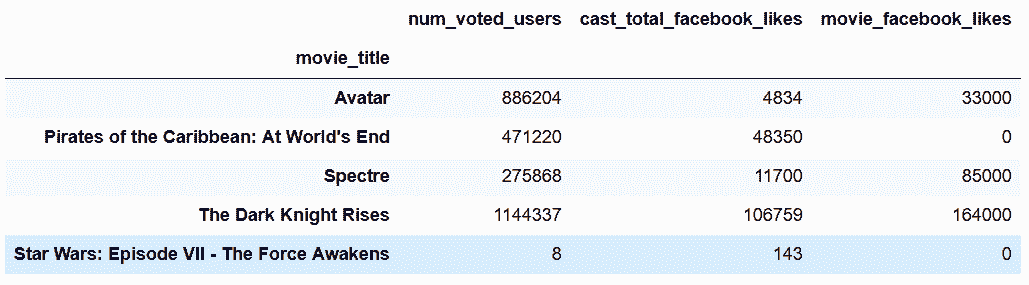
```py
# 因为criteria_col是包含行索引的一个Series,必须要使用底层的ndarray,才能使用,iloc
In[98]: movie.iloc[:, criteria_col.values].head()
Out[98]:
```
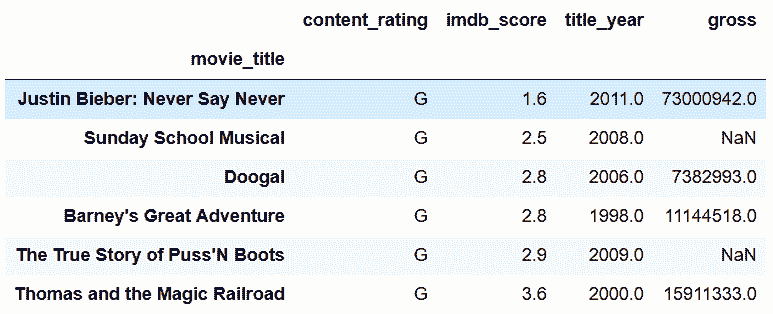
```py
# 选取'content_rating', 'imdb_score', 'title_year', 'gross'四列,按照imdb_score升序排列
In[99]: cols = ['content_rating', 'imdb_score', 'title_year', 'gross']
movie.loc[criteria, cols].sort_values('imdb_score')
Out[99]:
```
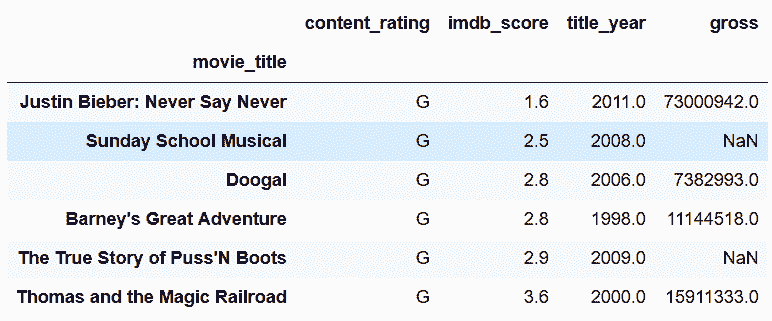
```py
# 用get_loc获取这四列的整数位置
In[100]: col_index = [movie.columns.get_loc(col) for col in cols]
col_index
Out[100]: [20, 24, 22, 8]
```
```py
# 这时候就可以使用iloc了
In[101]: movie.iloc[criteria.values, col_index].sort_values('imdb_score')
Out[101]:
```
### 原理
```py
# 查看Series的底层结构
In[102]: a = criteria.values
a[:5]
Out[102]: array([False, False, False, False, False], dtype=bool)
In[103]: len(a), len(criteria)
Out[103]: (4916, 4916)
```
### 更多
```py
# 传入的布尔索引可以跟要操作的DataFrame长度不同
In[104]: movie.loc[[True, False, True], [True, False, False, True]]
Out[104]:
```

