# 使用随机森林
随机森林算法建立在随机选择的观察和/或随机选择的特征上的聚合决策树上。我们不会介绍如何训练决策树,但会显示有些类型的随机森林可以使用梯度提升训练,TensorFlow 可以为我们计算。
## 做好准备
基于树的算法传统上是非平滑的,因为它们基于对数据进行分区以最小化目标输出中的方差。非光滑方法不适合基于梯度的方法。 TensorFlow 依赖于以下事实:模型中使用的函数是平滑的,并且它自动计算如何更改模型参数以最小化函数损失。 TensorFlow 绕过这个障碍的方式是对决策边界进行平滑逼近。可以使用 softmax 函数或类似形状函数来近似决策边界。
决策树将通过生成规则在数据集上提供硬拆分,例如,如果`x > 0.5`,则移动到树的这个分支....这告诉我们整个数据子集将组合在一起或拆分,取决于`x`的值。这个的平滑近似处理概率而不是整个分裂。这意味着数据集的每次观察都有可能存在于树的每个末端节点中。下图比较传统决策树和概率决策树,可以更好地说明这些差异。
下图说明了两个示例决策树之间的区别:
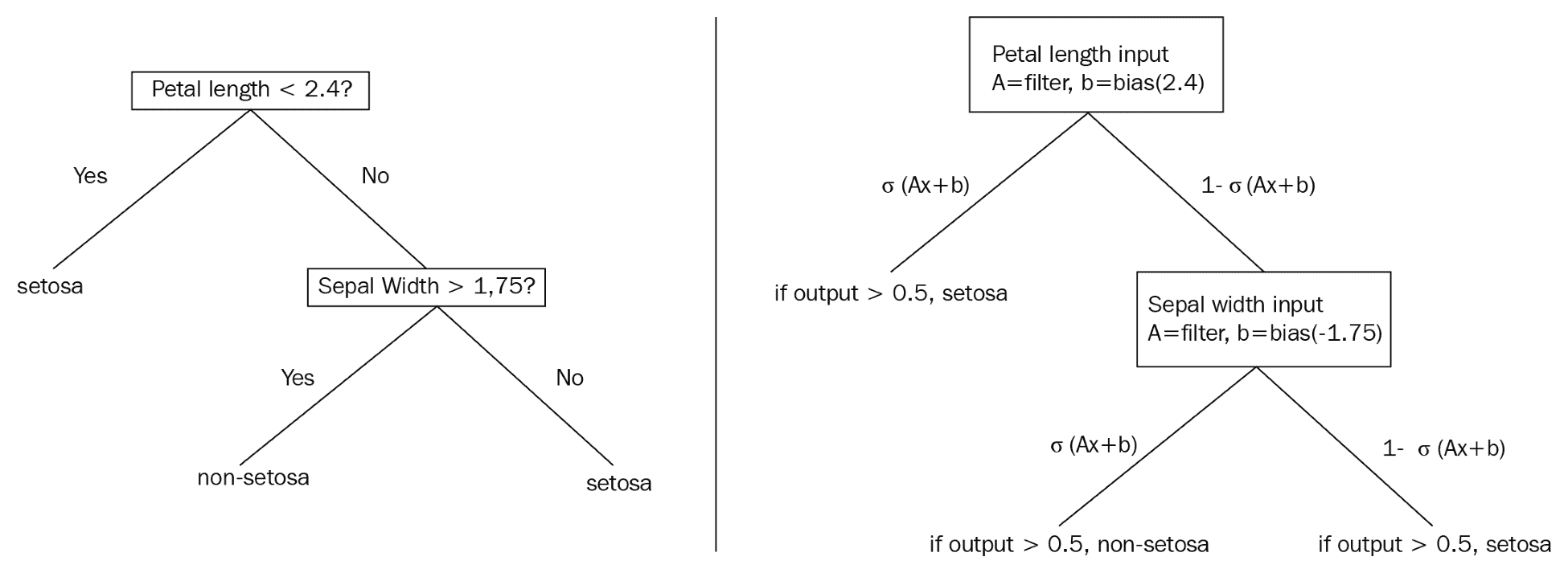
This diagram illustrates a standard decision tree (left) which is non-differentiable, and a smooth decision tree (right), which illustrates the usage of sigmoid functions to develop probabilities of an observation appearing in a labeled leaf or end-node.
