[TOC]
参考链接:[https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/notes/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87%20Offer%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3%20-%203~9.md](https://github.com/CyC2018/CS-Notes/blob/master/notes/%E5%89%91%E6%8C%87%20Offer%20%E9%A2%98%E8%A7%A3%20-%203~9.md)
## 1.字符串的排列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fe6b651b66ae47d7acce78ffdd9a96c7?tpId=13&tqId=11180&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串 abc,则打印出由字符 a, b, c 所能排列出来的所有字符串 abc, acb, bac, bca, cab 和 cba。
解题思路:
```js
function swap(arr, index1, index2) {
let tmp = arr[index1]
arr[index1] = arr[index2]
arr[index2] = tmp
}
// 去重的全排列就是从第一个数字起每个数分别与它后面非重复出现的数字交换。
// 用编程的话描述就是第 i 个数与第 j 个数交换时,要求 [i,j) 中没有与第 j 个数相等的数
function isSwap (arr, nBegin, nEnd) {
for (let i = nBegin; i < nEnd; i++) {
if (arr[i] === arr[nEnd]) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
/**
*
* @param {*} arr 数组
* @param {*} cur 当前待交换的数的下标
* @param {*} n 末尾下标
*/
const res = []
function myPermutation(arr, cur, n) {
if (cur === n-1) {
res.push(arr.join(''))
} else {
for (let i = cur; i < n; i++) {
if (isSwap(arr, cur, i)) { // isSwap() 去重
swap(arr, cur, i)
myPermutation(arr, cur + 1, n)
swap(arr, cur, i)
}
}
}
}
function Permutation(str)
{
const chars = str.split('')
chars.sort() // 先转换成数组升序排列
myPermutation(chars, 0, chars.length)
return res
}
console.log(Permutation('abc')) // [ 'abc', 'acb', 'bac', 'bca', 'cba', 'cab' ]
// 本地测试 ok,不知道为啥牛客输出不对
```
## 2.二维数组中的查找
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/abc3fe2ce8e146608e868a70efebf62e?tpId=13&tqId=11154&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:给定一个二维数组,其每一行从左到右递增排序,从上到下也是递增排序。给定一个数,判断这个数是否在该二维数组中。
```js
Consider the following matrix:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
Given target = 5, return true.
Given target = 20, return false.
```
解题思路:
要求时间复杂度 O(M + N),空间复杂度 O(1)。其中 M 为行数,N 为 列数。
该二维数组中的一个数,小于它的数一定在其左边,大于它的数一定在其下边。因此,从右上角开始查找,就可以根据 target 和当前元素的大小关系来缩小查找区间,当前元素的查找区间为左下角的所有元素。
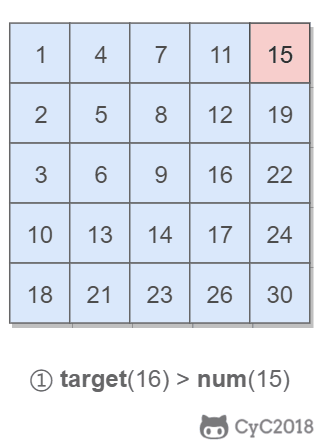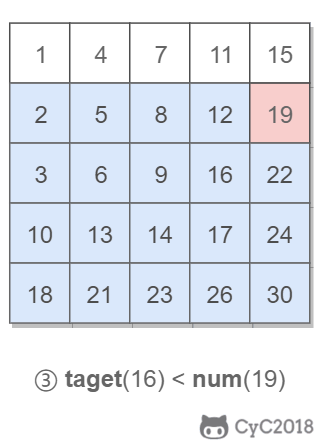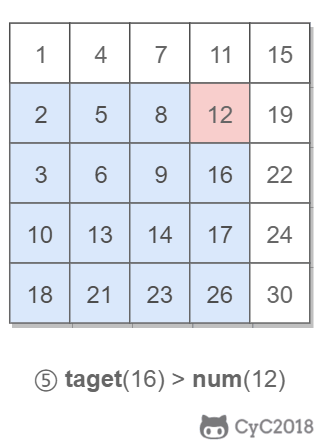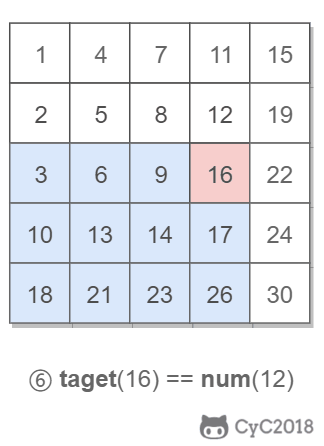
## 3.重建二叉树
题目描述:根据二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。

解题思路:
前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。

```js
function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
function reConstructBinaryTree(pre, vin)
{
/*
前序遍历的第一个值为根节点的值,使用这个值将中序遍历结果分成两部分,
左部分为树的左子树中序遍历结果,右部分为树的右子树中序遍历的结果。
*/
if (pre.length === 0 || vin.length === 0) {
return null
}
let indexOfRoot = vin.indexOf(pre[0])
const vinLeft = vin.slice(0, indexOfRoot)
const vinRight = vin.slice(indexOfRoot + 1)
let root = new TreeNode(pre[0])
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(1, indexOfRoot + 1), vinLeft) // 注意 pre 也要 slice
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(indexOfRoot + 1), vinRight)
return root
}
```
## 4.二叉树的下一个结点
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9023a0c988684a53960365b889ceaf5e?tpId=13&tqId=11210&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:给定一个二叉树和其中的一个结点,请找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点并且返回。注意,树中的结点不仅包含左右子结点,同时包含指向父结点的指针。
