思路:
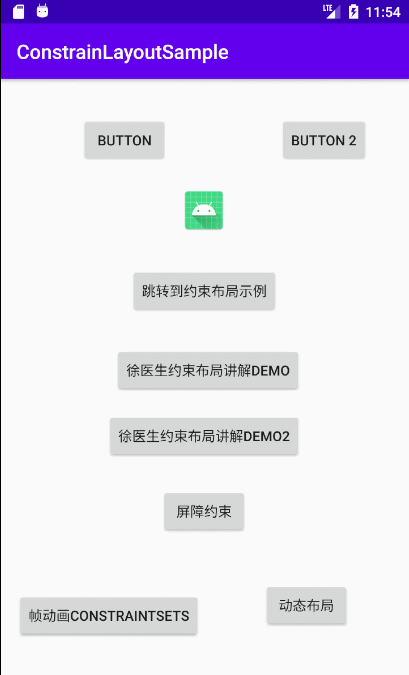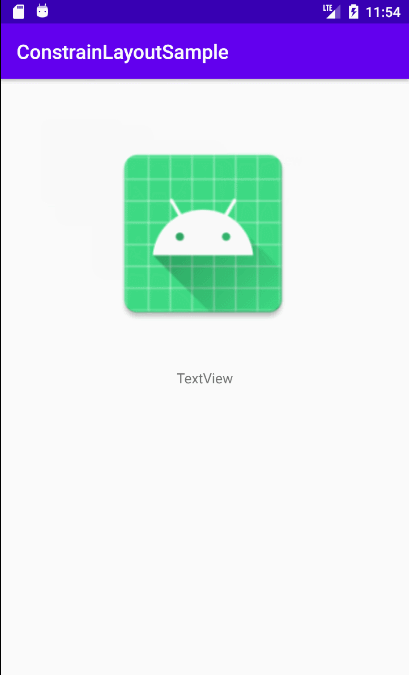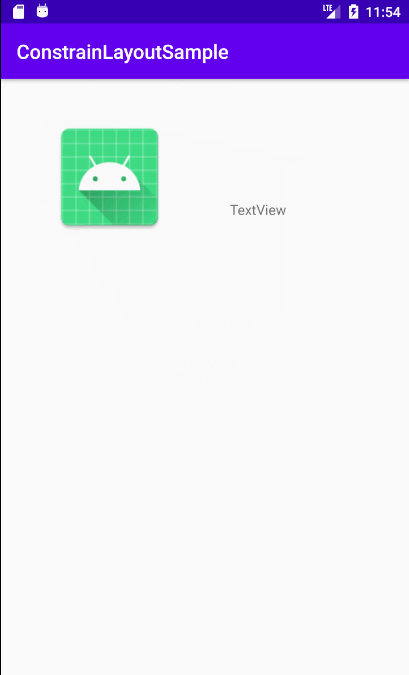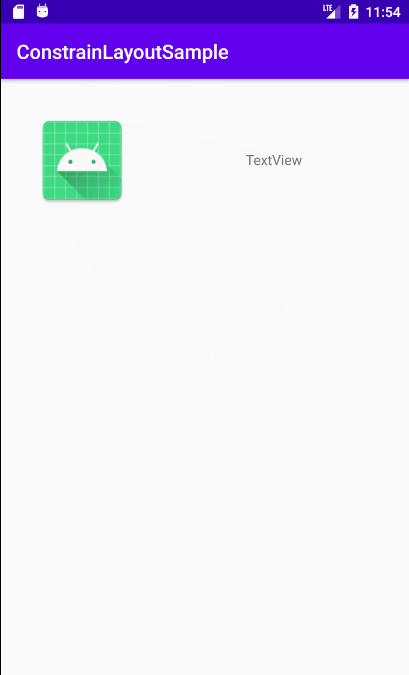
**`activity_constraint_layout_animation2.xml`文件**和`change.xml`文件有相同的组件,id也一样,只不过`change.xml`文件文件中的图片变大了,实现效果:点击第一个布局中图片,会导致图片放大,文本下移。实际上就是点击后布局文件由`activity_constraint_layout_animation2.xml`文件替换成`change.xml`文件。
直接上代码,如下所示
~~~
package com.wsc.constrainlayoutsample;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout;
import androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintSet;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.transition.TransitionManager;
import android.view.View;
/**
* ConstraintLayout动态布局与动画
* 共享元素动画效果
*/
public class ConstraintLayoutAnimation2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ConstraintSet mConstraintSet1;
private ConstraintSet mConstraintSet2;
private ConstraintLayout mConstraintLayout;
private boolean flag;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_constraint_layout_animation2);
mConstraintLayout = (ConstraintLayout) findViewById(R.id.root2);
mConstraintSet1 = new ConstraintSet();
mConstraintSet2 = new ConstraintSet();
mConstraintSet1.clone(mConstraintLayout);
mConstraintSet2.load(this, R.layout.change);
}
public void toggle(View view) {
TransitionManager.beginDelayedTransition(mConstraintLayout);
flag = !flag;
if (flag) {
mConstraintSet2.applyTo(mConstraintLayout);
} else {
mConstraintSet1.applyTo(mConstraintLayout);
}
}
}
~~~
**`activity_constraint_layout_animation2.xml`文件**
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/root2"
tools:context=".ConstraintLayoutAnimation2Activity">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView6"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_marginStart="32dp"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:onClick="toggle"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/ic_launcher" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginStart="8dp"
