## 1. 可共享可变状态是万恶之源
~~~
let objA = { name: 'zfpx' };
let objB = objA;
objB.name = '9';
console.log(objA.name);
~~~
## 2. 什么是 Immutable
## * Immutable Data 就是一旦创建,就不能再被更改的数据。对 Immutable 对象的任何修改或添加删除操作都会返回一个新的 Immutable 对象
* Immutable 实现的原理是 Persistent Data Structure(持久化数据结构),也就是使用旧数据创建新数据时,要保证旧数据同时可用且不变 同时为了避免 deepCopy 把所有节点都复制一遍带来的性能损耗
* Immutable 使用了 Structural Sharing(结构共享),即如果对象树中一个节点发生变化,只修改这个节点和受它影响的父节点,其它节点则进行共享
* [immutable-js](https://facebook.github.io/immutable-js/docs/#/)
[immutablejs](http://img.zhufengpeixun.cn/immutablejs.gif)
## 3\. Immutable类库
内部实现了一套完整的 Persistent Data Structure,还有很多易用的数据类型。像`Collection`、`List`、`Map`、`Set`、`Record`、`Seq`
### 3.1 Map
| 方法 | 作用 |
| --- | --- |
| isMap | 判断是否是Map |
| clear | 清空值 |
| set | 设置值 |
| delete | 删除值 |
| update | 更新值 |
| merge | 合并值 |
| setIn | 设置值 |
| deleteIn | 删除值 |
| updateIn | 更新值 |
| mergeIn | 合并值 |
| get | 获取值 |
| getIn | 获取值 |
| keys | key的数组 |
| values | value的数组 |
| entries | entry的数组 |
| toJS | 转成普通JS对象 |
| toObject | 转成普通对象 |
| toJSON | 转成JSON对象 |
| toArray | 转成数组 |
~~~
const immutable = require("immutable");
const assert = require("assert");
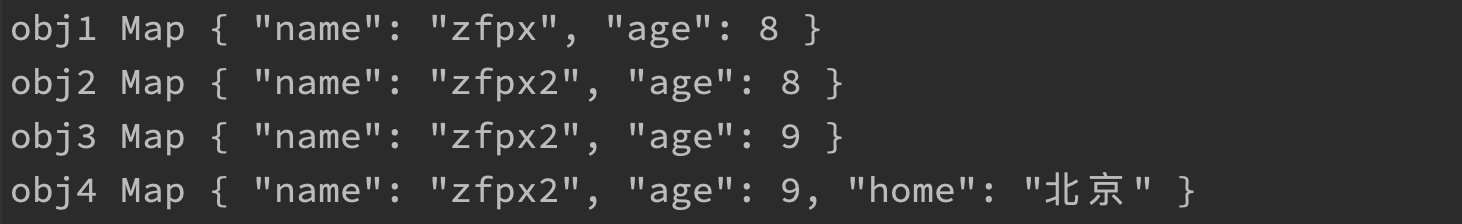
let obj1 = immutable.Map({ name: 'zfpx', age: 8 });
let obj2 = obj1.set('name', 'zfpx2');
let obj3 = obj2.update('age', x => x + 1);
let obj4 = obj3.merge({ home: '北京' });
console.log(obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4);
~~~
~~~
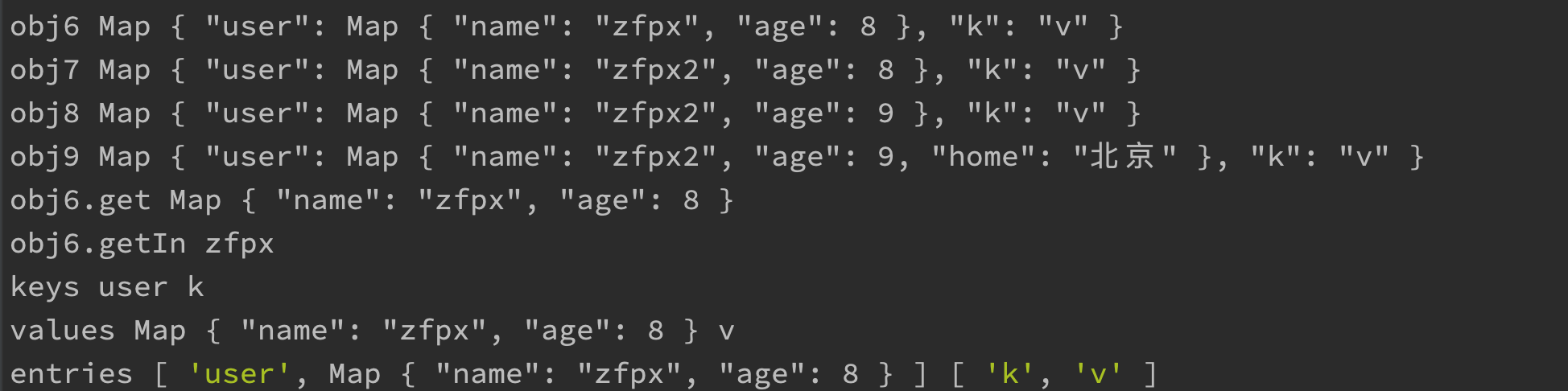
let obj6 = immutable.fromJS({ user: { name: 'zfpx', age: 8 }, 'k': 'v' });
let obj7 = obj6.setIn(['user', 'name'], 'zfpx2');
let obj8 = obj7.updateIn(['user', 'age'], x => x + 1);
let obj9 = obj8.mergeIn(["user"], { home: '北京' });
console.log(obj6, obj7, obj8, obj9);
console.log(obj6.get('user'));
console.log(obj6.getIn(['user', 'name']));
console.log(...obj6.keys());
console.log(...obj6.values());
console.log(...obj6.entries());
~~~
~~~
var map1 = immutable.Map({ name: 'zfpx', age: 9 });
var map2 = immutable.Map({ name: 'zfpx', age: 9 });
console.log(map1 !== map2);
console.log(Object.is(map1, map2) === false);
console.log(immutable.is(map1, map2) === true);
~~~

### 3.2 List
| 方法 | 作用 | |
| --- | --- | --- |
| isList | 判断是否是List | |
| size | 统计个数 | |
| push | 添加 | |
| pop | 弹出最后一个 | |
| update | 更新 | |
| delete | 删除指定元素的数组 | delete(2) |
| insert | 插入指定元素的数组 | insert(2) |
| clear | 清空数组 | clear() |
| concat | 合并 | |
| map | 映射 | |
| filter | 过滤 | |
| get | 获取 | |
| find | 查找 | |
| includes | 判断包含 | |
| last | 最后一个 | |
| reduce | 计算总和 | |
| count | 统计个数 |
~~~
let immutable = require('immutable');
let arr1 = immutable.fromJS([1, 2, 3]);
console.log(arr1.size); //3
let arr2 = arr1.push(4);
console.log(arr2); //List [ 1, 2, 3, 4 ]
let arr3 = arr2.pop();
console.log(arr3); //List [ 1, 2, 3 ]
