>[success] # 二叉搜索树
~~~
1.二叉查找树是为了实现快速查找而生的。能做到的原因也是因为,只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,
在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值
~~~
>[info] ## 分析概念
~~~
1.根据二叉查找树的特点来分析他的操作
~~~
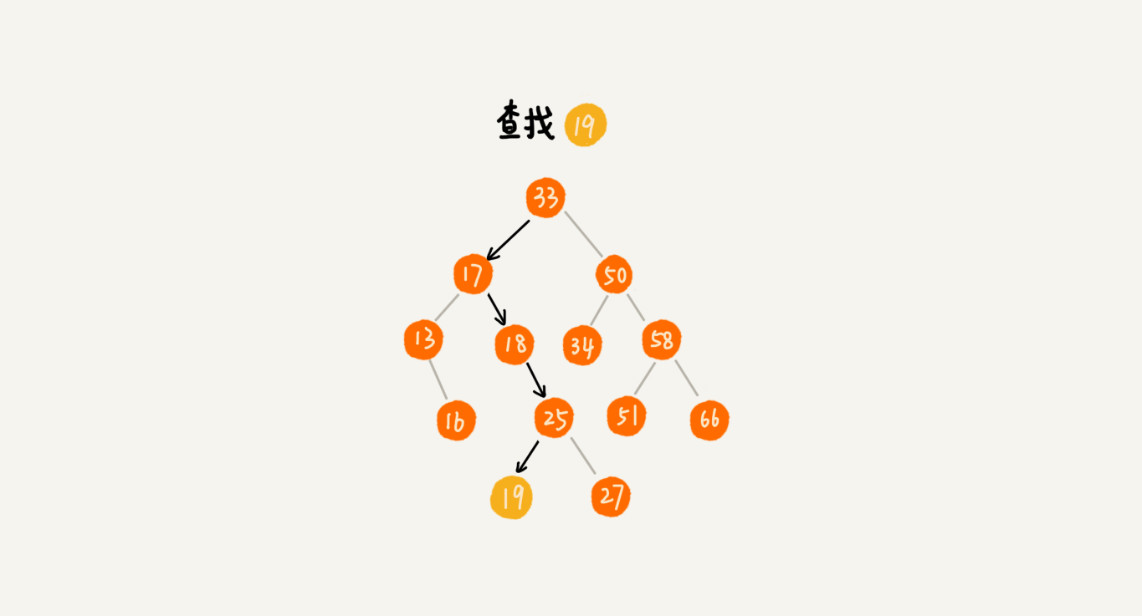
>[danger] ##### 查
~~~
1.首先左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值,也就当我们每次去查的时候,
只要去比较查询节点和当前比较父节点大小,来决定他是走左面查询,还是右面查询,这样就不用去遍历
整个树
~~~
>[danger] ##### 查最大值
~~~
1.只需要去右侧树查找
~~~
>[danger] ##### 查最小值
~~~
1.只需要去左侧树查找
~~~
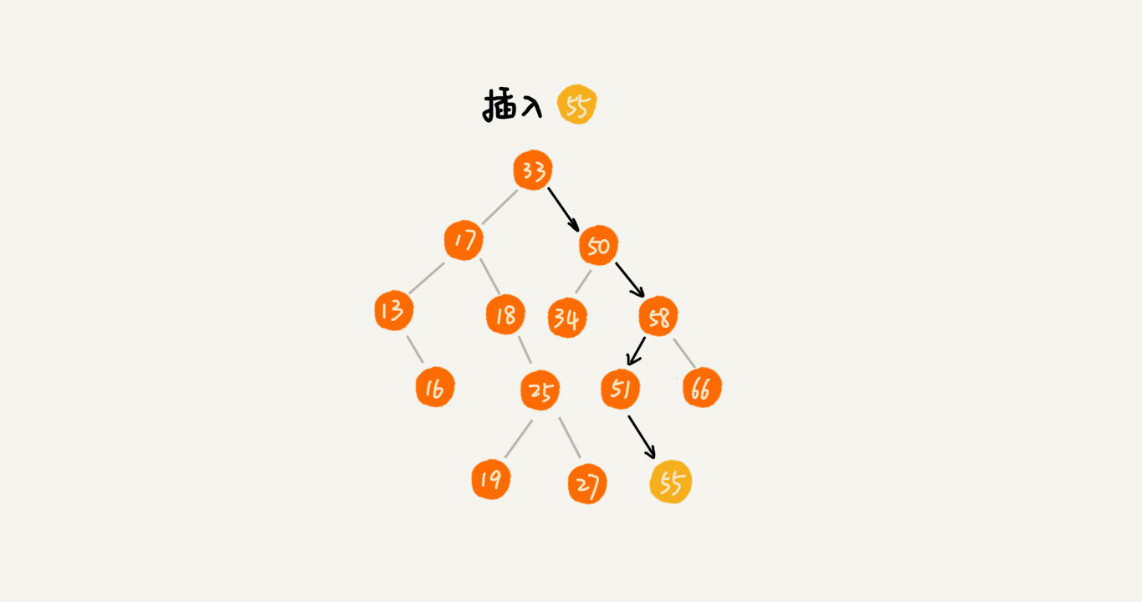
>[danger] ##### 插入
~~~
1.插入的后的数据一定要符合左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值,右侧节点存储(比父节点)大的值,
因此插入的时候也是要先和跟节点比较,直到一直找到末尾,来决定插入的值是作为叶节点左侧还是右侧
~~~
* 插入重复数据解决
~~~
1.二叉查找树中每一个节点不仅会存储一个数据,因此我们通过链表和支持动态扩容的数组等数据结构,把值相同的数
据都存储在同一个节点上
2.每个节点仍然只存储一个数据。在查找插入位置的过程中,如果碰到一个节点的值,与要插入数据的值相同,我们就
将这个要插入的数据放到这个节点的右子树,也就是说,把这个新插入的数据当作大于这个节点的值来处理
~~~
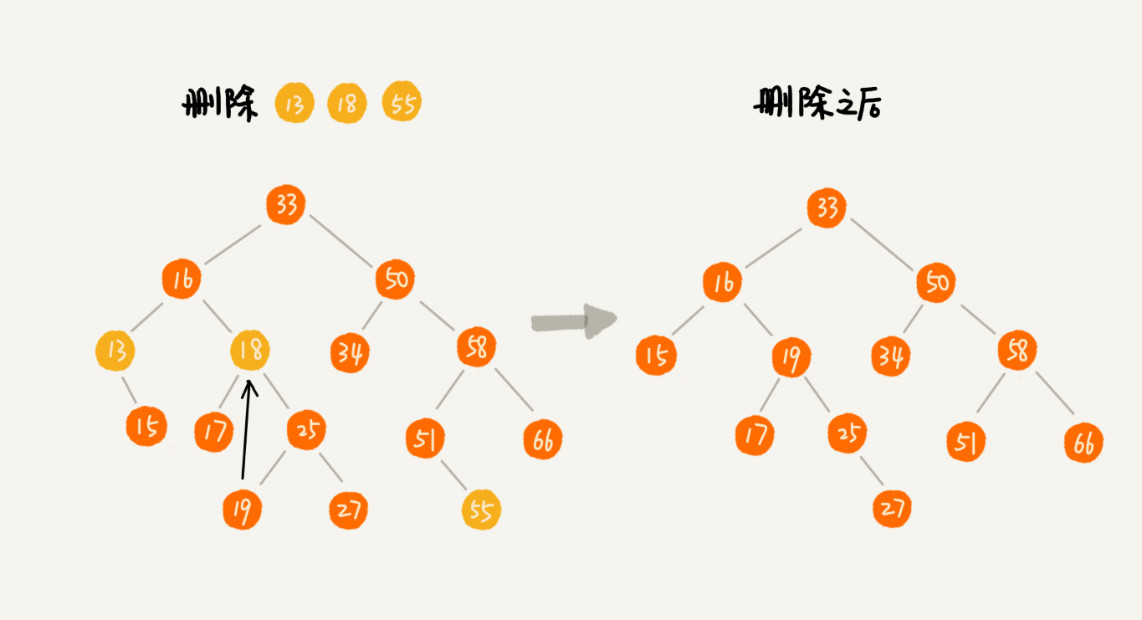
>[danger] ##### 二叉树的删除
~~~
1.如果要删除的节点没有子节点,我们只需要直接将父节点中,指向要删除节点的指针置为 null。比如图中的删除节点 55。
2.如果要删除的节点只有一个子节点(只有左子节点或者右子节点),我们只需要更新父节点中,指向要删除节点的指
针,让它指向要删除节点的子节点就可以了。比如图中的删除节点 13。
3.如果要删除的节点有两个子节点,这就比较复杂了。我们需要找到这个节点的右子树中的最小节点,把它替换到要删
除的节点上。然后再删除掉这个最小节点,因为最小节点肯定没有左子节点(如果有左子结点,那就不是最小节点
了),所以,我们可以应用上面两条规则来删除这个最小节点。比如图中的删除节点 18。
~~~
>[danger] ##### js 代码实现
~~~
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
EQUALS: 0
}
// 比较节点
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return Compare.EQUALS;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
// 创建节点对象
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = undefined;
this.right = undefined;
}
toString() {
return `${this.key}`;
}
}
// 创建一个二叉搜索树
