1、教程网址:
[https://piaosanlang.gitbooks.io/spiders/content/](https://piaosanlang.gitbooks.io/spiders/content/)
### 创建项目
在开始爬取之前,您必须创建一个新的`Scrapy`项目。 进入您打算存储代码的目录中,运行下列命令:
~~~
scrapy startproject tutorial
~~~
运行过程:
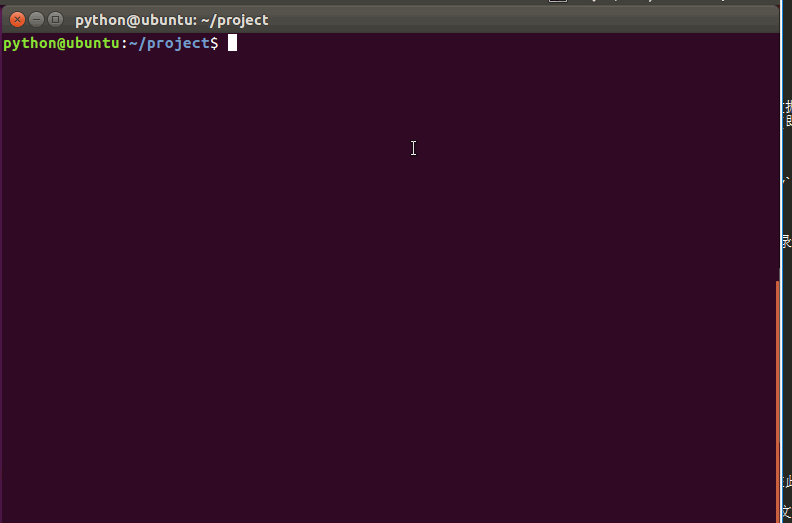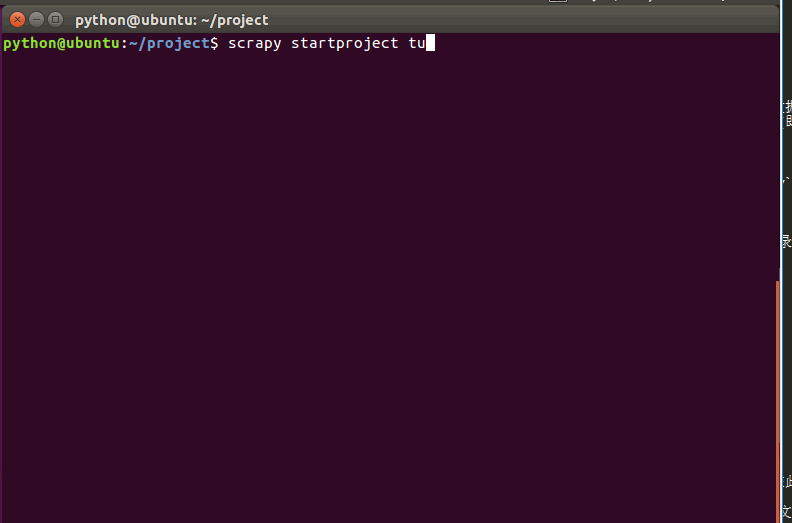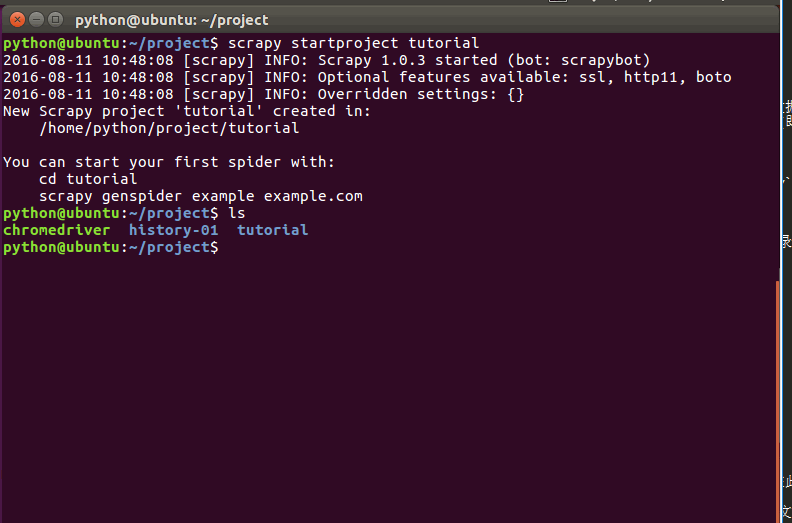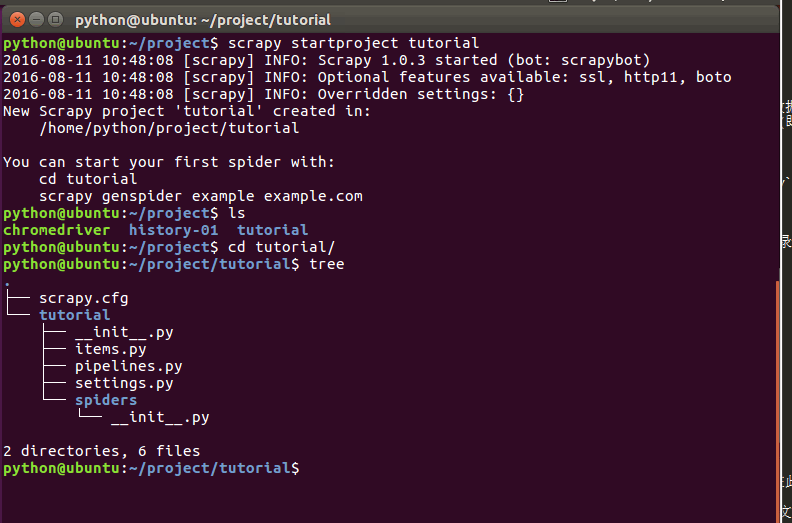
该命令将会创建包含下列内容的 tutorial 目录:
这些文件分别是:
~~~
scrapy.cfg: 项目的配置文件;(用于发布到服务器)
tutorial/: 该项目文件夹。之后将在此编写Python代码。
tutorial/items.py: 项目中的item文件;(定义结构化数据字段field).
tutorial/pipelines.py: 项目中的pipelines文件;(用于存放执行后期数据处理的功能,定义如何存储结构化数据)
tutorial/settings.py: 项目的设置文件;(如何修改User-Agent,设置爬取时间间隔,设置代理,配置中间件等等)
tutorial/spiders/: 放置spider代码的目录;(编写爬取网站规则)
~~~
### 定义Item
Item 定义结构化数据字段,用来保存爬取到的数据;其使用方法和python字典类似
可以通过创建一个`scrapy.Item`类, 并且定义类型为`scrapy.Field`的类属性来定义一个Item。
首先根据需要从[腾讯招聘](http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a)获取到的数据对item进行建模。 我们需要从`腾讯招聘`中获取 职位名称、`职位详情页url`、职位类别、人数、工作地点以及发布时间。 对此,在item中定义相应的字段。编辑`tutorial`目录中的`items.py`文件:
~~~
import scrapy
class RecruitItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
detailLink = scrapy.Field()
catalog = scrapy.Field()
recruitNumber = scrapy.Field()
workLocation = scrapy.Field()
publishTime = scrapy.Field()
~~~
### 编写第一个爬虫(Spider)
Spider是开发者编写用于从单个网站(或者一些网站)爬取数据的类。
创建一个Spider,必须继承 'scrapy.Spider' 类, 需要定义以下三个属性:
* name:
spider名字;必须是唯一的