```java
public class TreeLinkNode {
int val;
TreeLinkNode left = null;
TreeLinkNode right = null;
TreeLinkNode next = null;
TreeLinkNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
```
解题思路:
① 如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么该节点的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点;

② 否则,向上找第一个左链接指向的树包含该节点的祖先节点。

```js
function GetNext(pNode)
{
// 1.如果一个节点的右子树不为空,那么该节点的下一个节点是右子树的最左节点
// 2.否则,向上找第一个左链接指向的树包含该节点的祖先节点。
if (pNode.right !== null) {
let node = pNode.right
while (node.left !== null) {
node = node.left
}
return node
} else {
while (pNode.next !== null) {
let pFather = pNode.next
if (pFather.left === pNode) {
return pFather
}
pNode = pNode.next
}
}
return null
}
```
也可以先找到根节点,再顺着中序遍历的顺序得到该节点的下一个节点。
## 5.用两个栈实现队列
题目描述:用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的 Push 和 Pop 操作。
解题思路:
in 栈用来处理入栈(push)操作,out 栈用来处理出栈(pop)操作。一个元素进入 in 栈之后,出栈的顺序被反转。当元素要出栈时,需要先进入 out 栈,此时元素出栈顺序再一次被反转,因此出栈顺序就和最开始入栈顺序是相同的,先进入的元素先退出,这就是队列的顺序。

## 6.旋转数组的最小数字
题目描述:把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个非递减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。

解题思路:
将旋转数组对半分可以得到一个包含最小元素的新旋转数组,以及一个非递减排序的数组。新的旋转数组的数组元素是原数组的一半,从而将问题规模减少了一半,这种折半性质的算法的时间复杂度为 O(logN)(为了方便,这里将 log2N 写为 logN)。

此时问题的关键在于确定对半分得到的两个数组哪一个是旋转数组,哪一个是非递减数组。我们很容易知道非递减数组的第一个元素一定小于等于最后一个元素。
通过修改二分查找算法进行求解(l 代表 low,m 代表 mid,h 代表 high):
* 当 nums\[m\] <= nums\[h\] 时,表示 \[m, h\] 区间内的数组是非递减数组,\[l, m\] 区间内的数组是旋转数组,此时令 h = m;
* 否则 \[m + 1, h\] 区间内的数组是旋转数组,令 l = m + 1。
如果数组元素允许重复,会出现一个特殊的情况:nums\[l\] == nums\[m\] == nums\[h\],此时无法确定解在哪个区间,需要切换到顺序查找。例如对于数组 {1,1,1,0,1},l、m 和 h 指向的数都为 1,此时无法知道最小数字 0 在哪个区间。
~~~
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (nums[l] == nums[m] && nums[m] == nums[h])
return minNumber(nums, l, h);
else if (nums[m] <= nums[h])
h = m;
else
l = m + 1;
}
return nums[l];
}
private int minNumber(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
for (int i = l; i < h; i++)
if (nums[i] > nums[i + 1])
return nums[i + 1];
return nums[l];
}
~~~
## 7.矩阵中的路径
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c61c6999eecb4b8f88a98f66b273a3cc?tpId=13&tqId=11218&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
判断在一个矩阵中是否存在一条包含某字符串所有字符的路径。路径可以从矩阵中的任意一个格子开始,每一步可以在矩阵中向上下左右移动一个格子。如果一条路径经过了矩阵中的某一个格子,则该路径不能再进入该格子。
例如下面的矩阵包含了一条 bfce 路径。

**解题思路:**
使用回溯法(backtracking)进行求解,它是一种暴力搜索方法,通过搜索所有可能的结果来求解问题。回溯法在一次搜索结束时需要进行回溯(回退),将这一次搜索过程中设置的状态进行清除,从而开始一次新的搜索过程。例如下图示例中,从 f 开始,下一步有 4 种搜索可能,如果先搜索 b,需要将 b 标记为已经使用,防止重复使用。在这一次搜索结束之后,需要将 b 的已经使用状态清除,并搜索 c。

~~~
private final static int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int rows;
private int cols;
public boolean hasPath(char[] array, int rows, int cols, char[] str) {
if (rows == 0 || cols == 0) return false;
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
char[][] matrix = buildMatrix(array);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
private boolean backtracking(char[][] matrix, char[] str,
