[代码地址链接](https://github.com/fujiazhang/vuex/tree/master/my-project)
看了vuex源码后,觉得vuex很简单,但是又比redux复杂一点,想动手写写,这篇文章会记录写一个简易版的vuex,能在项目中直接替换用我们手写的vuex替代真实的vuex,目前没有Map语法糖的辅助函数,后面有时间的话会加上。
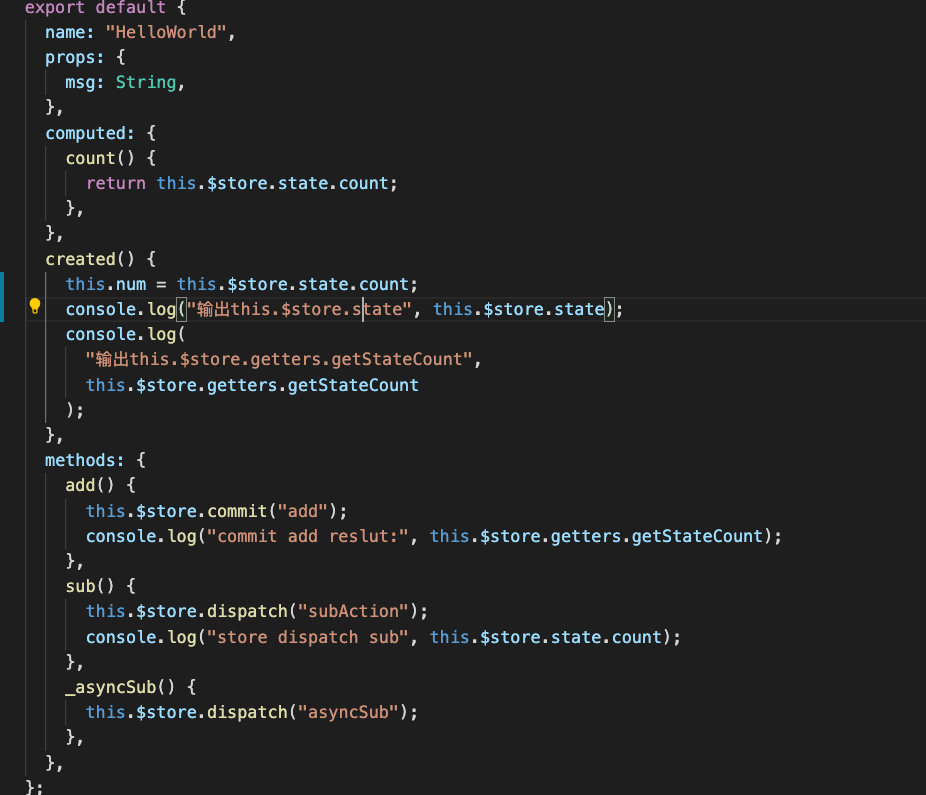
首先在main.js中导入,我们自己的vuex.js,同时定义一些Store的 options 供测试,这里的 new Vuex.Store和里面的state、action、mutations等等使用都和官方的使用无差异,不必过多纠结。
```
import Vuex from '../vuex/index'
Vue.use(Vuex)
let store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 520
},
getters: {
getStateCount(state) {
return state.count
}
},
actions: {
subAction(context, payload) { //context = {commint,dispatch}
context.commit('sub')
},
asyncSub(context, payload) { //context = {commint,dispatch}
setTimeout(() = >{
context.commit('sub')
},
1000);
},
},
mutations: {
add(state) {
state.count = state.count + 1
},
sub(state) {
state.count = state.count - 1
},
}
},
Vue)
new Vue({
name: "root",
store,
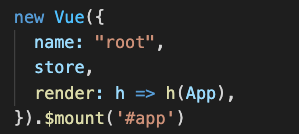
render: h = >h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
```
这里 Vue.use是vue提供给第三方插件的预留接口,源码中,Vue.use接收一个第三方的插件作为参数,同时回去调用install方法,所以我们要在插件中写好install方法,共外面注册插件的use方法的时候使用。
在我们自己的vuex/index.js中,导出一个class store 和install方法(供Vus.use自动调用)
```
class Store {
}
// 插件的作用 需要在所有的组件中添加 $store对象
// 让所有的组件中可以使用访问到 this.$store对象
const install = (v) = >{
Vue = v
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
console.log(this.$options.name)
if (this.$options && this.$options.store) { //root
this.$store = this.$options.store
} else {
this.$store = this.$parent && this.$parent.$store
}
}
})
}
```
这里install方法的是一个箭头函数,参数接收一个 vue作为参数,同时,把这个vue参数,保存一下,存到外面(供后面实现响应式数据时用),调用Vue.mixin,在每一个组件生成前调用,判断一下当前组件是否有this.$options.store这个这个玩意儿(根组件是有的,在初始化的时候传了)