* start\_urls:
初始的URL列表
* parse(self, response):
每个初始URL完成下载后被调用
这个函数要完成的功能:
~~~
1.负责解析返回的网页数据(response.body),提取结构化数据(生成item)
2.生成需要下一页的请求URL。
~~~
以下为我们的第一个Spider代码,保存在 tutorial/spiders 目录下的 tencent\_spider.py 文件中:
~~~
import scrapy
class RecruitSpider(scrapy.spiders.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
def parse(self, response):
f = open('tengxun.txt', 'wb')
f.write(response.body)
f.close()
~~~
### 爬取
进入项目的根目录,执行下列命令启动spider:
~~~
scrapy crawl tencent
~~~
crawl tencent 启动用于爬取 tencent 的spider,您将得到类似的输出:
现在,查看当前目录,会注意到有文件被创建了: tengxun.txt,正如我们的 parse 方法里做的一样。
**注意,在刚启动的时候会有一段error信息,不用理会**
在第六天作业里面有说明原因
~~~
2016-08-11 13:07:35 [boto] ERROR: Caught exception reading instance data
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/boto/utils.py", line 210, in retry_url
r = opener.open(req, timeout=timeout)
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/urllib2.py", line 429, in open
response = self._open(req, data)
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/urllib2.py", line 447, in _open
'_open', req)
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/urllib2.py", line 407, in _call_chain
result = func(*args)
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/urllib2.py", line 1228, in http_open
return self.do_open(httplib.HTTPConnection, req)
File "/usr/lib/python2.7/urllib2.py", line 1198, in do_open
raise URLError(err)