let arr4 = arr3.update(2, x => x + 1);
console.log(arr4); //List [ 1, 2, 4 ]
let arr5 = arr4.concat([5, 6]);
console.log(arr5); //List [ 1, 2, 4, 5, 6 ]
let arr6 = arr5.map(item => item * 2);
console.log(arr6); /List [ 2, 4, 8, 10, 12 ]
let arr7 = arr6.filter(item => item >= 10);
console.log(arr7); //List [ 10, 12 ]
console.log(arr7.get(0)); //10
console.log(arr7.includes(10)); //true
console.log(arr7.last()); //12
let val = arr7.reduce((val, item) => val + item, 0);
console.log(val); //22
console.log(arr7.count()); //2
~~~
## 4\. Immutable优势
### 4.1 降低复杂度
~~~
let obj1 = immutable.fromJS({ user: { name: 'zfpx', age: 8 }, 'k': 'v' });
let obj2 = obj1.setIn(['user', 'name'], 'zfpx2');
~~~
### 4.2 节省内存
~~~
let Immutable=require('immutable');
let p1=Immutable.fromJS({
name: 'zfpx',
home:{name:'beijing'}
});
let p2 = p1.set('name','zfpx2');
console.log(p1.get('home')== p2.get('home')); //true
~~~
### 4.3 方便回溯
只要把每次的状态都放在一个数组中就可以很方便的实现撤销重做功能
## 5\. React性能优化
### 5.1 计数器
* 每次调用setState的时候组件都会刷新
~~~
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
class Counter extends Component {
state = {counter:{number:0}}
handleClick = () => {
let amount = this.amount.value ? Number(this.amount.value) : 0;
this.state.counter.number = this.state.counter.number + amount;
this.setState(this.state);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return true;
}
render() {
console.log('render');
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.number}</p>
<input ref={input => this.amount = input} />
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Caculator />,
document.getElementById('root')
)
~~~
### 5.2 深度克隆+浅比较
* 可以通过浅比较判断是否需要刷新组件
* 浅比较要求每次修改的时候都通过深度克隆每次都产生一个新对象
~~~
import _ from 'lodash';
handleClick = () => {
let amount = this.amount.value ? Number(this.amount.value) : 0;
let state = _.cloneDeep(this.state);
state.counter.number = this.state.counter.number + amount;
this.setState(state);
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
for (const key in nextState) {
if (this.State[key] !== nextState[key]) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
~~~
### 5.3 深比较
* 也可以通过深度比较的方式判断两个状态的值是否相等
* 这样做的话性能非常低
~~~
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, prevState) {
return !_.isEqual(prevState, this.state);
}
~~~
### 5.4 immutable
~~~
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { is, Map } from 'immutable';
class Caculator extends Component {
state = {
counter: Map({ number: 0 })
}
handleClick = () => {
let amount = this.amount.value ? Number(this.amount.value) : 0;
let counter = this.state.counter.update('number', val => val + amount);
this.setState({counter});
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps = {}, nextState = {}) {
if (Object.keys(this.state).length !== Object.keys(nextState).length) {