其他组件都没有,所以判断一下,如果this.$options.store存在那么就是根组件 直接将this.$store = this.$options.store,如果没有,就去父组件里面找,因为我们父组件都是一层一层的渲染下去,所以可以保证子组件一定能找到store。
总结一下 这个install方法 就一个作用:给所有组件中 添加$store 对象。
在 class Store 中,代码如下:
```
constructor(options) {
this.vm = new Vue({ //将options.state放到vue的data里 以便监听数据
data: {
state: options.state
}
})
// getters
let getters = options.getters
this.getters = {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName = >{
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () = >{
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})
// actions
let actions = options.actions this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName = >{
this.actions[actionName] = (payload) = >{
actions[actionName](this, payload)
}
})
// mutations
let mutations = options.mutations this.mutations = {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName = >{
this.mutations[mutationName] = (payload) = >{
mutations[mutationName](this.state, payload)
}
})
}
dispatch(type, payload) {
this.actions[type](payload)
}
commit(type, payload) {
this.mutations[type](payload)
}
get state() {
return this.vm.state
}
}
```
此时的界面代码:
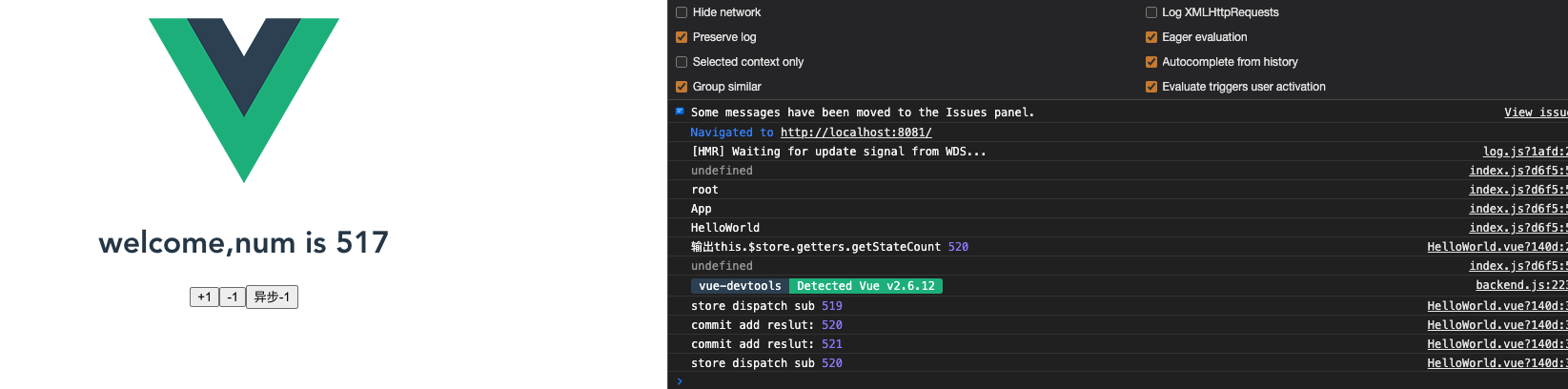
说一下 class Store 中代码的实现:
```
this.vm = new Vue({
data: {
state: options.state
}
})
```
这里是将接收到初始化参数options.state放到vue的data里 以便监听数据与响应。
下面是实现getters,其实就是,将传进来的参数options.getters 复制一份到我们得this.getters,然后获取返回到我们store中的的值。
```
// getters
let getters = options.getters
this.getters = {}
Object.keys(getters).forEach(getterName = >{
Object.defineProperty(this.getters, getterName, {
get: () = >{
return getters[getterName](this.state)
}
})
})
```
下面的actIons和mutations的实现其实方法都差不多类似
```
// actions
let actions = options.actions
this.actions = {}
Object.keys(actions).forEach(actionName = >{