URLError: <urlopen error timed out>
~~~
### 刚才发生了什么?
Scrapy为Spider的 start\_urls 属性中的每个URL创建了`scrapy.Request`对象,并将 parse 方法作为回调函数(callback)赋值给了Request。
Request对象经过调度,执行生成`scrapy.http.Response`对象并送回给`parse()`方法。
### 提取Item
#### Selectors选择器简介
`Scrapy Selectors`内置`XPath`和`CSS Selector`表达式机制
XPath表达式的例子及对应的含义:
~~~
/html/head/title: 选择<HTML>文档中 <head> 标签内的 <title> 元素
/html/head/title/text(): 选择上面提到的 <title> 元素的文字
//td: 选择所有的 <td> 元素
//div[@class="mine"]: 选择所有具有 class="mine" 属性的 div 元素
~~~
Selector有四个基本的方法:
~~~
xpath(): 传入xpath表达式,返回该表达式所对应的所有节点的selector list列表 。
css(): 传入CSS表达式,返回该表达式所对应的所有节点的selector list列表.
extract(): 序列化该节点为unicode字符串并返回list。
re(): 根据传入的正则表达式对数据进行提取,返回unicode字符串list列表。
~~~
### 尝试Selector选择器
为了介绍Selector的使用方法,接下来我们将要使用内置的 scrapy shell 。Scrapy Shell需要您预装好IPython(一个扩展的Python终端)。
您需要进入项目的根目录,执行下列命令来启动shell:
~~~
scrapy shell "http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
~~~
注解: 当您在终端运行Scrapy时,请一定记得给url地址加上引号,否则包含参数的url(例如 & 字符)会导致Scrapy运行失败。
shell的输出类似:
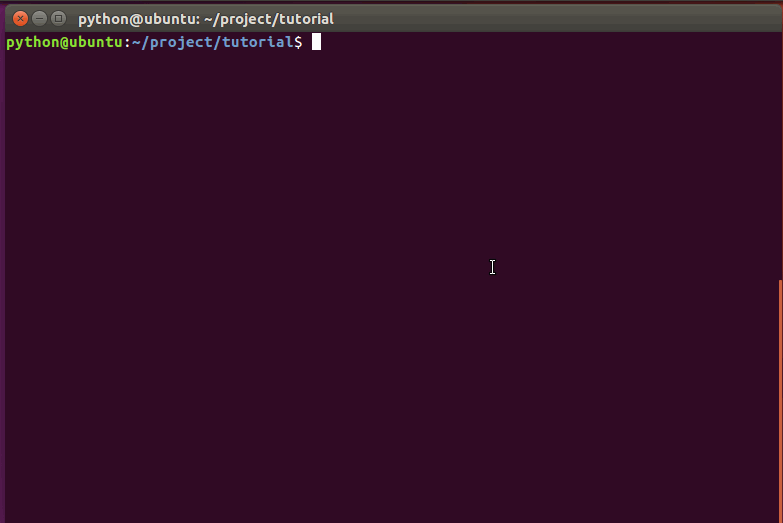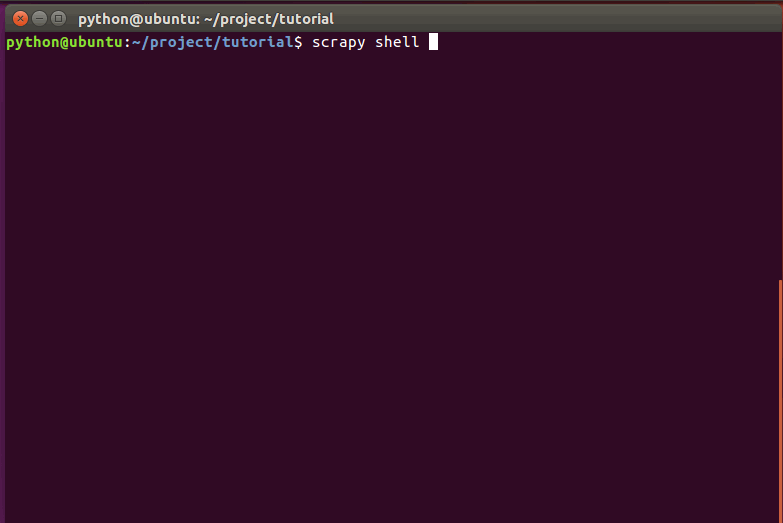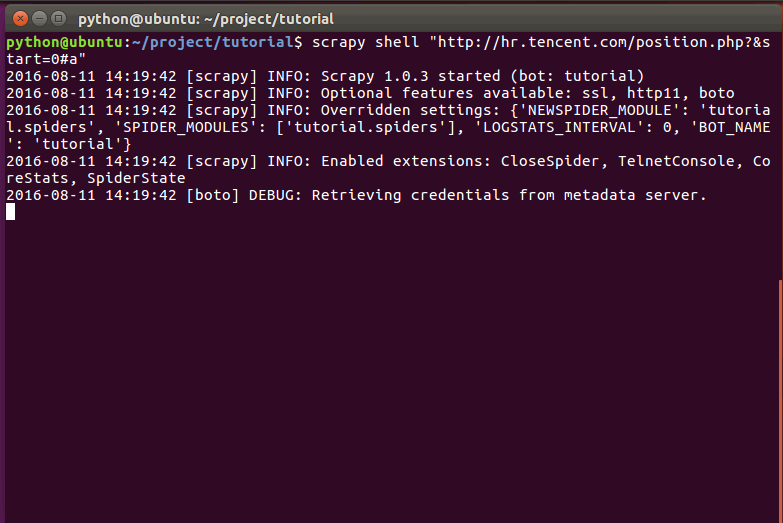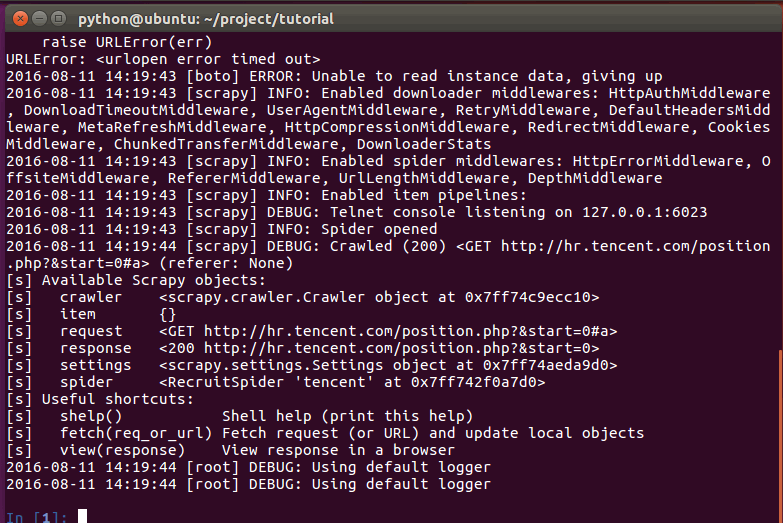
