## 1.数据类型有哪些?
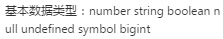

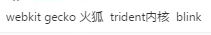
## 2.浏览器的内核?
3.数据类型的区别?
基本数据类型存储在栈内存中,引用数据类型存储在堆内存中

~~~
var a = 'abc' + 123 + 456;
/*
* +在JS中除了数学运算还有字符串拼接
* 'abc' + 123 => 'abc123'
* 'abc123' + 456 => 'abc123456'
*/
var b = '456' - '123';
/*
* -/*%这些运算符都是数学运算(要把其它类型值基于Number()转换为数字再进行运算)
* + 字符串中只要出现非有效数字字符结果就是NaN,空字符串变为0
* + true 1 false 0 null 0 undefined NaN symbol不能转-报错
* + 对象是先转换为字符串 toString,然后在转换为数字
* 456 - 123 => 333
*/
var c = 100 + true + 21.2 + null + undefined + "Tencent" + [] + null + 9 + false;
/*
* 100 + true => 101
* 101 + 21.2 => 122.2
* 122.2 + null => 122.2
* 122.2 + undefined => NaN
* NaN + 'Tencent' => 'NaNTencent'
* 'NaNTencent' + ... 都是字符串拼接了 => 'NaNTencentnull9false'
*/
console.log(a, b, c);
~~~
~~~
// parseInt 是把一个字符串转换为数字(如果值不是字符串,也要先转换为字符串),从字符串最左侧开始查找,把找到的有效数字字符转换为数字,一旦遇到一个非有效数字字符,则停止向后查找(不管后面是否还有数字都不在找了)
var str = 'abc123';
var num = parseInt(str); //=>NaN
if (num == NaN) { //=> NaN==NaN 不相等,NaN和谁都不相等(包括自己)
alert(NaN);
} else if (num == 123) { //=>NaN==123 不成立
alert(123);
} else if (typeof num == 'number') { //=> typeof NaN = "number" //=>"number"==="number" 条件成立
alert('number');
} else {
alert('str');
}
// 在浏览器中弹出一个窗口 输出 "number"
~~~
~~~
//能输出"1"的有哪些
alert(1) //=>输出的是"1",因为基于alert/confirm等输出结果,都会把内容转换为字符串再输出
console.log(parseInt(1.3)) //=>parseInt('1.3') =>数字1
console.log(1) //=>1 console.log输出的内容还是原本的数据格式
console.log(isNaN(1)) //=>false
console.log(parseInt("1")) //=>数字1
~~~
~~~
// 输出undefined是谁?
console.log(alert(1));//=>先执行ALERT(输出"1"),然后把ALERT执行的返回结果再输出 =>undefined
typeof undefined; //=>"undefined" typeof返回的结果首先是一个字符串
console.log(parseInt(undefined)); //=>parseInt(undefined) =>parseInt("undefined") =>NaN
isNaN(undefined); //=>isNaN检测值,如果值不是数字类型,先基于Number把其转换为数字类型,然后再检测 =>Number(undefined) =>NaN =>isNaN(NaN) =>true
~~~
~~~
//下面能得到结果是true的
isNaN(null) //=>isNaN(0) =>false
isNaN(parseInt(null)) //=>parseInt("null") =>NaN =>isNaN(NaN) =>true
Number(null) //=>0
parseFloat(null) //=>parseFloat("null") =>NaN
~~~
~~~
下面输出的结果是?
