## 1.抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree)
`webpack`和`Lint`等很多的工具和库的核心都是通过`Abstract Syntax Tree`抽象语法树这个概念来实现对代码的检查、分析等操作的
* 通过了解抽象语法树这个概念,你也可以随手编写类似的工具
## 2.抽象语法树用途
* 代码语法的检查、代码风格的检查、代码的格式化、代码的高亮、代码错误提示、代码自动补全等等
* 如JSLint、JSHint对代码错误或风格的检查,发现一些潜在的错误
* IDE的错误提示、格式化、高亮、自动补全等等
* 代码混淆压缩
* UglifyJS2等
* 优化变更代码,改变代码结构使达到想要的结构
* 代码打包工具webpack、rollup等等
* CommonJS、AMD、CMD、UMD等代码规范之间的转化
* CoffeeScript、TypeScript、JSX等转化为原生Javascript
## 3.抽象语法树定义
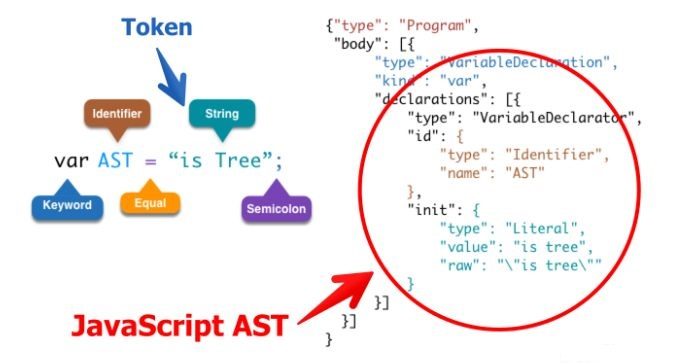
这些工具的原理都是通过`JavaScript Parser`把代码转化为一颗抽象语法树(AST),这颗树定义了代码的结构,通过操纵这颗树,我们可以精准的定位到声明语句、赋值语句、运算语句等等,实现对代码的分析、优化、变更等操作
> 在计算机科学中,抽象语法树(abstract syntax tree或者缩写为AST),或者语法树(syntax tree),是源代码的抽象语法结构的树状表现形式,这里特指编程语言的源代码。
> Javascript的语法是为了给开发者更好的编程而设计的,但是不适合程序的理解。所以需要转化为AST来使之更适合程序分析,浏览器编译器一般会把源码转化为AST来进行进一步的分析等其他操作。
## 4.JavaScript Parser
* JavaScript Parser,把js源码转化为抽象语法树的解析器。
* 浏览器会把js源码通过解析器转为抽象语法树,再进一步转化为字节码或直接生成机器码。
* 一般来说每个js引擎都会有自己的抽象语法树格式,Chrome的v8引擎,firefox的SpiderMonkey引擎等等,MDN提供了详细SpiderMonkey AST format的详细说明,算是业界的标准。
### 4.1 常用的JavaScript Parser
* esprima
* traceur
* acorn
* shift
### 4.2 esprima
* 通过[esprima](https://www.npmjs.com/package/esprima)把源码转化为AST
* 通过[estraverse](https://www.npmjs.com/package/estraverse)遍历并更新AST
* 通过[escodegen](https://www.npmjs.com/package/escodegen)将AST重新生成源码
* [astexplorer](https://astexplorer.net/)AST的可视化工具
~~~
mkdir zhufengast
cd zhufengast
cnpm i esprima estraverse escodegen- S
~~~
~~~
let esprima = require('esprima');
var estraverse = require('estraverse');
var escodegen = require("escodegen");
let code = 'function ast(){}';
let ast=esprima.parse(code);
let indent=0;
function pad() {
return ' '.repeat(indent);
}
estraverse.traverse(ast,{
enter(node) {
console.log(pad()+node.type);
if(node.type == 'FunctionDeclaration'){
node.id.name = 'ast_rename';
}
indent+=2;
},
leave(node) {
indent-=2;
console.log(pad()+node.type);
}
});
let generated = escodegen.generate(ast);
console.log(generated);
~~~
~~~
Program
FunctionDeclaration
Identifier
Identifier
BlockStatement
BlockStatement
FunctionDeclaration
Program
~~~
~~~
let esprima = require('esprima');//源代码转成AST语法树
let estraverse = require('estraverse');//遍历语法树
let escodegen = require('escodegen');//把AST语法树重新生成代码的工具
let sourceCode = 'function ast(){}';
let ast = esprima.parse(sourceCode);//源代码转成AST语法树
let indent =0;
function pad(){
return " ".repeat(indent);
}
estraverse.traverse(ast,{
enter(node){
console.log(pad()+node.type);
indent+=2;
},
leave(node){
indent-=2;
console.log(pad()+node.type);
}
});
~~~
## 5.babel插件
* 访问者模式Visitor 对于某个对象或者一组对象,不同的访问者,产生的结果不同,执行操作也不同