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(compareFn = defaultCompare) {
this.compareFn = compareFn;
this.root = undefined;
}
insert(key) {
// 如果根节点为空说明树没有被创建
if (this.root == null) {
this.root = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(this.root, key);
}
}
/*
遵循子节点和父亲节点关系为左小右大原则
*/
insertNode(node, key) {
// 先比和根节点大小,如果小于,看当前父节点左侧是否有值
// 如果没有就加入当前左侧,如果有就递归依次找到能插入的位置
// 同理右侧也是一样的
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
if (node.left == null) {
node.left = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.left, key);
}
} else if (node.right == null) {
node.right = new Node(key);
} else {
this.insertNode(node.right, key);
}
}
// 遍历每个节点 这里采用中期调用
// callback 是个回调函数 可以传参(node)=>{console.log(node)}
inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node != null) {
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.key);
this.inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
// 最小值
min() {
return this.minNode(this.root);
}
minNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.left != null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
}
// 最大值
max() {
return this.maxNode(this.root);
}
maxNode(node) {
let current = node;
while (current != null && current.right != null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
}
// 搜索当前值是否在树中
search(key) {
return this.searchNode(this.root, key);
}
// 先判读当前值是大于根节点还是小于,然后决定左面分支还是右面分支
// 当然这种方法是针对二叉搜索树
searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return false;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return this.searchNode(node.left, key);
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
}
return true;
}
remove(key) {
console.log(this.removeNode(this.root, key));