Number和parseInt在转换为数字的时候,规则是不一样的,先转为字符串,然后从第一个字符串开始找数字。
parseInt("") //=>NaN
Number("") //=>0
isNaN("") //=>需要先调用Number转换为数字再检测 isNaN(0) =>false
parseInt(null) //=>先把值转换为字符串 parseInt("null") =>NaN
Number(null) //=>0
isNaN(null) //=>isNaN(Number(null)) => isNaN(0) =>false
parseInt("12px") //=>12
Number("12px") //=>NaN
isNaN("12px") //=>isNaN(Number('12px')) =>isNaN(NaN) =>true
~~~

~~~
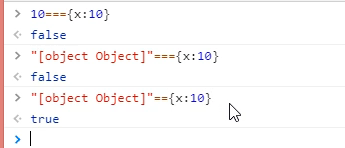
// 知识点:在JS中,比较两个值是否相等,我们有以下几种方式
// 1. == 相等(相等比较中,如果左右两边数据类型不同,则默认先转换为相同的数据类型,然后再进行比较)
// 2. ==== 绝对相等(需要保证左右两边数据类型和值都一样,才会相等,只要有一样不一样,结果都是不相等的)
// 3. Object.is ES6规范中新增加的方式(暂时不讲)
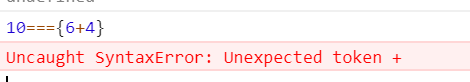
console.log(10 == "10"); //=>TRUE 默认先把"10"->10,然后再比较
console.log(10 === "10"); //=>FALSE
console.log("10" === "10"); //=>TRUE
/*
* isNaN(NaN) == "" 条件是否成立
* + isNaN(NaN) =>true
* + true=="" 两个等于号比较,默认会转换数据类型(此处都转换为数字,再进行比较) => 1==0 条件是不成立的
*/
if (isNaN(NaN) == "") {
console.log("珠峰")
} else {
console.log("培训") //培训
}
//培训
~~~
- 0001.开课说明
- 0002.ECMAScript的发展历程
- 0003.WEB2.0时代-服务器端渲染,前后端不分离
- 0004.WEB2.0时代-前后端分离模式
- 0005.大前端时代概述
- 0006.前端需要的技术栈和学习技巧
- 0007.浏览器
- 0008.JS的三部分组成
- 0009.JS中创建变量的6种形式
- 0010.JS中变量的命名规范
- 0011.JS中的数据类型分类
- 0012.JS中常用的几种输出方式
- 0013.number属性类型详细解读1
- 0014.number数据类型详细解读2
- 0015.string数据类型详细解读1
- 0016.string数据类型详细解读2
- 0017.boolean数据类型详细解读
- 0018.object数据类型详细解读1
- 0019.object数据类型详细解读2
- 0020.谈谈学习
- 0021.数据类型检测
- 0022.浏览器底层渲染机制(堆栈内存和数据类型区别)
- 0023.关于数据类型区别的面试题
- 0024.课后作业讲解:数据类型转换
- 0025.课后作业讲解:堆栈内存处理
- 0026.课后作业讲解:阿里的一道经典面试题
- 0027.JS中三种常用的判断语句
- 0028.小实战:开关灯特效
- 0029.FOR循环和FOR IN循环
- 0030.课后作业讲解:关于循环判断和数据转化
- 0031.课后作业讲解:关于DOM对象的深入理解
- 0032.关于元素集合的相关操作(奇偶行变色)
- 0033.课后作业讲解:逻辑思维判断题
- reset.min.css
- 0034.(复习)前四天内容的综合复习梳理
- 0035.初窥函数:函数的作用、语法、形参
- 0036-0038.选项卡案例
- 0039.隔行变色案例:进一步强化自定义属性编程思想
- 0040.其它作业题的讲解(自定义属性强化)
- 0041.函数创建和执行的堆栈运行机制
- 0042.函数中的形参和实参
- 0043.函数中的实参集合ARGUMENTS
- 0044.函数中的返回值RETURN
- 0045.箭头函数和匿名函数
- 0046.两个等于比较时候的数据类型转换规则
- 0047.数组的基础结构和常规操作
- 0048.数组常用方法:增删改的五个方法
- 0049.数组常用方法:查询、拼接、转换为字符串
- 0050.数组常用方法:检测是否包含、排序和迭代
- 0051.数组去重:双FOR循环(数组塌陷和SPLICE删除优化)
- 0052.数组去重:对象键值对方式(ES6中SET)
- 0053.Math数学函数对象中常用的方法
- 0054.String字符串中常用的方法
- 0055.实战案例:时间字符串格式化
- 0056.实战案例:queryURLParams1
- 0057.实战案例:queryURLParams2
- 0058.实战案例:获取四位不重复的验证码
- 0059.阶段作业题讲解1(基础知识)
- 0060.阶段作业题讲解2(实战案例)
- 0061-0062.DOM操作中相关知识的复习
- 0063.DOM中的节点操作1
- 0064.DOM中的节点操作2
- utils
- 65.关于DOM的增删改