* [@babel/core](https://www.npmjs.com/package/@babel/core)Babel 的编译器,核心 API 都在这里面,比如常见的 transform、parse
* [babylon](http://www.zhufengpeixun.cn/2020/html/26.webpack-5-AST.html)Babel 的解析器
* [babel-types](https://github.com/babel/babel/tree/master/packages/babel-types)用于 AST 节点的 Lodash 式工具库, 它包含了构造、验证以及变换 AST 节点的方法,对编写处理 AST 逻辑非常有用
* [babel-traverse](https://www.npmjs.com/package/babel-traverse)用于对 AST 的遍历,维护了整棵树的状态,并且负责替换、移除和添加节点
* [babel-types-api](https://babeljs.io/docs/en/next/babel-types.html)
* [Babel 插件手册](https://github.com/brigand/babel-plugin-handbook/blob/master/translations/zh-Hans/README.md#asts)
* [babeljs.io](https://babeljs.io/en/repl.html)babel可视化编译器
### 5.1 转换箭头函数
* [babel-plugin-transform-es2015-arrow-functions](https://www.npmjs.com/package/babel-plugin-transform-es2015-arrow-functions)
转换前
~~~
const sum = (a,b)=>a+b
~~~

转换后
~~~
var sum = function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
};
~~~

~~~
npm i @babel/core babel-types -D
~~~
实现
~~~
let babel = require('@babel/core');
let t = require('babel-types');
const code = `const sum = (a,b)=>a+b`;
let transformArrowFunctions = {
visitor: {
ArrowFunctionExpression: (path) => {
let node = path.node;
let id = path.parent.id;
let params = node.params;
let body=t.blockStatement([
t.returnStatement(node.body)
]);
let functionExpression = t.functionExpression(id,params,body,false,false);
path.replaceWith(functionExpression);
}
}
}
const result = babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [transformArrowFunctions]
});
console.log(result.code);
~~~
### 5.2. 预计算babel插件
* path.parentPath 父路径
转换前
~~~
const result = 1 + 2;
~~~

转换后
~~~
const result = 3;
~~~

```
let babel = require('@babel/core'); let t=require('babel-types'); let preCalculator={ visitor: { BinaryExpression(path) { let node=path.node; let left=node.left; let operator=node.operator; let right=node.right; if (!isNaN(left.value) && !isNaN(right.value)) { let result=eval(left.value+operator+right.value); path.replaceWith(t.numericLiteral(result)); if (path.parent&& path.parent.type == 'BinaryExpression') { preCalculator.visitor.BinaryExpression.call(null,path.parentPath); } } } } } const result = babel.transform('const sum = 1+2+3',{ plugins:\[ preCalculator \] }); console.log(result.code);
```
## 9\. AST
### 9.1 解析过程
AST整个解析过程分为两个步骤
* 分词:将整个代码字符串分割成语法单元数组
* 语法分析:建立分析语法单元之间的关系
### 9.2 语法单元
Javascript 代码中的语法单元主要包括以下这么几种
* 关键字:`const`、`let`、`var`等
* 标识符:可能是一个变量,也可能是 if、else 这些关键字,又或者是 true、false 这些常量
* 运算符
* 数字
* 空格
* 注释
### 9.3 词法分析
~~~
let jsx = `let element=<h1>hello</h1>`;
function lexical(code) {