return true;
}
for (const key in nextState) {
if (!is(this.state[key], nextState[key])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>{this.state.counter.get('number')}</p>
<input ref={input => this.amount = input} />
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>+</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Caculator />,
document.getElementById('root')
)
~~~
## 6\. redux+immutable手工实现
~~~
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import { Provider, connect } from 'react-redux'
import immutable, { is, Map } from 'immutable';
import PureComponent from './PureComponent';
const ADD = 'ADD';
const initState = Map({ number: 0 });
function counter(state = initState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case ADD:
return state.update('number', (value) => value + action.payload);
default:
return state
}
}
const store = createStore(counter);
class Caculator extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>{this.props.number}</p>
<input ref={input => this.amount = input} />
<button onClick={() => this.props.add(this.amount.value ? Number(this.amount.value) : 0)}>+</button>
</div>
)
}
}
let actions = {
add(payload) {
return { type: ADD, payload }
}
}
const ConnectedCaculator = connect(
state => ({ number: state.get('number') }),
actions
)(Caculator)
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}><ConnectedCaculator /></Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
)
~~~
## 7\. redux-immutable中间件
* [redux-immutable](https://github.com/gajus/redux-immutable#readme)
~~~
import { combineReducers } from 'redux-immutable';
function combineReducers(reducers) {
return function (state = Map(), action) {
let newState = Map();
for (let key in reducers) {
newState = newState.set(key, reducers[key](state.get(key), action));
}
return newState;
}
}
let reducers = combineReducers({
counter
});
const ConnectedCaculator = connect(
state => {
return ({ number: state.getIn(['counter', 'number']) })
},
actions
)(Caculator)
~~~
## 8\. react-router-redux使用
~~~
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import { combineReducers } from 'redux-immutable';
import createHistory from "history/createBrowserHistory";
import { Route } from "react-router";
import { Map } from 'immutable';
import {
ConnectedRouter,
routerMiddleware,
push,
LOCATION_CHANGE
} from "react-router-redux";
const initialRouterState = Map({
location: null,
action: null
});
export function routerReducer(state = initialRouterState, { type, payload = {} } = {}) {
if (type === LOCATION_CHANGE) {
const location = payload.location || payload;
const action = payload.action;
return state
.set('location', location)
.set('action', action);
}
return state;
}
const history = createHistory();
const middleware = routerMiddleware(history);
