# Python 异常处理
> 原文: [https://thepythonguru.com/python-exception-handling/](https://thepythonguru.com/python-exception-handling/)
* * *
于 2020 年 1 月 7 日更新
* * *
异常处理使您能够优雅地处理错误并对其进行有意义的处理。 如果未找到所需文件,则向用户显示一条消息。 Python 使用`try`和`except`块处理异常。
**语法**:
```py
try:
# write some code
# that might throw exception
except <ExceptionType>:
# Exception handler, alert the user
```
如您在`try`块中看到的那样,您需要编写可能引发异常的代码。 当发生异常时,将跳过`try`块中的代码。 如果`except`子句中存在匹配的异常类型,则执行其处理器。
让我们举个例子:
```py
try:
f = open('somefile.txt', 'r')
print(f.read())
f.close()
except IOError:
print('file not found')
```
上面的代码如下:
1. 执行`try`和`except`块之间的第一条语句。
2. 如果没有异常发生,则将跳过`except`子句下的代码。
3. 如果文件不存在,则会引发异常,并且`try`块中的其余代码将被跳过
4. 发生异常时,如果异常类型与`except`关键字后的异常名称匹配,则将执行该`except`子句中的代码。
**注意**:
上面的代码仅能处理`IOError`异常。 要处理其他类型的异常,您需要添加更多的`except`子句。
`try`语句可以具有多个`except`子句,也可以具有可选的`else`和/或`finally`语句。
```py
try:
<body>
except <ExceptionType1>:
<handler1>
except <ExceptionTypeN>:
<handlerN>
except:
<handlerExcept>
else:
<process_else>
finally:
<process_finally>
```
`except`子句类似于`elif`。 发生异常时,将检查该异常以匹配`except`子句中的异常类型。 如果找到匹配项,则执行匹配大小写的处理器。 另请注意,在最后的`except`子句中,`ExceptionType`被省略。 如果异常不匹配最后一个`except`子句之前的任何异常类型,则执行最后一个`except`子句的处理器。
**注意**:
`else`子句下的语句仅在没有引发异常时运行。
**注意**:
无论是否发生异常,`finally`子句中的语句都将运行。
现在举个例子。
```py
try:
num1, num2 = eval(input("Enter two numbers, separated by a comma : "))
result = num1 / num2
print("Result is", result)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Division by zero is error !!")
except SyntaxError:
print("Comma is missing. Enter numbers separated by comma like this 1, 2")
except:
print("Wrong input")
else:
print("No exceptions")
finally:
print("This will execute no matter what")
```
**注意**:
`eval()`函数允许 python 程序在其内部运行 python 代码,`eval()`需要一个字符串参数。
要了解有关`eval()`的更多信息,请访问 Python 中的[`eval()`](/python-builtin-functions/eval/)。
## 引发异常
* * *
要从您自己的方法引发异常,您需要像这样使用`raise`关键字
```py
raise ExceptionClass("Your argument")
```
让我们举个例子
```py
def enterage(age):
if age < 0:
raise ValueError("Only positive integers are allowed")
if age % 2 == 0:
print("age is even")
else:
print("age is odd")
try:
num = int(input("Enter your age: "))
enterage(num)
except ValueError:
print("Only positive integers are allowed")
except:
print("something is wrong")
```
运行程序并输入正整数。
**预期输出**:
```py
Enter your age: 12
age is even
```
再次运行该程序并输入一个负数。
**预期输出**:
```py
Enter your age: -12
Only integers are allowed
```
## 使用异常对象
* * *
现在您知道如何处理异常,在本节中,我们将学习如何在异常处理器代码中访问异常对象。 您可以使用以下代码将异常对象分配给变量。