当shell载入后,将得到一个包含response数据的本地`response`变量。输入`response.body`将输出response的包体, 输出`response.headers`可以看到response的包头。
* 当输入`response.selector`时, 将获取到一个response 初始化的类`Selector`的对象
* 此时,可以通过使用 response.selector.xpath() 或 response.selector.css() 来对 response 进行查询。
* 或者,scrapy也对 response.selector.xpath() 及 response.selector.css() 提供了一些快捷方式, 例如 response.xpath() 或 response.css()
让我们来试试:
~~~
response.xpath('//title')
[<Selector xpath='//title' data=u'<title>\u804c\u4f4d\u641c\u7d22 | \u793e\u4f1a\u62db\u8058 | Tencent \u817e\u8baf\u62db\u8058</title'>]
response.xpath('//title').extract()
[u'<title>\u804c\u4f4d\u641c\u7d22 | \u793e\u4f1a\u62db\u8058 | Tencent \u817e\u8baf\u62db\u8058</title>']
print response.xpath('//title').extract()[0]
<title>职位搜索 | 社会招聘 | Tencent 腾讯招聘</title>
response.xpath('//title/text()')
<Selector xpath='//title/text()' data=u'\u804c\u4f4d\u641c\u7d22 | \u793e\u4f1a\u62db\u8058 | Tencent \u817e\u8baf\u62db\u8058'>
response.xpath('//title/text()')[0].extract()
u'\u804c\u4f4d\u641c\u7d22 | \u793e\u4f1a\u62db\u8058 | Tencent \u817e\u8baf\u62db\u8058'