const tokens=[];
for (let i=0;i<code.length;i++){
let char=code.charAt(i);
if (char == '=') {
tokens.push({
type: 'operator',
value:char
});
}
if (char=='<') {
const token={
type: 'JSXElement',
value:char
}
tokens.push(token);
let isClose = false;
for (i++;i<code.length;i++){
char=code.charAt(i);
token.value+=char;
if (char=='>') {
if (isClose) {
break;
} else {
isClose=true;
}
}
}
continue;
}
if (/[a-zA-Z\$\_]/.test(char)) {
const token={
type: 'Identifier',
value:char
}
tokens.push(token);
for (i++;i<code.length;i++){
char=code.charAt(i);
if (/[a-zA-Z\$\_]/.test(char)) {
token.value+=char;
} else {
i--;
break;
}
}
continue;
}
if (/\s/.test(char)) {
const token={
type: 'whitespace',
value:char
}
tokens.push(token);
for (i++;i<code.length;i++){
char=code.charAt[i];
if (/\s/.test(char)) {
token.value+=char;
} else {
i--;
break;
}
}
continue;
}
}
return tokens;
}
let result=lexical(jsx);
console.log(result);
~~~
~~~
[
{ type: 'Identifier', value: 'let' },
{ type: 'whitespace', value: ' ' },
{ type: 'Identifier', value: 'element' },
{ type: 'operator', value: '=' },
{ type: 'JSXElement', value: '<h1>hello</h1>' }
]
~~~
### 9.4 语法分析
* 语义分析则是将得到的词汇进行一个立体的组合,确定词语之间的关系
* 简单来说语法分析是对语句和表达式识别,这是个递归过程
~~~
// babylon7 https://astexplorer.net/
// babylon7 https://astexplorer.net/
function parse(tokens) {
const ast={
type: 'Program',
body: [],
sourceType:'script'
}
let i=0;//标示当前位置
let currentToken;//当前的符号
while ((currentToken = tokens[i])) {
if (currentToken.type == 'Identifier' && (currentToken.value == 'let'||currentToken.value == 'var')) {
const VariableDeclaration={
type: 'VariableDeclaration',
declarations:[]
}
i+=2;
currentToken=tokens[i];
let VariableDeclarator = {
type: 'VariableDeclarator',
id: {
type: 'Identifier',
name:currentToken.value
}
};
VariableDeclaration.declarations.push(VariableDeclarator);
i+=2;
currentToken=tokens[i];
if (currentToken.type=='JSXElement') {
let value=currentToken.value;
let [,type,children]=value.match(/([^<]+?)>([^<]+)<\/\1>/);
VariableDeclarator.init={
type: 'JSXElement',
openingElement:{
type:'JSXOpeningElement',
name:{
type:'JSXIdentifier',
name:'h1'
}
},
closingElement:{
type:'JSXClosingElement',
name:{
type:'JSXIdentifier',
name:'h1'
}
},
name: type,
children:[
{
type:'JSXText',
value:'hello'
}
]
}
} else {
VariableDeclarator.init={
type: 'Literal',
value:currentToken.value
}
}
ast.body.push(VariableDeclaration);
}
i++;
}
return ast;
}
let tokens=[
{type: 'Identifier',value: 'let'},
{type: 'whitespace',value: ' '},
{type: 'Identifier',value: 'element'},
{type: 'operator',value: '='},
{type: 'JSXElement',value: '<h1>hello</h1>'}