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({
router: routerReducer
}),
applyMiddleware(middleware)
);
window.push = push;
window.store = store;
let Home = () => <div>Home</div>
let About = () => <div>About</div>
let Topics = () => <div>Topics</div>
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<ConnectedRouter history={history}>
<div>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/topics" component={Topics} />
</div>
</ConnectedRouter>
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
~~~
## 9\. react-router-redux实现
~~~
import React, { Component } from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import createHistory from "history/createBrowserHistory";
import { Router, Route } from "react-router";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import PropTypes from 'prop-types';
// import {
// ConnectedRouter,
// routerReducer,
// routerMiddleware,
// push
// } from "react-router-redux";
const CALL_HISTORY_METHOD = '@@router/CALL_HISTORY_METHOD';
const LOCATION_CHANGE = 'LOCATION_CHANGE';
var initialRouteState = {
location: null
}
class ConnectedRouter extends Component {
static contextTypes = {
store: PropTypes.object
};
handleLocationChange = (location) => {
this.store.dispatch({
type: LOCATION_CHANGE,
payload: location
});
}
componentWillMount() {
this.store = this.context.store;
this.history = this.props.history;
history.listen(this.handleLocationChange);
}
render() {
return <Router {...this.props} />
};
}
function routerReducer(state = initialRouteState, action) {
let { type, payload } = action;
if (type === LOCATION_CHANGE) {
return { ...state, location: payload };
}
return state;
}
function routerMiddleware(history) {
return function () {
return function (next) {
return function (action) {
if (action.type !== CALL_HISTORY_METHOD) {
return next(action);
}
var _action$payload = action.payload,
method = _action$payload.method,
args = _action$payload.args;
history[method].apply(history, args);
};
};
};
}
//push
function push(...args) {
return {
type: CALL_HISTORY_METHOD,
payload: { method: 'push', args: args }
};
}
// Create a history of your choosing (we're using a browser history in this case)
const history = createHistory();
// Build the middleware for intercepting and dispatching navigation actions
const middleware = routerMiddleware(history);
// Add the reducer to your store on the `router` key
// Also apply our middleware for navigating
const store = createStore(
combineReducers({
router: routerReducer
}),
applyMiddleware(middleware)
);
window.push = push;
window.store = store;
// Now you can dispatch navigation actions from anywhere!
// store.dispatch(push('/foo'))
let Home = () => <div>Home</div>
let About = () => <div>About</div>
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
