# 学习 TensorFlow 线性回归方法
虽然使用矩阵和分解方法非常强大,但 TensorFlow 还有另一种解决斜率和截距的方法。 TensorFlow 可以迭代地执行此操作,逐步学习最小化损失的线性回归参数。
## 做好准备
在这个秘籍中,我们将遍历批量数据点并让 TensorFlow 更新斜率和`y`截距。我们将使用内置于 scikit-learn 库中的 iris 数据集,而不是生成的数据。具体来说,我们将通过数据点找到最佳线,其中`x`值是花瓣宽度,`y`值是萼片长度。我们选择了这两个,因为它们之间似乎存在线性关系,我们将在最后的绘图中看到。我们还将在下一节中详细讨论不同损失函数的影响,但对于这个秘籍,我们将使用 L2 损失函数。
## 操作步骤
我们按如下方式处理秘籍:
1. 我们首先加载必要的库,创建图并加载数据:
```py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
sess = tf.Session()
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([x[3] for x in iris.data])
y_vals = np.array([y[0] for y in iris.data])
```
1. 然后我们声明我们的学习率,批量大小,占位符和模型变量:
```py
learning_rate = 0.05
batch_size = 25
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
```
1. 接下来,我们编写线性模型的公式`y = Ax + b`:
```py
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)
```
1. 然后,我们声明我们的 L2 损失函数(包括批量的平均值),初始化变量,并声明我们的优化器。请注意,我们选择`0.05`作为我们的学习率:
```py
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_target - model_output))
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
```
1. 我们现在可以在随机选择的批次上循环并训练模型。我们将运行 100 个循环并每 25 次迭代打印出变量和损失值。请注意,在这里,我们还保存了每次迭代的损失,以便我们以后可以查看它们:
```py
loss_vec = []
for i in range(100):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size)
rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals[rand_index]])
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
loss_vec.append(temp_loss)
if (i+1)%25==0:
print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)) + ' b = ' + str(sess.run(b)))
print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))
Step #25 A = [[ 2.17270374]] b = [[ 2.85338426]]
Loss = 1.08116
Step #50 A = [[ 1.70683455]] b = [[ 3.59916329]]
Loss = 0.796941
Step #75 A = [[ 1.32762754]] b = [[ 4.08189011]]
Loss = 0.466912
Step #100 A = [[ 1.15968263]] b = [[ 4.38497639]]
Loss = 0.281003
```
1. 接下来,我们将提取我们找到的系数并创建一个最合适的线以放入图中:
```py
[slope] = sess.run(A)
[y_intercept] = sess.run(b)
best_fit = []
for i in x_vals:
best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept)
```
1. 在这里,我们将创建两个图。第一个是覆盖拟合线的数据。第二个是 100 次迭代中的 L2 损失函数。这是生成两个图的代码。
```py
plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, 'o', label='Data Points')
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit, 'r-', label='Best fit line', linewidth=3)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.title('Sepal Length vs Petal Width')
plt.xlabel('Petal Width')
plt.ylabel('Sepal Length')
plt.show()
plt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')
plt.title('L2 Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('L2 Loss')
plt.show()
```
此代码生成以下拟合数据和损失图。
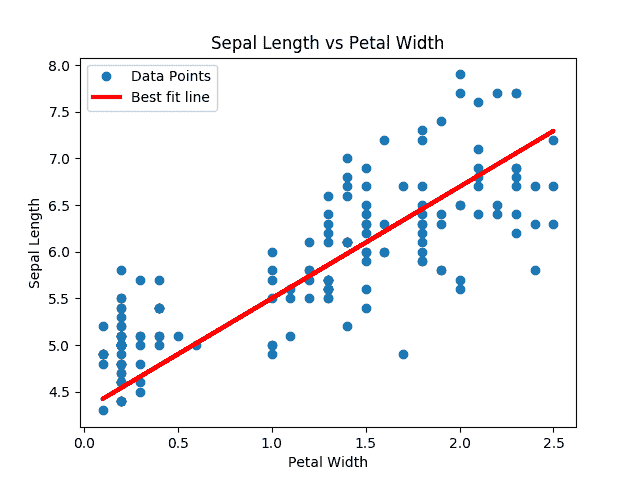
图 3:来自虹膜数据集的数据点(萼片长度与花瓣宽度)重叠在 TensorFlow 中找到的最佳线条拟合。
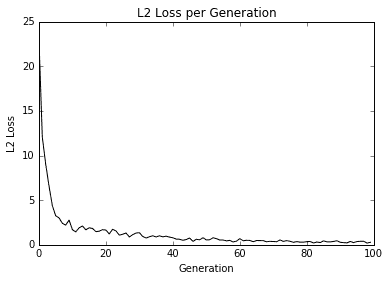
图 4:用我们的算法拟合数据的 L2 损失;注意损失函数中的抖动,可以通过较大的批量大小减小抖动,或者通过较小的批量大小来增加。
Here is a good place to note how to see whether the model is overfitting or underfitting the data. If our data is broken into test and training sets, and the accuracy is greater on the training set and lower on the test set, then we are overfitting the data. If the accuracy is still increasing on both test and training sets, then the model is underfitting and we should continue training.
## 工作原理
找到的最佳线不保证是最合适的线。最佳拟合线的收敛取决于迭代次数,批量大小,学习率和损失函数。随着时间的推移观察损失函数总是很好的做法,因为它可以帮助您解决问题或超参数变化。
- TensorFlow 入门
- 介绍
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 声明变量和张量
- 使用占位符和变量
- 使用矩阵
- 声明操作符
- 实现激活函数
- 使用数据源
- 其他资源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介绍
- 计算图中的操作
- 对嵌套操作分层
- 使用多个层
- 实现损失函数
- 实现反向传播
- 使用批量和随机训练
- 把所有东西结合在一起
- 评估模型
- 线性回归
- 介绍
- 使用矩阵逆方法
- 实现分解方法
- 学习 TensorFlow 线性回归方法
- 理解线性回归中的损失函数
- 实现 deming 回归
- 实现套索和岭回归
- 实现弹性网络回归
- 实现逻辑回归
- 支持向量机
- 介绍
- 使用线性 SVM
- 简化为线性回归
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用内核
- 实现非线性 SVM
- 实现多类 SVM
- 最近邻方法
- 介绍
- 使用最近邻
- 使用基于文本的距离
- 使用混合距离函数的计算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近邻进行图像识别
- 神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现操作门
- 使用门和激活函数
- 实现单层神经网络
- 实现不同的层
- 使用多层神经网络
- 改进线性模型的预测
- 学习玩井字棋
- 自然语言处理
- 介绍
- 使用词袋嵌入
- 实现 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 进行预测
- 使用 doc2vec 进行情绪分析
- 卷积神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现简单的 CNN
- 实现先进的 CNN
- 重新训练现有的 CNN 模型
- 应用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 项目
- 实现 DeepDream
- 循环神经网络
- 介绍
- 为垃圾邮件预测实现 RNN
- 实现 LSTM 模型
- 堆叠多个 LSTM 层
- 创建序列到序列模型
- 训练 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 介绍
- 实现单元测试
- 使用多个执行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 生产环境 TensorFlow 的一个例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服务
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介绍
- 可视化 TensorBoard 中的图
- 使用遗传算法
- 使用 k 均值聚类
- 求解常微分方程组
- 使用随机森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