boolean[][] marked, int pathLen, int r, int c) {
if (pathLen == str.length) return true;
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols
|| matrix[r][c] != str[pathLen] || marked[r][c]) {
return false;
}
marked[r][c] = true;
for (int[] n : next)
if (backtracking(matrix, str, marked, pathLen + 1, r + n[0], c + n[1]))
return true;
marked[r][c] = false;
return false;
}
private char[][] buildMatrix(char[] array) {
char[][] matrix = new char[rows][cols];
for (int r = 0, idx = 0; r < rows; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < cols; c++)
matrix[r][c] = array[idx++];
return matrix;
}
~~~
## 8.机器人的运动范围
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e5207314b5241fb83f2329e89fdecc8?tpId=13&tqId=11219&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格。一个机器人从坐标 (0, 0) 的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左右上下四个方向移动一格,但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。
例如,当 k 为 18 时,机器人能够进入方格 (35,37),因为 3+5+3+7=18。但是,它不能进入方格 (35,38),因为 3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
**解题思路:**
使用深度优先搜索(Depth First Search,DFS)方法进行求解。回溯是深度优先搜索的一种特例,它在一次搜索过程中需要设置一些本次搜索过程的局部状态,并在本次搜索结束之后清除状态。而普通的深度优先搜索并不需要使用这些局部状态,虽然还是有可能设置一些全局状态。
~~~
private static final int[][] next = {{0, -1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {1, 0}};
private int cnt = 0;
private int rows;
private int cols;
private int threshold;
private int[][] digitSum;
public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
this.rows = rows;
this.cols = cols;
this.threshold = threshold;
initDigitSum();
boolean[][] marked = new boolean[rows][cols];
dfs(marked, 0, 0);
return cnt;
}
private void dfs(boolean[][] marked, int r, int c) {
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols || marked[r][c])
return;
marked[r][c] = true;
if (this.digitSum[r][c] > this.threshold)
return;
cnt++;
for (int[] n : next)
dfs(marked, r + n[0], c + n[1]);
}
private void initDigitSum() {
int[] digitSumOne = new int[Math.max(rows, cols)];
for (int i = 0; i < digitSumOne.length; i++) {
int n = i;
while (n > 0) {
digitSumOne[i] += n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
}
this.digitSum = new int[rows][cols];
for (int i = 0; i < this.rows; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < this.cols; j++)
this.digitSum[i][j] = digitSumOne[i] + digitSumOne[j];
}
~~~
## 9.剪绳子
[Leetcode](https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-break/description/)
**题目描述:**
把一根绳子剪成多段,并且使得每段的长度乘积最大
~~~
n = 2
return 1 (2 = 1 + 1)
n = 10
return 36 (10 = 3 + 3 + 4)
~~~
**解题思路:**
1、贪心
尽可能多剪长度为 3 的绳子,并且不允许有长度为 1 的绳子出现。如果出现了,就从已经切好长度为 3 的绳子中拿出一段与长度为 1 的绳子重新组合,把它们切成两段长度为 2 的绳子。
证明:当 n >= 5 时,3(n - 3) - n = 2n - 9 > 0,且 2(n - 2) - n = n - 4 > 0。因此在 n >= 5 的情况下,将绳子剪成一段为 2 或者 3,得到的乘积会更大。又因为 3(n - 3) - 2(n - 2) = n - 5 >= 0,所以剪成一段长度为 3 比长度为 2 得到的乘积更大。
~~~java
public int integerBreak(int n) {
if (n < 2)
return 0;
if (n == 2)
return 1;
if (n == 3)
return 2;
int timesOf3 = n / 3;
if (n - timesOf3 * 3 == 1)
timesOf3--;
int timesOf2 = (n - timesOf3 * 3) / 2;
return (int) (Math.pow(3, timesOf3)) * (int) (Math.pow(2, timesOf2));
}
~~~
2、动态规划???
