>[success] # 散列表js
[js 的对象就是'基于哈希表结构的'](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24291761)
~~~
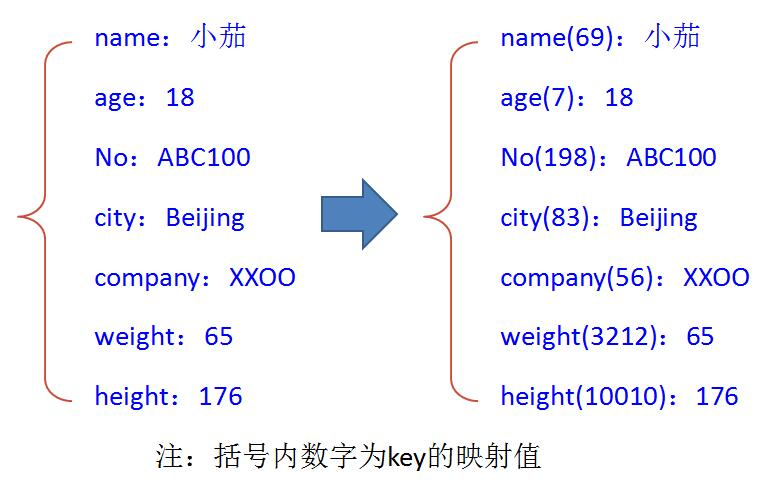
1.刚才对散列表的概念有了初步的理解,可能还是有点懵,现在用js最常见的对象来举个例子,
这个例子可能不恰当但是方便理解(实际上js对象就是散列表)
存储js对象的时候,我们的key是各种各样的数据类型,但是key的可能性是无限制,那如果系统
真的是一个萝卜一个坑来来做这件事,可能出现一个超大的储存空间,我们可以用上节的思路
如果将这些key 转换成asii码会不会实际对应的数据会减少
3.因为js 自带特效'对象',形成一个很好的实现储存的基本参数,转数字作为key,更多是没有js这种
自带buff加成的语言使用数组最为他们的基本储存参数
~~~
* 如图
* 再用js数据结构与算法书中的图更形象的来看
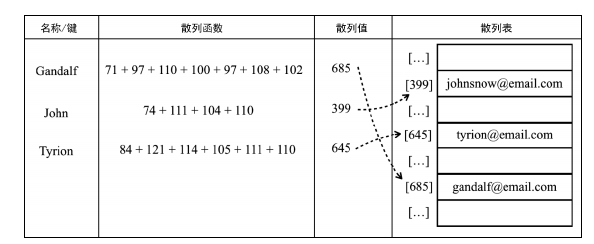
>[info] ## 实现一个自己的散列表
~~~
1.put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)。
2.remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值。
3.get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值。
4.loseloseHashCode: 散列函数生成散列值也就是key
~~~
>[danger] ##### 代码
~~~
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
toString() {
return `[#${this.key}: ${this.value}]`;
}
}
function defaultToString(item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'NULL';
} if (item === undefined) {
return 'UNDEFINED';
} if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`;
}
return item.toString();
}
class HashTable{
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString){
this.table = {} // 用来存储值的
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
}
// 散列函数,可以的转换规则的函数
// 我们的规则是用ascii 码来做
loseloseHashCode(key){
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key); // 要先将对应的类型转出字符串
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37; // 这可以规避操作数超过数值变量最大表示范围的风险 37不是固定的
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
put(key,value){
if(key!=null && value !=null){
const position = hashCode(key)
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key,value)
return true
}
return false
}
// 通过key 获取值
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
// 删除
remove(key) {
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
const valuePair = this.table[hash];
if (valuePair != null) {
delete this.table[hash];
return true;
}
return false;
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
~~~
- 接触数据结构和算法
- 数据结构与算法 -- 大O复杂度表示法
- 数据结构与算法 -- 时间复杂度分析
- 最好、最坏、平均、均摊时间复杂度
- 基础数据结构和算法
- 线性表和非线性表
- 结构 -- 数组
- JS -- 数组
- 结构 -- 栈
- JS -- 栈
- JS -- 栈有效圆括号
- JS -- 汉诺塔
- 结构 -- 队列
- JS -- 队列
- JS -- 双端队列
- JS -- 循环队列
- 结构 -- 链表
- JS -- 链表
- JS -- 双向链表
- JS -- 循环链表
- JS -- 有序链表
- 结构 -- JS 字典
- 结构 -- 散列表
- 结构 -- js 散列表
- 结构 -- js分离链表
- 结构 -- js开放寻址法
- 结构 -- 递归
- 结构 -- js递归经典问题
- 结构 -- 树
- 结构 -- js 二搜索树
- 结构 -- 红黑树
- 结构 -- 堆
- 结构 -- js 堆
- 结构 -- js 堆排序
- 结构 -- 排序
- js -- 冒泡排序
- js -- 选择排序
- js -- 插入排序
- js -- 归并排序
- js -- 快速排序
- js -- 计数排序
- js -- 桶排序
- js -- 基数排序
- 结构 -- 算法
- 搜索算法
- 二分搜索
- 内插搜索
- 随机算法
- 简单
- 第一题 两数之和
- 第七题 反转整数
- 第九题 回文数
- 第十三题 罗马数字转整数
- 常见一些需求
- 把原始 list 转换成树形结构