];
let result = parse(tokens);
console.log(result);
console.log(JSON.stringify(result));
~~~
~~~
{
"type": "Program",
"body": [{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"declarations": [{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "element"
},
"init": {
"type": "JSXElement",
"openingElement": {
"type": "JSXOpeningElement",
"name": {
"type": "JSXIdentifier",
"name": "h1"
}
},
"closingElement": {
"type": "JSXClosingElement",
"name": {
"type": "JSXIdentifier",
"name": "h1"
}
},
"name": "h1",
"children": [{
"type": "JSXText",
"value": "hello"
}]
}
}]
}],
"sourceType": "script"
}
~~~
```
letutil\=require('util');
functionparse(tokens){
letast\= { type:'Program',body:\[\],sourceType:'module'};
leti\=0;//当前的索引
letcurrToken;//当前的token
while(currToken\=tokens\[i\]){
//第一次的时候 currToken = { type: 'Keyword', value: 'let' }
if(currToken.type\=='Keyword'&&currToken.value\=='let'){
letVariableDeclaration\= {type:'VariableDeclaration',declarations:\[\]};
ast.body.push(VariableDeclaration);
i+=2;//i=2
currToken\=tokens\[i\];//{ type: 'Identifier', value: 'element' },
letvariableDeclarator\= {
type:'VariableDeclarator',
id:{type:'Identifier',name:currToken.value}
}
VariableDeclaration.declarations.push(variableDeclarator);
i+=2;//i=4
currToken\=tokens\[i\];// { type: 'String', value: 'hello' }
if(currToken.type\=='String'){
variableDeclarator.init\= {type:'StringLiteral',value:currToken.value};
}elseif(currToken.type\=='JSXElement'){
letvalue\=currToken.value;
//type=h1 children=hello
let \[,type,children\] \=value.match(/\]+?)>(\[^/); //hello
variableDeclarator.init\= {
type:'JSXElement',//类型JSX元素
openingElement:{
type:'OpeningElement',
name:{type:'JSXIdentifier',name:type}
},
closingElement:{
type:'ClosingElement',
name:{type:'JSXIdentifier',name:type}
},
children:\[
{type:'JSXText',value:children}
\]
}
}
}
i++;
}
returnast;
}
lettokens\= \[
{ type: 'Keyword', value: 'let' },
{ type: 'WhiteSpace', value: ' ' },
{ type: 'Identifier', value: 'element' },
{ type: 'Equal', value: '=' },
{type:"JSXElement",value:'hello'}
\];
//{ type: 'JSXElement', value: 'hello' }
letast\=parse(tokens);
ast.body\[0\].declarations\[0\].init\= {
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"callee": {
"type": "MemberExpression",
"computed": false,
"object": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "React",
},
"property": {
"type": "Identifier",
"name": "createElement",
}
},
"arguments": \[
{
"type": "Literal",
"value": "h1",
"raw": "\\"h1\\""
},
{
"type": "Literal",
"value": null,
"raw": "null"
},
{
"type": "Literal",