~~~
public int integerBreak(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), dp[j] * (i - j)));
return dp[n];
}
~~~
## 10.二进制中 1 的个数
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8ee967e43c2c4ec193b040ea7fbb10b8?tpId=13&tqId=11164&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。
`n&(n-1)`
该位运算去除 n 的位级表示中最低的那一位。
~~~
n : 10110100
n-1 : 10110011
n&(n-1) : 10110000
~~~
~~~
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int cnt = 0;
while (n != 0) {
cnt++;
n &= (n - 1);
}
return cnt;
}
~~~
## 11.数值的整数次方
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/1a834e5e3e1a4b7ba251417554e07c00?tpId=13&tqId=11165&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
给定一个 double 类型的浮点数 base 和 int 类型的整数 exponent,求 base 的 exponent 次方。
**解题思路:**
快速幂算法
```js
function Power(base, exponent)
{
// write code here
if (exponent === 0) return 1
let p = Math.abs(exponent)
let res = 1 // 记录乘积
while (p) {
if (p & 1) { // 当前最后1位为1
res *= base
}
base *= base
p = p >> 1
}
return exponent > 0 ? res : (1 / res) // 指数为负
}
module.exports = {
Power : Power
};
```
## 12.删除链表中的重复结点
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fc533c45b73a41b0b44ccba763f866ef?tpId=13&tqId=11209&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**

**解题思路:**
```js
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return pHead;
ListNode next = pHead.next;
if (pHead.val == next.val) {
while (next != null && pHead.val == next.val)
next = next.next;
return deleteDuplication(next);
} else {
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
return pHead;
}
}
```
## 13.链表中环的入口
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/253d2c59ec3e4bc68da16833f79a38e4?tpId=13&tqId=11208&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
一个链表中包含环,请找出该链表的环的入口结点。要求不能使用额外的空间。
**解题思路:**
使用双指针,一个指针 fast 每次移动两个节点,一个指针 slow 每次移动一个节点。因为存在环,所以两个指针必定相遇在环中的某个节点上。假设相遇点在下图的 z1 位置,此时 fast 移动的节点数为 x+2y+z,slow 为 x+y,由于 fast 速度比 slow 快一倍,因此 x+2y+z=2(x+y),得到 x=z。
在相遇点,slow 要到环的入口点还需要移动 z 个节点,如果让 fast 重新从头开始移动,并且速度变为每次移动一个节点,那么它到环入口点还需要移动 x 个节点。在上面已经推导出 x=z,因此 fast 和 slow 将在环入口点相遇。

~~~
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null)
return null;
ListNode slow = pHead, fast = pHead;
do {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
} while (slow != fast);
fast = pHead;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
~~~
## 14.反转链表
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/75e878df47f24fdc9dc3e400ec6058ca?tpId=13&tqId=11168&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
递归:
~~~
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = null;
ListNode newHead = ReverseList(next);
next.next = head;
return newHead;
}
~~~
迭代:
```js
function ReverseList(pHead)
{
// write code here
if (pHead === null) return null
let prev = null, curr = pHead, next
while (curr !== null) {
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
}
return prev
}
```
## 15.合并两个排序的链表
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d8b6b4358f774294a89de2a6ac4d9337?tpId=13&tqId=11169&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**

**解题思路:**
递归:
```js
function Merge(pHead1, pHead2)
{
if (pHead1 === null) {
return pHead2
}
if (pHead2 === null) {
return pHead1
}
if (pHead1.val <= pHead2.val) {
pHead1.next = Merge(pHead1.next, pHead2)
return pHead1
} else {
pHead2.next = Merge(pHead1, pHead2.next)
return pHead2
}
}
```
迭代:
```js
function ListNode(x){
this.val = x;
this.next = null;
}
function Merge(pHead1, pHead2)
{
let head = new ListNode(-1) // 头插
let curr = head
while (pHead1 !== null && pHead2 !== null) {
if (pHead1.val <= pHead2.val) {
curr.next = pHead1
pHead1 = pHead1.next
} else {
curr.next = pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
}
curr = curr.next
}
if (pHead1 === null) {
curr.next = pHead2
}
if (pHead2 === null) {