{/* ConnectedRouter will use the store from Provider automatically */}
<ConnectedRouter history={history}>
<div>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
</div>
</ConnectedRouter>
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);
~~~
- 文档简介
- 基础面试题【珠峰2019.8】
- P01_call,aplly区别
- P02_综合面试题讲解2-2
- P03_箭头函数和普通函数区别-综合面试题讲解2-3
- P05_实现indexOf
- P06_综合面试题讲解2-6
- P07_URL解析题
- P08_原型题
- P09_图片延时加载
- P10_正则-包含数字字母下划线
- P11_综合面试题讲解2-11
- P12_英文字母加空格
- P13_数组扁平化并去重
- P14_模拟实现new
- P15_合并数组
- P16_定时器,打印012345
- P17_匿名函数输出值问题
- P18_a在什么情况下打印输出+1+1+1
- P19_对数组的理解
- P20_冒泡排序
- P21_插入排序
- P22_快速排序
- P23_销售额存在对象中
- P24_求数组的交集
- P25_旋转数组
- P26_ [函数柯理化思想]
- P27_ [柯理化函数的递归]
- 网络协议【珠峰2019.6】
- TypeScript+Axios入门+实战【珠峰2019.11】
- 1.数据结构
- 2.函数和继承
- 3.装饰器
- 4.抽象类-接口-泛型
- 05-结构类型系统和类型保护
- 06-类型变换
- AST-抽象语法树
- React性能优化【珠峰2019.10】
- 1-react性能优化
- 2-react性能优化
- 3.react-immutable
- React Hooks【珠峰2019.12】
- 前端框架及项目面试
- 第07章 React 使用
- 7-1 React使用-考点串讲
- 7-2 JSX基本知识点串讲
- 7-3 JSX如何判断条件和渲染列表
- 7-4 React事件为何bind this
- 7-5 React事件和DOM事件的区别
- 7-6 React表单知识点串讲
- 7-7 React父子组件通讯
- 7-8 setState为何使用不可变值
- 7-9 setState是同步还是异步
- 7-10 setState合适会合并state
- 7-11 React组件生命周期
- 7-12 React基本使用-知识点总结和复习
- 7-13 React函数组件和class组件有何区别
- 7-14 什么是React非受控组件
- 7-15 什么场景需要用React Portals
- 7-16 是否用过React Context
- 7-17 React如何异步加载组件
- 7-18 React性能优化-SCU的核心问题在哪里
- 7-19 React性能优化-SCU默认返回什么
- 7-20 React性能优化-SCU一定要配合不可变值
- 7-21 React性能优化-PureComponent和memo
- 7-22 React性能优化-了解immutable.js
- 7-23 什么是React高阶组件
- 7-24 什么是React Render Props
- 7-25 React高级特性考点总结
- 7-26 Redux考点串讲
- 7-27 描述Redux单项数据流
- 7-28 串讲react-redux知识点
- 7-29 Redux action如何处理异步
- 7-30 简述Redux中间件原理
- 7-31 串讲react-router知识点
- 7-32 React使用-考点总结
- 第08章 React 原理
- 8-1 React原理-考点串讲
- 8-2 再次回顾不可变值
- 8-3 vdom和diff是实现React的核心技术
- 8-4 JSX本质是什么
- 8-5 说一下React的合成事件机制
- 8-6 说一下React的batchUpdate机制
- 8-7 简述React事务机制
- 8-8 说一下React组件渲染和更新的过程
- 8-9 React-fiber如何优化性能
- 第09章 React 面试真题演练
- 9-1 React真题演练-1-组件之间如何通讯
- 9-2 React真题演练-2-ajax应该放在哪个生命周期
- 9-3 React真题演练-3-组件公共逻辑如何抽离
- 9-4 React真题演练-4-React常见性能优化方式
- 9-5 React真题演练-5-React和Vue的区别
- 第10章 webpack 和 babel
- 10-1 webpack考点梳理
- 10-2 webpack基本配置串讲(上)
- 10-3 webpack基本配置串讲(下)
- 10-4 webpack如何配置多入口
- 10-5 webpack如何抽离压缩css文件
- 10-6 webpack如何抽离公共代码和第三方代码
- 10-7 webpack如何实现异步加载JS
- 10-8 module chunk bundle 的区别
- 10-9 webpack优化构建速度-知识点串讲
- 10-11 happyPack是什么
- 10-12 webpack如何配置热更新
- 10-13 何时使用DllPlugin
- 10-14 webpack优化构建速度-考点总结和复习
- 10-15 webpack优化产出代码-考点串讲
- 10-16 什么是Tree-Shaking
- 10-17 ES Module 和 Commonjs 的区别
- 10-18 什么是Scope Hostin
- 10-19 babel基本概念串讲
- 10-20 babel-polyfill是什么
- 10-21 babel-polyfill如何按需引入
- 10-22 babel-runtime是什么
- 10-23 webpack考点总结和复习
- 10-24 webpack面试真题-前端代码为何要打包
- 10-25 webpack面试真题-为何Proxy不能被Polyfill
- 10-26 webpack面试真题-常见性能优化方法