}
removeNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) {
return undefined;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
}
if (this.compareFn(key, node.key) === Compare.BIGGER_THAN) {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
}
// key is equal to node.item
// handle 3 special conditions
// 1 - a leaf node
// 2 - a node with only 1 child
// 3 - a node with 2 children
// case 1
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
node = undefined;
return 1;
}
// case 2
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
}
if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
// case 3
const aux = this.minNode(node.right);
node.key = aux.key;
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
return node;
}
getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
}
const tt = new BinarySearchTree();
tt.insert(10);
tt.insert(15);
tt.insert(14);
tt.insert(16);
tt.insert(8);
tt.insert(7);
tt.remove(10);
console.log(tt.getRoot());
~~~
- 接触数据结构和算法
- 数据结构与算法 -- 大O复杂度表示法
- 数据结构与算法 -- 时间复杂度分析
- 最好、最坏、平均、均摊时间复杂度
- 基础数据结构和算法
- 线性表和非线性表
- 结构 -- 数组
- JS -- 数组
- 结构 -- 栈
- JS -- 栈
- JS -- 栈有效圆括号
- JS -- 汉诺塔
- 结构 -- 队列
- JS -- 队列
- JS -- 双端队列
- JS -- 循环队列
- 结构 -- 链表
- JS -- 链表
- JS -- 双向链表
- JS -- 循环链表
- JS -- 有序链表
- 结构 -- JS 字典
- 结构 -- 散列表
- 结构 -- js 散列表
- 结构 -- js分离链表
- 结构 -- js开放寻址法
- 结构 -- 递归
- 结构 -- js递归经典问题
- 结构 -- 树
- 结构 -- js 二搜索树
- 结构 -- 红黑树
- 结构 -- 堆
- 结构 -- js 堆
- 结构 -- js 堆排序
- 结构 -- 排序
- js -- 冒泡排序
- js -- 选择排序
- js -- 插入排序
- js -- 归并排序
- js -- 快速排序
- js -- 计数排序
- js -- 桶排序
- js -- 基数排序
- 结构 -- 算法
- 搜索算法
- 二分搜索
- 内插搜索
- 随机算法
- 简单
- 第一题 两数之和
- 第七题 反转整数
- 第九题 回文数
- 第十三题 罗马数字转整数
- 常见一些需求
- 把原始 list 转换成树形结构