curr.next = pHead1
}
return head.next
}
```
## 16.顺时针打印矩阵
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9b4c81a02cd34f76be2659fa0d54342a?tpId=13&tqId=11172&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
下图的矩阵顺时针打印结果为:1, 2, 3, 4, 8, 12, 16, 15, 14, 13, 9, 5, 6, 7, 11, 10

**解题思路:**
~~~
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {
for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[r1][i]);
for (int i = r1 + 1; i <= r2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[i][c2]);
if (r1 != r2)
for (int i = c2 - 1; i >= c1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[r2][i]);
if (c1 != c2)
for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[i][c1]);
r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;
}
return ret;
}
~~~
## 17.树的子结构
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6e196c44c7004d15b1610b9afca8bd88?tpId=13&tqId=11170&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)

```js
function HasSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2)
{
if (pRoot1 === null || pRoot2 === null) {
return false
}
return isSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) || HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2) || HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
}
function isSubtree (p1, p2) {
if (p2 === null) {
return true
}
if (p1 === null) {
return false
}
if (p1.val !== p2.val) {
return false
}
return isSubtree(p1.left, p2.left) && isSubtree(p1.right, p2.right)
}
```
## 18.对称的二叉树
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ff05d44dfdb04e1d83bdbdab320efbcb?tpId=13&tqId=11211&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
```js
function isSymmetrical(pRoot)
{
if (pRoot === null) {
return true
}
return fn(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)
}
function fn (t1, t2) {
if (t1 === null && t2 === null) {
return true
}
if (t1 === null || t2 === null) {
return false
}
if (t1.val !== t2.val) {
return false
}
return fn(t1.left, t2.right) && fn(t1.right, t2.left)
}
```
## 19.栈的压入、弹出序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d77d11405cc7470d82554cb392585106?tpId=13&tqId=11174&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。
例如序列 1,2,3,4,5 是某栈的压入顺序,序列 4,5,3,2,1 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 4,3,5,1,2 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
解题思路:
```js
function IsPopOrder(pushV, popV)
{
let n = pushV.length
const stack = []
for (let pushIndex = 0, popIndex = 0; pushIndex < n; pushIndex++) {
stack.push(pushV[pushIndex])
// 按入栈序列压入,当栈顶元素对应于出栈序列元素时弹出(用 popIndex 记录),注意是用 while
while (popIndex < n && stack.length !== 0 && stack[stack.length - 1] === popV[popIndex]) {
stack.pop()
popIndex++
}
}
return stack.length === 0 ? true : false
}
```
## 20.把二叉树打印成多行
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/445c44d982d04483b04a54f298796288?tpId=13&tqId=11213&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
```js
function Print(pRoot)
{
const Q = [], res = []
if (pRoot === null) return Q
Q.push(pRoot)
while (Q.length !== 0) {
let low = 0, high = Q.length // 这两个变量确定了本层的结点数量
const line = []
while (low++ < high) {
let tmp = Q.shift()
line.push(tmp.val)
if (tmp.left !== null) {
Q.push(tmp.left)
}
if (tmp.right !== null) {
Q.push(tmp.right)
}
}
res.push(line)
}
return res
}
```
## 21.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/a861533d45854474ac791d90e447bafd?tpId=13&tqId=11176&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
```js
function VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence)
{
// BST特性:左子结点比根结点小,右子结点大于根结点
let size = sequence.length
if (size === 0) return false
let i = 0
while (--size) {
while (sequence[i++] < sequence[size]);
while (sequence[i++] > sequence[size]);
if (i < size) return false
i = 0
}
return true
}
```