print response.xpath('//title/text()')[0].extract()
职位搜索 | 社会招聘 | Tencent 腾讯招聘
response.xpath('//title/text()').re('(\w+):')
[u'\u804c\u4f4d\u641c\u7d22',
u'\u793e\u4f1a\u62db\u8058',
u'Tencent',
u'\u817e\u8baf\u62db\u8058']
~~~
### 提取数据
现在,我们来尝试从这些页面中提取些有用的数据。
我们可以通过XPath选择该页面中网站列表里所有`lass=even`元素:
~~~
site = response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]')
~~~
职位名称:
~~~
print site[0].xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
TEG15-运营开发工程师(深圳)
~~~
职位名称详情页:
~~~
print site[0].xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
position_detail.php?id=20744&keywords=&tid=0&lid=0
~~~
职位类别:
~~~
print site[0].xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
技术类
~~~
对于`.xpath()`调用返回`selector`组成的`list`, 因此可以拼接更多的 .xpath() 来进一步获取某个节点。
~~~
for sel in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
catalog = sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
recruitNumber = sel.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = sel.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = sel.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
~~~
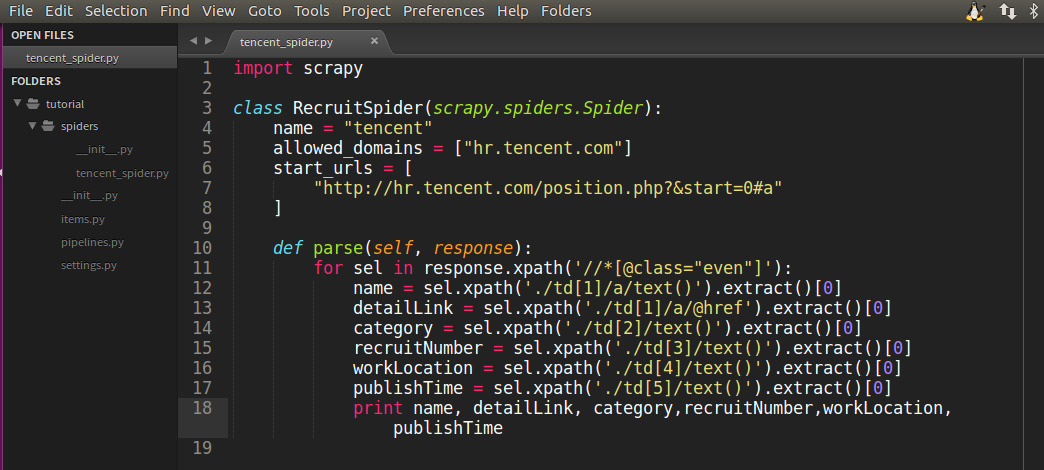