"value": "hello",
"raw": "\\"hello\\""
}
\]
}
}
console.log(JSON.stringify(ast))
```
- 文档简介
- 基础面试题【珠峰2019.8】
- P01_call,aplly区别
- P02_综合面试题讲解2-2
- P03_箭头函数和普通函数区别-综合面试题讲解2-3
- P05_实现indexOf
- P06_综合面试题讲解2-6
- P07_URL解析题
- P08_原型题
- P09_图片延时加载
- P10_正则-包含数字字母下划线
- P11_综合面试题讲解2-11
- P12_英文字母加空格
- P13_数组扁平化并去重
- P14_模拟实现new
- P15_合并数组
- P16_定时器,打印012345
- P17_匿名函数输出值问题
- P18_a在什么情况下打印输出+1+1+1
- P19_对数组的理解
- P20_冒泡排序
- P21_插入排序
- P22_快速排序
- P23_销售额存在对象中
- P24_求数组的交集
- P25_旋转数组
- P26_ [函数柯理化思想]
- P27_ [柯理化函数的递归]
- 网络协议【珠峰2019.6】
- TypeScript+Axios入门+实战【珠峰2019.11】
- 1.数据结构
- 2.函数和继承
- 3.装饰器
- 4.抽象类-接口-泛型
- 05-结构类型系统和类型保护
- 06-类型变换
- AST-抽象语法树
- React性能优化【珠峰2019.10】
- 1-react性能优化
- 2-react性能优化
- 3.react-immutable
- React Hooks【珠峰2019.12】
- 前端框架及项目面试
- 第07章 React 使用
- 7-1 React使用-考点串讲
- 7-2 JSX基本知识点串讲
- 7-3 JSX如何判断条件和渲染列表
- 7-4 React事件为何bind this
- 7-5 React事件和DOM事件的区别
- 7-6 React表单知识点串讲
- 7-7 React父子组件通讯
- 7-8 setState为何使用不可变值
- 7-9 setState是同步还是异步
- 7-10 setState合适会合并state
- 7-11 React组件生命周期
- 7-12 React基本使用-知识点总结和复习
- 7-13 React函数组件和class组件有何区别
- 7-14 什么是React非受控组件
- 7-15 什么场景需要用React Portals
- 7-16 是否用过React Context
- 7-17 React如何异步加载组件
- 7-18 React性能优化-SCU的核心问题在哪里
- 7-19 React性能优化-SCU默认返回什么
- 7-20 React性能优化-SCU一定要配合不可变值
- 7-21 React性能优化-PureComponent和memo
- 7-22 React性能优化-了解immutable.js
- 7-23 什么是React高阶组件
- 7-24 什么是React Render Props
- 7-25 React高级特性考点总结
- 7-26 Redux考点串讲
- 7-27 描述Redux单项数据流
- 7-28 串讲react-redux知识点
- 7-29 Redux action如何处理异步
- 7-30 简述Redux中间件原理
- 7-31 串讲react-router知识点
- 7-32 React使用-考点总结
- 第08章 React 原理
- 8-1 React原理-考点串讲
- 8-2 再次回顾不可变值
- 8-3 vdom和diff是实现React的核心技术
- 8-4 JSX本质是什么
- 8-5 说一下React的合成事件机制
- 8-6 说一下React的batchUpdate机制
- 8-7 简述React事务机制
- 8-8 说一下React组件渲染和更新的过程
- 8-9 React-fiber如何优化性能
- 第09章 React 面试真题演练
- 9-1 React真题演练-1-组件之间如何通讯
- 9-2 React真题演练-2-ajax应该放在哪个生命周期
- 9-3 React真题演练-3-组件公共逻辑如何抽离
- 9-4 React真题演练-4-React常见性能优化方式
- 9-5 React真题演练-5-React和Vue的区别
- 第10章 webpack 和 babel
- 10-1 webpack考点梳理
- 10-2 webpack基本配置串讲(上)
- 10-3 webpack基本配置串讲(下)
- 10-4 webpack如何配置多入口
- 10-5 webpack如何抽离压缩css文件
- 10-6 webpack如何抽离公共代码和第三方代码
- 10-7 webpack如何实现异步加载JS
- 10-8 module chunk bundle 的区别
- 10-9 webpack优化构建速度-知识点串讲
- 10-11 happyPack是什么
- 10-12 webpack如何配置热更新
- 10-13 何时使用DllPlugin
- 10-14 webpack优化构建速度-考点总结和复习
- 10-15 webpack优化产出代码-考点串讲
- 10-16 什么是Tree-Shaking
- 10-17 ES Module 和 Commonjs 的区别
- 10-18 什么是Scope Hostin
- 10-19 babel基本概念串讲
- 10-20 babel-polyfill是什么
- 10-21 babel-polyfill如何按需引入
- 10-22 babel-runtime是什么
- 10-23 webpack考点总结和复习
- 10-24 webpack面试真题-前端代码为何要打包
- 10-25 webpack面试真题-为何Proxy不能被Polyfill
- 10-26 webpack面试真题-常见性能优化方法