## 22.二叉树中和为某一值的路径
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/b736e784e3e34731af99065031301bca?tpId=13&tqId=11177&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
**题目描述:**
输入一颗二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
下图的二叉树有两条和为 22 的路径:10, 5, 7 和 10, 12

**解题思路:**
```js
let res = []
let path = []
function FindPath(root, expectNumber)
{
if (root === null) { return [] }
backtracking(root, expectNumber)
return res
}
function backtracking (node, target) {
if (root === null) {
return
}
path.push(node.val)
if (node.val === target && node.left === null && node.right === null) {
res.push(path)
} else {
backtracking(node.left, target - node.val)
backtracking(node.right, target - node.val)
}
path.pop()
}
```
## 23.复杂链表的复制
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/f836b2c43afc4b35ad6adc41ec941dba?tpId=13&tqId=11178&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:输入一个复杂链表(每个节点中有节点值,以及两个指针,一个指向下一个节点,另一个特殊指针指向任意一个节点),返回结果为复制后复杂链表的 head。
解题思路:
第一步,在每个节点的后面插入复制的节点。

第二步,对复制节点的 random 链接进行赋值。

第三步,拆分。

```js
function RandomListNode(x){
this.label = x;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
function Clone(pHead)
{
/*
1、复制每个节点,如:复制节点 A 得到 A1,将 A1 插入节点 A 后面
2、遍历链表,A1->random = A->random->next;
3、将链表拆分成原链表和复制后的链表
*/
if (!pHead) return null
let currNode = pHead
// step1
while (currNode) {
let newNode = new RandomListNode(currNode.label)
newNode.next = currNode.next
currNode.next = newNode
currNode = newNode.next
}
// step2
currNode = pHead
while (currNode) {
let tempNode = currNode.next
if (currNode.random) {
tempNode.random = currNode.random.next
}
currNode = tempNode.next
}
// step3 拆分
let pCloneHead = pHead.next
let temp
currNode = pHead
while (currNode.next) {
temp = currNode.next
currNode.next = temp.next
currNode = temp
}
return pCloneHead
}
```
## 24.序列化二叉树
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/cf7e25aa97c04cc1a68c8f040e71fb84?tpId=13&tqId=11214&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
```js
function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
const arr = []
function Serialize(pRoot)
{
if (pRoot === null) {
arr.push('#')
return
}
arr.push(pRoot.val)
Serialize(pRoot.left)
Serialize(pRoot.right)
}
function Deserialize(s)
{
if (arr.length < 1) {
return null
}
let root = null // '#' -> null
let temp = arr.shift()
if (typeof temp === 'number') {
root = new TreeNode(temp)
root.left = Deserialize('')
root.right = Deserialize('')
}
return root
}
```
## 25.最小的 K 个数
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6a296eb82cf844ca8539b57c23e6e9bf?tpId=13&tqId=11182&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
解题思路:
1.快速选择
* 复杂度:O(N) + O(1)
* 只有当允许修改数组元素时才可以使用
快速排序的 partition() 方法,会返回一个整数 j 使得 a\[l..j-1\] 小于等于 a\[j\],且 a\[j+1..h\] 大于等于 a\[j\],此时 a\[j\] 就是数组的第 j 大元素。可以利用这个特性找出数组的第 K 个元素,这种找第 K 个元素的算法称为快速选择算法。
```java
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return ret;
findKthSmallest(nums, k - 1);
/* findKthSmallest 会改变数组,使得前 k 个数都是最小的 k 个数 */
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
ret.add(nums[i]);
return ret;
}
public void findKthSmallest(int[] nums, int k) {
int l = 0, h = nums.length - 1;
while (l < h) {
int j = partition(nums, l, h);
if (j == k)
break;
if (j > k)
h = j - 1;
else
l = j + 1;
}
}
private int partition(int[] nums, int l, int h) {
int p = nums[l]; /* 切分元素 */
int i = l, j = h + 1;
while (true) {
while (i != h && nums[++i] < p) ;
while (j != l && nums[--j] > p) ;
if (i >= j)
break;
swap(nums, i, j);
}
swap(nums, l, j);
return j;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
```
2.大小为 K 的最小堆
* 复杂度:O(NlogK) + O(K)
* 特别适合处理海量数据
应该使用大顶堆来维护最小堆,而不能直接创建一个小顶堆并设置一个大小,企图让小顶堆中的元素都是最小元素。
维护一个大小为 K 的最小堆过程如下:在添加一个元素之后,如果大顶堆的大小大于 K,那么需要将大顶堆的堆顶元素去除。
```java
public ArrayList<Integer> GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int[] nums, int k) {