this.actions[actionName] = (payload) = >{
actions[actionName](this, payload)
}
})
// mutations
let mutations = options.mutations
this.mutations = {}
Object.keys(mutations).forEach(mutationName = >{
this.mutations[mutationName] = (payload) = >{
mutations[mutationName](this.state, payload)
}
})
```
主要需要 dispatch和commit函数
```
dispatch(type, payload) {
this.actions[type](payload)
}
commit(type, payload) {
this.mutations[type](payload)
}
```
需要注意一点的是,mutations接受的参数是state ,而actions接受的参数是 ({commint,dispatch},payload)。如下:
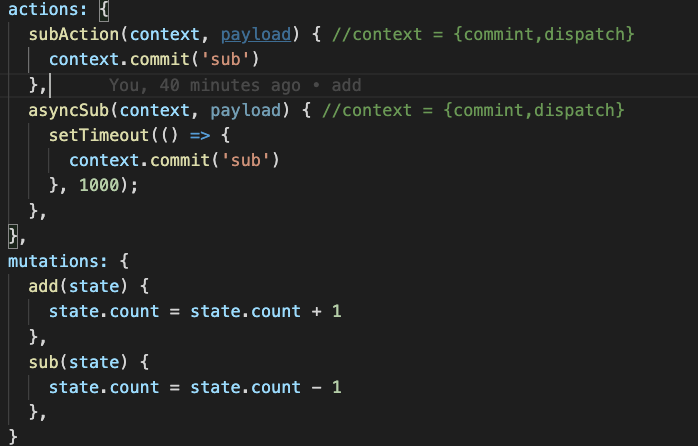
所以要定义好 dispatch和commit函数。
嘻嘻,是不是很简单,和官方相比,也就差一个Module和Map语法糖,但是基本的都有了哦。
**总结:Vuex的双向绑定通过调用 new Vue实现,然后通过 Vue.mixin 注入到Vue组件的生命周期中,再通过劫持state.get将数据放入组件中**
参考资料:
>[vuex 源码:如何实现一个简单的 vuex](https://juejin.im/post/5a7a935851882524713dcd05)
>[从0开始写一个自己的Vuex](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010888395)
>[Vue 源码(三) —— Vuex](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48516116)
>[浅谈Vue.use](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012296163)
>[Vuex官方文档](https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/)
>[vuex Github仓库](https://github.com/vuejs/vuex)
- 前言
- 工作中的一些记录
- 破解快手直播间的webSocket的连接
- 快手「反」反爬虫的研究记录
- HTML AND CSS
- 遇到的一些还行的css笔试题
- css常见面试题
- JavaScript 深度剖析
- ES6到ESNext新特性
- 关于http与缓存
- 关于页面性能
- 关于浏览器的重排(reflow、layout)与重绘
- 手写函数节流
- 手写promise
- 手写函数防抖
- 手写图片懒加载
- 手写jsonp
- 手写深拷贝
- 手写new
- 数据结构和算法
- 前言
- 时间复杂度
- 栈
- 队列
- 集合
- 字典
- 链表
- 树
- 图
- 堆
- 排序
- 搜索
- Webpack
- Webpack原理与实践
- Vue
- Vuejs的Virtual Dom的源码实现
- minVue
- Vuex实现原理
- 一道关于diff算法的面试题
- Vue2源码笔记:源码目录设计
- vue-router源码分析(v4.x)
- React及周边
- 深入理解redux(一步步实现一个 redux)
- React常见面试题汇总
- Taro、小程序等
- TypeScript
- CI/CD
- docker踩坑笔记
- jenkins
- 最后