在我们的`tencent_spider.py`文件修改成如下代码:
~~~
import scrapy
class RecruitSpider(scrapy.spiders.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
def parse(self, response):
for sel in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
catalog = sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
recruitNumber = sel.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = sel.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = sel.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
~~~
如图所示:
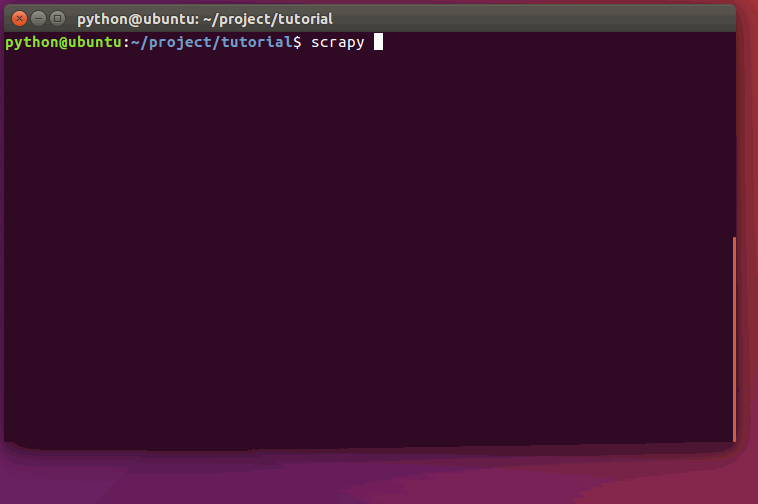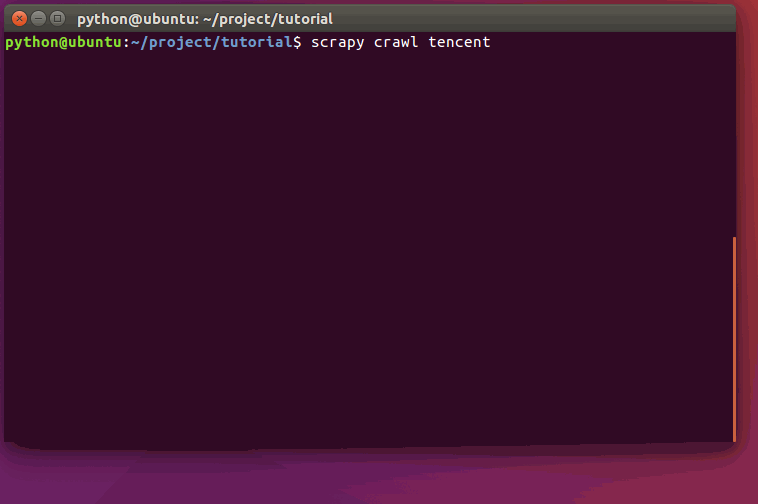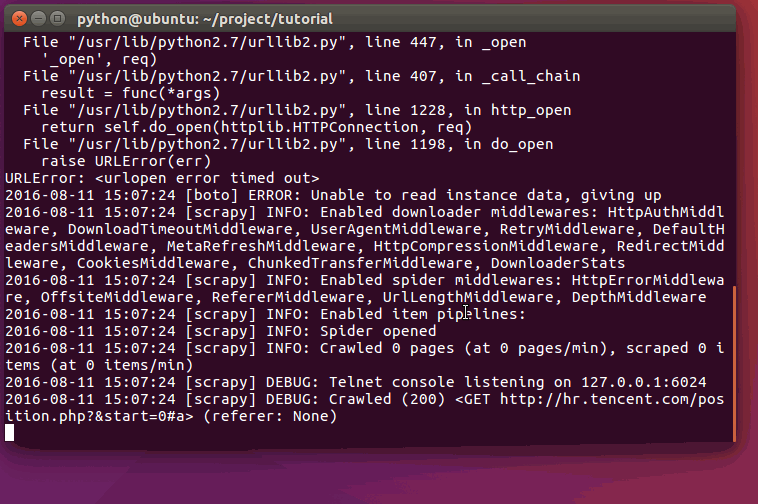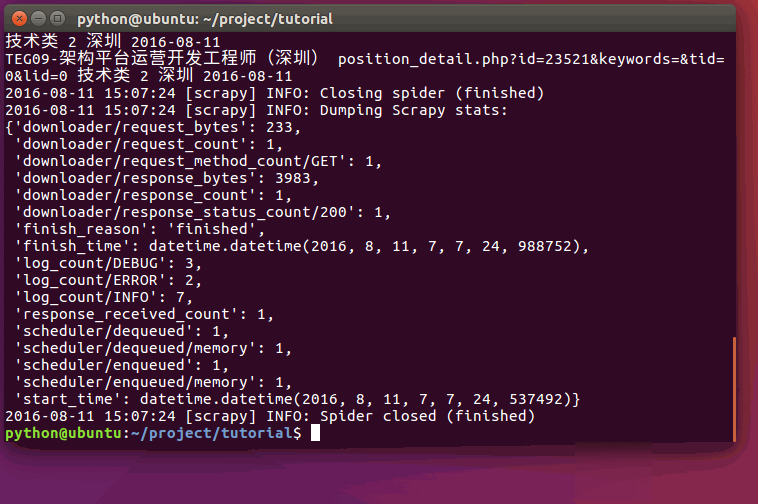
现在尝试再次爬取`hr.tencent.com`,您将看到爬取到的网站信息被成功输出:
~~~
scrapy crawl tencent
~~~
运行过程:
### 使用item
Item 对象是自定义的python字典。可以使用标准的字典语法来获取到其每个字段的值。
输入 `scrapy shell'
~~~
import scrapy
class RecruitItem(scrapy.Item):
name = scrapy.Field()
detailLink = scrapy.Field()
catalog = scrapy.Field()
recruitNumber = scrapy.Field()
workLocation = scrapy.Field()
publishTime = scrapy.Field()
item = RecruitItem()
item['name'] = 'sanlang'
item['name']
'sanlang'
~~~