if (k > nums.length || k <= 0)
return new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o2 - o1);
for (int num : nums) {
maxHeap.add(num);
if (maxHeap.size() > k)
maxHeap.poll();
}
return new ArrayList<>(maxHeap);
}
```
## 26.连续子数组的最大和
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/459bd355da1549fa8a49e350bf3df484?tpId=13&tqId=11183&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:{6, -3, -2, 7, -15, 1, 2, 2},连续子数组的最大和为 8(从第 0 个开始,到第 3 个为止)。
```js
function FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(array)
{
const d = []
d[0] = array[0]
for (let i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {
d[i] = Math.max(d[i - 1] + array[i], array[i])
}
return Math.max(...d)
}
```
## 27.把数组排成最小的数
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8fecd3f8ba334add803bf2a06af1b993?tpId=13&tqId=11185&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组 {3,32,321},则打印出这三个数字能排成的最小数字为 321323。
```js
function PrintMinNumber(numbers)
{
// write code here
numbers.sort(compare)
return numbers.join('')
}
/*
根据拼接后的字符串比较大小
ab < ba : a < b 如323 < 332 -> 32 < 3
ab > ba : a > b
ab = ba : a = b
*/
function compare(a, b) {
let ab = a + '' + b
let ba = b + '' + a
if (ab < ba) {
return -1 // 如果第一个参数应该在第二个参数之前,返回一个负数
} else if (ab > ba) {
return 1
} else {
return 0
}
}
```
## 28.丑数
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6aa9e04fc3794f68acf8778237ba065b?tpId=13&tqId=11186&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:把只包含因子 2、3 和 5 的数称作丑数(Ugly Number)。例如 6、8 都是丑数,但 14 不是,因为它包含因子 7。习惯上我们把 1 当做是第一个丑数。求按从小到大的顺序的第 N 个丑数。
```js
function GetUglyNumber_Solution(index)
{
if (index < 7) return index
let p2 = 0, p3 = 0, p5 = 0, newNum = 1 // 三个队列的指针,newNum为从队列头选出来的最小数
const arr = []
arr.push(newNum)
while (arr.length < index) {
newNum = Math.min(arr[p2] * 2, arr[p3] * 3, arr[p5] * 5) // 选出三个队列头最小的数
// 这三个if有可能进入一个或者多个,进入多个是三个队列头最小的数有多个的情况
if (arr[p2] * 2 === newNum) p2++
if (arr[p3] * 3 === newNum) p3++
if (arr[p5] * 5 === newNum) p5++
arr.push(newNum)
}
return newNum
}
```
## 29.两个链表的第一个公共结点
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/6ab1d9a29e88450685099d45c9e31e46?tpId=13&tqId=11189&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:

解题思路:
设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a。
当访问链表 A 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 B 的头部重新开始访问链表 B;同样地,当访问链表 B 的指针访问到链表尾部时,令它从链表 A 的头部重新开始访问链表 A。这样就能控制访问 A 和 B 两个链表的指针能同时访问到交点。
```js
function FindFirstCommonNode(pHead1, pHead2)
{
// 设 A 的长度为 a + c,B 的长度为 b + c,其中 c 为尾部公共部分长度,可知 a + c + b = b + c + a
// 当 A 指针走到尾部时让其指向 B 头部,当 B 指针走到尾部时让其指向 A 头部
let l1 = pHead1
let l2 = pHead2
while (l1 !== l2) {
l1 = l1 === null ? pHead2 : l1.next
l2 = l2 === null ? pHead1 : l2.next
}
return l1
}
```
## 30.和为 S 的两个数字
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/390da4f7a00f44bea7c2f3d19491311b?tpId=13&tqId=11195&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字 S,在数组中查找两个数,使得他们的和正好是 S。如果有多对数字的和等于 S,输出两个数的乘积最小的。
解题思路:
使用双指针,一个指针指向元素较小的值,一个指针指向元素较大的值。指向较小元素的指针从头向尾遍历,指向较大元素的指针从尾向头遍历。
* 如果两个指针指向元素的和 sum == target,那么得到要求的结果;
* 如果 sum > target,移动较大的元素,使 sum 变小一些;
* 如果 sum < target,移动较小的元素,使 sum 变大一些。
```js
function FindNumbersWithSum(array, sum)
{
let low = 0, high = array.length - 1
let multi = 10000000, res = []
while (low < high) {
let add = array[low] + array[high]
if (add === sum) {
if (array[low] * array[high] < multi) {
res = [array[low], array[high]]
multi = array[low] * array[high]
}
low++
high--
} else if (add > sum) {
high--
} else {
low++
}
}
return res
}
```
## 31.和为 S 的连续正数序列
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/c451a3fd84b64cb19485dad758a55ebe?tpId=13&tqId=11194&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:
输出所有和为 S 的连续正数序列。
例如和为 100 的连续序列有:
~~~