android:layout_marginTop="72dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="8dp"
android:text="TextView"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.519"
app:layout_constraintStart_toEndOf="@+id/imageView6"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
~~~
**`change.xml`文件**
~~~
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/linearLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView6"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginStart="104dp"
android:layout_marginTop="56dp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:srcCompat="@mipmap/ic_launcher" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
~~~
实际效果如下
- 前言
- Android系统的体系结构
- Dalvik VM 和 JVM 的比较
- Android 打包应用程序并安装的过程
- Android ADB工具
- Android应用开发
- Android UI相关知识总结
- Android 中window 、view、 Activity的关系
- Android应用界面
- Android中的drawable和bitmap
- AndroidUI组件adapterView及其子类和Adapter的关系
- Android四大组件
- Android 数据存储
- SharedPreference
- Android应用的资源
- 数组资源
- 使用Drawable资源
- Material Design
- Android 进程和线程
- 进程
- 线程
- Android Application类的介绍
- 意图(Intent)
- Intent 和 Intent 过滤器(Google官网介绍)
- Android中关于任务栈的总结
- 任务和返回栈(官网译文)
- 总结
- Android应用安全现状与解决方案
- Android 安全开发
- HTTPS
- 安卓 代码混淆与打包
- 动态注入技术(hook技术)
- 一、什么是hook技术
- 二、常用的Hook 工具
- Xposed源码剖析——概述
- Xposed源码剖析——app_process作用详解
- Xposed源码剖析——Xposed初始化
- Xposed源码剖析——hook具体实现
- 无需Root也能Hook?——Depoxsed框架演示
- 三、HookAndroid应用
- 四、Hook原生应用程序
- 五、Hook 检测/修复
- Android 应用的逆向与加固保护技术
- OpenCV在Android中的开发
- Android高级开发进阶
- 高级UI
- UI绘制流程及原理
- Android新布局ConstraintLayout约束布局
- 关键帧动画
- 帧动画共享元素变换
- Android异步消息处理机制完全解析,带你从源码的角度彻底理解
- Android中为什么主线程不会因为Looper.loop()里的死循环卡死?
- 为什么 Android 要采用 Binder 作为 IPC 机制?
- JVM 中一个线程的 Java 栈和寄存器中分别放的是什么?
- Android源码的Binder权限是如何控制?
- 如何详解 Activity 的生命周期?
- 为什么Android的Handler采用管道而不使用Binder?
- ThreadLocal,你真的懂了吗?
- Android屏幕刷新机制