一般来说,Spider将会将爬取到的数据以Item对象返回。所以为了将爬取的数据返回,最终`tencent_spider.py`代码将是:
~~~
import scrapy
from tutorial.items import RecruitItem
class RecruitSpider(scrapy.spiders.Spider):
name = "tencent"
allowed_domains = ["hr.tencent.com"]
start_urls = [
"http://hr.tencent.com/position.php?&start=0#a"
]
def parse(self, response):
for sel in response.xpath('//*[@class="even"]'):
name = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/text()').extract()[0]
detailLink = sel.xpath('./td[1]/a/@href').extract()[0]
catalog = sel.xpath('./td[2]/text()').extract()[0]
recruitNumber = sel.xpath('./td[3]/text()').extract()[0]
workLocation = sel.xpath('./td[4]/text()').extract()[0]
publishTime = sel.xpath('./td[5]/text()').extract()[0]
print name, detailLink, catalog,recruitNumber,workLocation,publishTime
item = RecruitItem()
item['name']=name.encode('utf-8')
item['detailLink']=detailLink.encode('utf-8')
item['catalog']=catalog.encode('utf-8')
item['recruitNumber']=recruitNumber.encode('utf-8')
item['workLocation']=workLocation.encode('utf-8')
item['publishTime']=publishTime.encode('utf-8')
yield item
~~~
现在对`hr.tencent.com`进行爬取将会产生 RecruitItem 对象:
运行过程:
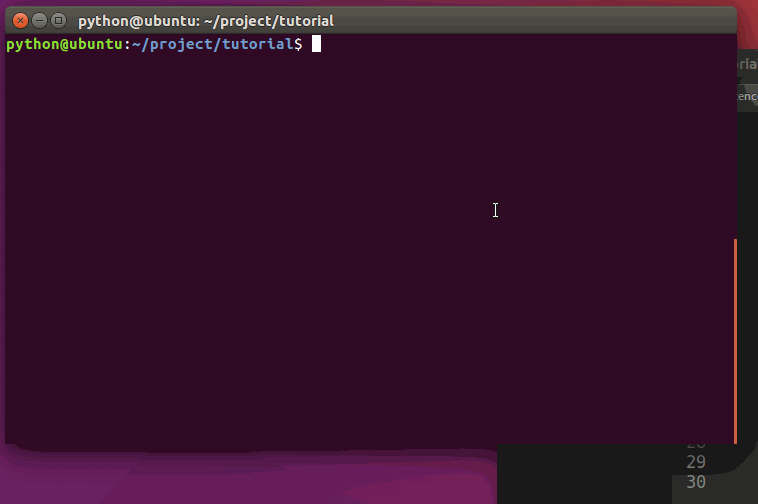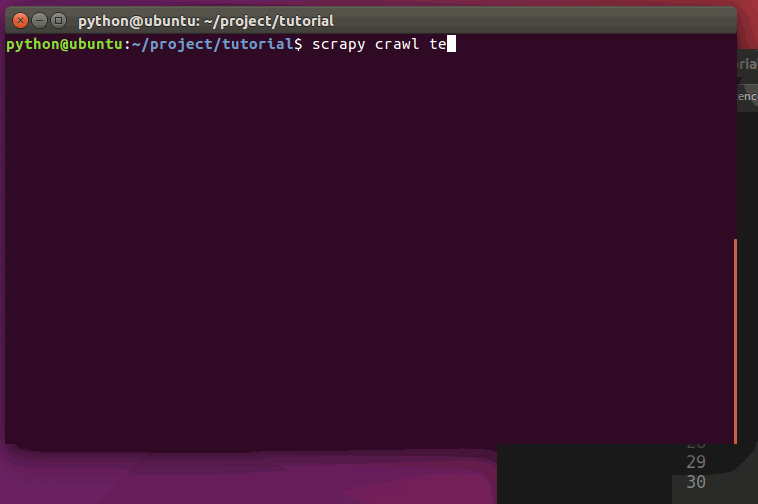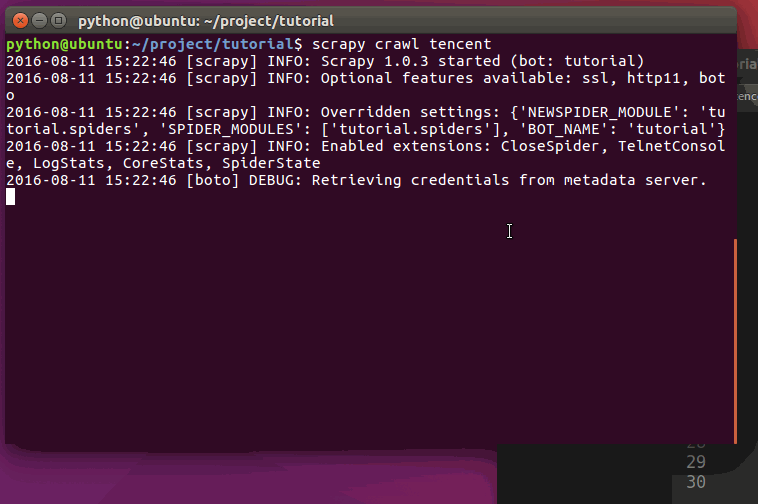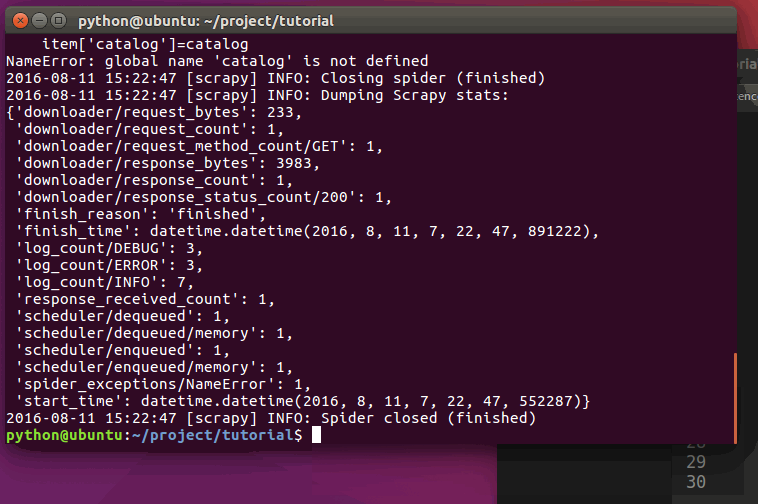
### 保存爬取到的数据
最简单存储爬取的数据的方式是使用`Feed exports`:
~~~
scrapy crawl tencent -o items.json
~~~
该命令将采用 JSON 格式对爬取的数据进行序列化,生成 items.json 文件。
如果需要对爬取到的item做更多更为复杂的操作,您可以编写 Item Pipeline 。 类似于我们在创建项目时对Item做的,用于您编写自己的 tutorial/pipelines.py 也被创建。 不过如果您仅仅想要保存item,您不需要实现任何的pipeline。
- thinkphp
- thinkphp笔记
- 后台登陆退出
- config配置
- 隐藏后台模块
- 单独调用腾讯云行为验证码
- api接口跨域问题
- api接口创建案例代码
- 使用gateway worker
- 使用swoole代码笔记
- 使用队列 think-queue笔记
- 后台布局
- MySQL
- 1、关于lnmp mysql的一个坑
- 2、mysql实现group by后取各分组的最新一条
- 其他
- 搞笑的注释代码
- 分页类
- nodejs 打包网址为exe
- 免费天气预报API接口
- Ajax
- 简单的ajax分页1
- 通用ajax-post提交
- 引用的类库文件
- Auth.php
- Auth.php权限控制对应的数据库表结构
- Layui.php
- Pinyin.php
- Random.php
- Tree.php
- Tree2.php
- Js-Jq
- Git的使用
- 3、bootstrap-datetimepicker实现两个时间范围输入
- CentOS安装SSR做梯子
- Python爬虫
- 1、安装Gerapy
- 2、安装Scrapy
- 3、Scrapy使用
- 4、Scrapy框架,爬取网站返回json数据(spider源码)
- 0、Python pip更换国内源(一句命令换源)
- 服务器运维
- 1、宝塔使用webhook更新服务器代码
- 2、搭建内网穿透
- 3、数据库主从同步
- 4、数据库复制
- hui-Shop问题
- 1、前端模板的注意事项
- 2、模板标签