[9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16]
[18, 19, 20, 21, 22]。
~~~
解题思路:
```js
function FindContinuousSequence(sum)
{
const res = []
let pHigh = 2, pLow = 1 // 双指针,总和小于 sum,high ++,否则 low++
while (pHigh > pLow) {
let currSum = (pHigh + pLow) * (pHigh - pLow + 1) / 2 // 等差数列
if (currSum < sum) pHigh++
else if (currSum === sum) {
let temp = []
for (let i = pLow; i <= pHigh; i++) {
temp.push(i)
}
res.push(temp)
pHigh++
} else {
pLow++
}
}
return res
}
```
## 32.不用加减乘除做加法
题目描述:写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求不得使用 +、-、\*、/ 四则运算符号。
解题思路:
```js
function Add(num1, num2)
{
while (num2 !== 0) {
let temp = num1 ^ num2 // 不算进位部分
num2 = (num1 & num2) << 1 // 进位部分
num1 = temp
}
return num1
}
```
## 33.构建乘积数组
[NowCoder](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/94a4d381a68b47b7a8bed86f2975db46?tpId=13&tqId=11204&tPage=1&rp=1&ru=/ta/coding-interviews&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
题目描述:给定一个数组 A\[0, 1,..., n-1\],请构建一个数组 B\[0, 1,..., n-1\],其中 B 中的元素 B\[i\]=A\[0\]\*A\[1\]\*...\*A\[i-1\]\*A\[i+1\]\*...\*A\[n-1\]。要求不能使用除法。
**解题思路:**
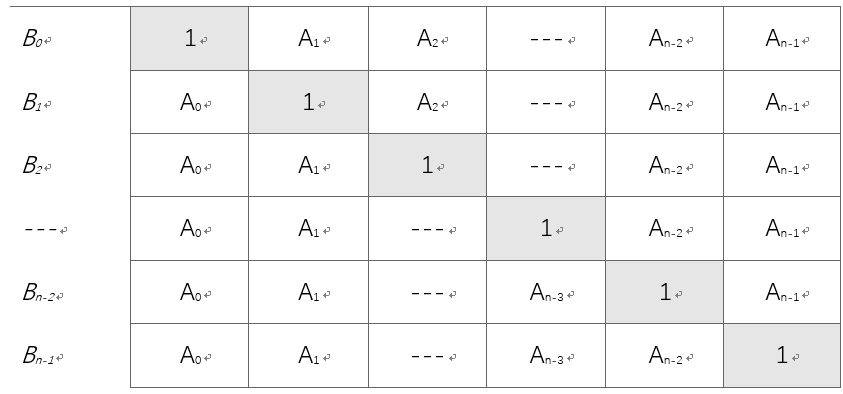
B\[i\]的值可以看作下图的矩阵中每行的乘积。
```js
function multiply(array)
{
let len = array.length
const B = []
B[0] = 1
// 计算下三角连乘
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
B[i] = B[i-1] * array[i-1]
}
// 计算上三角
let temp = 1
for (let j = len - 2; j >= 0; j--) {
temp *= array[j+1]
B[j] *= temp
}
return B
}
```
## 34.树中两个节点的最低公共祖先
### 二叉查找树
[Leetcode : 235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/)
二叉查找树中,两个节点 p, q 的公共祖先 root 满足 root.val >= p.val && root.val <= q.val。

```js
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if (root === null) return null
if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
}
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
}
return root // we allow a node to be a descendant of itself
};
```
### 普通二叉树
[Leetcode : 236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree](https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/)
在左右子树中查找是否存在 p 或者 q,如果 p 和 q 分别在两个子树中,那么就说明根节点就是最低公共祖先。

```js
var lowestCommonAncestor = function(root, p, q) {
if (root === null || root === p || root === q) return root
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
if (left !== null && right !== null) return root
return left !== null ? left : right
};
```
- 序言 & 更新日志
- H5
- Canvas
- 序言
- Part1-直线、矩形、多边形
- Part2-曲线图形
- Part3-线条操作
- Part4-文本操作
- Part5-图像操作
- Part6-变形操作
- Part7-像素操作
- Part8-渐变与阴影
- Part9-路径与状态
- Part10-物理动画
- Part11-边界检测
- Part12-碰撞检测
- Part13-用户交互
- Part14-高级动画
- CSS
- SCSS
- codePen
- 速查表
- 面试题
- 《CSS Secrets》
- SVG
- 移动端适配
- 滤镜(filter)的使用
- JS
- 基础概念
- 作用域、作用域链、闭包
- this
- 原型与继承
- 数组、字符串、Map、Set方法整理
- 垃圾回收机制
- DOM
- BOM
- 事件循环
- 严格模式
- 正则表达式
- ES6部分
- 设计模式
- AJAX
- 模块化
- 读冴羽博客笔记
- 第一部分总结-深入JS系列
- 第二部分总结-专题系列
- 第三部分总结-ES6系列
- 网络请求中的数据类型
- 事件
- 表单
- 函数式编程
- Tips
- JS-Coding
- Framework
- Vue
- 书写规范
- 基础
- vue-router & vuex
- 深入浅出 Vue
- 响应式原理及其他
- new Vue 发生了什么
- 组件化
- 编译流程
- Vue Router
- Vuex
- 前端路由的简单实现
- React
- 基础
- 书写规范
- Redux & react-router
- immutable.js
- CSS 管理
- React 16新特性-Fiber 与 Hook
- 《深入浅出React和Redux》笔记
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- react-transition-group
- Vue 与 React 的对比
- 工程化与架构
- Hybird
- React Native
- 新手上路
- 内置组件
- 常用插件
- 问题记录
- Echarts
- 基础
- Electron
- 序言
- 配置 Electron 开发环境 & 基础概念
- React + TypeScript 仿 Antd
- TypeScript 基础
- 样式设计
- 组件测试
- 图标解决方案
- Algorithm
- 排序算法及常见问题
- 剑指 offer
- 动态规划
- DataStruct
- 概述
- 树
- 链表
- Network
- Performance
- Webpack
- PWA
- Browser
- Safety
- 微信小程序
- mpvue 课程实战记录
- 服务器
- 操作系统基础知识
- Linux
- Nginx
- redis
- node.js
- 基础及原生模块
- express框架
- node.js操作数据库
- 《深入浅出 node.js》笔记
- 前半部分
- 后半部分
- 数据库
- SQL
- 面试题收集
- 智力题
- 面试题精选1
- 面试题精选2
- 问答篇
- Other
- markdown 书写
- Git
- LaTex 常用命令