```py
try:
# this code is expected to throw exception
except ExceptionType as ex:
# code to handle exception
```
如您所见,您可以将异常对象存储在变量`ex`中。 现在,您可以在异常处理器代码中使用此对象。
```py
try:
number = eval(input("Enter a number: "))
print("The number entered is", number)
except NameError as ex:
print("Exception:", ex)
```
运行程序并输入一个数字。
**预期输出**:
```py
Enter a number: 34
The number entered is 34
```
再次运行程序并输入一个字符串。
**预期输出**:
```py
Enter a number: one
Exception: name 'one' is not defined
```
## 创建自定义异常类
* * *
您可以通过扩展`BaseException`类或`BaseException`的子类来创建自定义异常类。
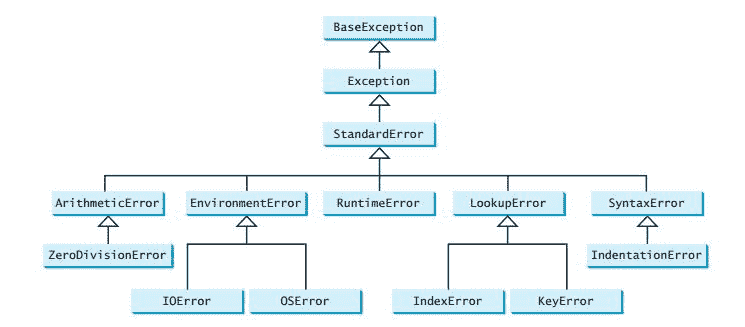
如您所见,python 中的大多数异常类都是从`BaseException`类扩展而来的。 您可以从`BaseException`类或`BaseException`的子类(例如`RuntimeError`)派生自己的异常类。
创建一个名为`NegativeAgeException.py`的新文件,并编写以下代码。
```py
class NegativeAgeException(RuntimeError):
def __init__(self, age):
super().__init__()
self.age = age
```
上面的代码创建了一个名为`NegativeAgeException`的新异常类,该异常类仅由使用`super().__init__()`调用父类构造器并设置`age`的构造器组成。
## 使用自定义异常类
* * *
```py
def enterage(age):
if age < 0:
raise NegativeAgeException("Only positive integers are allowed")
if age % 2 == 0:
print("age is even")
else:
print("age is odd")
try:
num = int(input("Enter your age: "))
enterage(num)
except NegativeAgeException:
print("Only positive integers are allowed")
except:
print("something is wrong")
```
在下一篇文章中,我们将学习 [Python 模块](/python-modules/)。
* * *
* * *
- 初级 Python
- python 入门
- 安装 Python3
- 运行 python 程序
- 数据类型和变量
- Python 数字
- Python 字符串
- Python 列表
- Python 字典
- Python 元组
- 数据类型转换
- Python 控制语句
- Python 函数
- Python 循环
- Python 数学函数
- Python 生成随机数
- Python 文件处理
- Python 对象和类
- Python 运算符重载
- Python 继承与多态
- Python 异常处理
- Python 模块
- 高级 Python
- Python *args和**kwargs
- Python 生成器
- Python 正则表达式
- 使用 PIP 在 python 中安装包
- Python virtualenv指南
- Python 递归函数
- __name__ == "__main__"是什么?
- Python Lambda 函数
- Python 字符串格式化
- Python 内置函数和方法
- Python abs()函数
- Python bin()函数
- Python id()函数
- Python map()函数
- Python zip()函数
- Python filter()函数
- Python reduce()函数
- Python sorted()函数
- Python enumerate()函数
- Python reversed()函数
- Python range()函数
- Python sum()函数
- Python max()函数
- Python min()函数
- Python eval()函数
- Python len()函数
- Python ord()函数
- Python chr()函数
- Python any()函数
- Python all()函数
- Python globals()函数
- Python locals()函数
- 数据库访问
- 安装 Python MySQLdb
- 连接到数据库
- MySQLdb 获取结果
- 插入行
- 处理错误
- 使用fetchone()和fetchmany()获取记录
- 常见做法
- Python:如何读取和写入文件
- Python:如何读取和写入 CSV 文件
- 用 Python 读写 JSON
- 用 Python 转储对象