> 我们选择不详细介绍函数的可微性,连续性和平滑性。本节的目的是提供关于如何通过可微分模型近似非可微分模型的直观描述。有关更多数学详细信息,我们建议读者查看本秘籍末尾的“另请参阅”部分。
## 操作步骤
TensorFlow 包含了一些我们将依赖于此秘籍的默认模型估计函数。有两个主要的梯度提升模型,回归树和分类树。对于此示例,我们将使用回归树来预测波士顿房价数据集( [https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~delve/data/boston/bostonDetail.html](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~delve/data/boston/bostonDetail.html) )。
1. 首先,我们加载必要的库:
```py
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from keras.datasets import boston_housing
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
```
1. 接下来,我们从 TensorFlow 估计器库中设置我们将要使用的模型。在这里,我们将使用`BoostedTreesRegressor`模型,该模型用于使用梯度提升树进行回归:
```py
regression_classifier = tf.estimator.BoostedTreesRegressor
```
> 或者,对于二分类问题,读者可以使用估计器`BoostedTreesClassifier`。目前不支持多类别分类,尽管它将来会在路线图上。
1. 现在,我们可以使用 Keras 数据导入函数将波士顿住房价格数据集加载到一行中,如下所示:
```py
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = boston_housing.load_data()
```
1. 在这里,我们可以设置一些模型参数;批量大小是一次训练的训练观测数量,我们将训练`500`迭代,梯度提升森林将有`100`树,每棵树的最大深度(分裂数)为`6`。
```py
# Batch size
batch_size = 32
# Number of training steps
train_steps = 500
# Number of trees in our 'forest'
n_trees = 100
# Maximum depth of any tree in forest
max_depth = 6
```
1. TensorFlow 提供的模型估计器需要输入函数。我们将为估计器函数创建数据输入函数。但首先,我们需要将数据放入正确标记的`numpy`数组格式的字典中。这些在 TensorFlow 中称为特征列。纯数字列尚不支持,因此我们将数字列放入自动存储桶中,如下所示:(a)二进制特征将具有两个存储桶,(b)其他连续数字特征将被划分为 5 个存储桶。
```py
binary_split_cols = ['CHAS', 'RAD']
col_names = ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'CHAS', 'NOX', 'RM', 'AGE', 'DIS', 'RAD', 'TAX', 'PTRATIO', 'B', 'LSTAT']
X_dtrain = {col: x_train[:, ix] for ix, col in enumerate(col_names)}
X_dtest = {col: x_test[:, ix] for ix, col in enumerate(col_names)}
# Create feature columns!
feature_cols = []
for ix, column in enumerate(x_train.T):
col_name = col_names[ix]
# Create binary split feature
if col_name in binary_split_cols:
# To create 2 buckets, need 1 boundary - the mean
bucket_boundaries = [column.mean()]
numeric_feature = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(col_name)
final_feature = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(source_column=numeric_feature, boundaries=bucket_boundaries)
# Create bucketed feature
else:
# To create 5 buckets, need 4 boundaries
bucket_boundaries = list(np.linspace(column.min() * 1.1, column.max() * 0.9, 4))
numeric_feature = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(col_name)
final_feature = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(source_column=numeric_feature, boundaries=bucket_boundaries)
# Add feature to feature_col list
feature_cols.append(final_feature)
```
> 将输入函数的 shuffle 选项设置为`True`进行训练,`False`进行测试是个好主意。我们想在每个周期改变`X`和`Y`训练集,但不是在测试期间。
1. 我们现在使用 TensorFlow 估计器中输入库的`numpy`输入函数声明我们的数据输入函数。我们将指定我们创建的训练观察词典和一组`y`目标。
```py
input_fun = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(X_dtrain, y=y_train, batch_size=batch_size, num_epochs=10, shuffle=True)
```
1. 现在,我们宣布我们的模型并开始训练:
```py
model = regression_classifier(feature_columns=feature_cols,
n_trees=n_trees,
max_depth=max_depth,
learning_rate=0.25,
n_batches_per_layer=batch_size)
model.train(input_fn=input_fun, steps=train_steps)
```
1. 在训练期间,我们应该看到类似的输出如下:
```py
INFO:tensorflow:Using default config.
WARNING:tensorflow:Using temporary folder as model directory: /tmp/tmpqxyd62cu
INFO:tensorflow:Using config: {'_model_dir': '/tmp/tmpqxyd62cu', '_tf_random_seed': None, '_save_summary_steps': 100, '_save_checkpoints_steps': None, '_save_checkpoints_secs': 600, '_session_config': None, '_keep_checkpoint_max': 5, '_keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours': 10000, '_log_step_count_steps': 100, '_train_distribute': None, '_device_fn': None, '_service': None, '_cluster_spec': <tensorflow.python.training.server_lib.ClusterSpec object at 0x7f43129d77b8>, '_task_type': 'worker', '_task_id': 0, '_global_id_in_cluster': 0, '_master': '', '_evaluation_master': '', '_is_chief': True, '_num_ps_replicas': 0, '_num_worker_replicas': 1}
INFO:tensorflow:Calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Done calling model_fn.
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook.
INFO:tensorflow:Graph was finalized.
INFO:tensorflow:Running local_init_op.
INFO:tensorflow:Done running local_init_op.
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 0 into /tmp/tmpqxyd62cu/model.ckpt.
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 691.09814, step = 1
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 587.923
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 178.62021, step = 101 (0.171 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 127 into /tmp/tmpqxyd62cu/model.ckpt.
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 37.436565.
Out[190]: <tensorflow.python.estimator.canned.boosted_trees.BoostedTreesRegressor at 0x7f43129d7470>
```
1. 为了评估我们的模型,我们为测试数据创建了另一个输入函数,并获得每个测试数据点的预测。以下是获取预测并打印平均绝对误差(MAE)的代码:
```py
p_input_fun = tf.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(X_dtest, y=y_test, batch_size=batch_size, num_epochs=1, shuffle=False)
# Get predictions
predictions = list(model.predict(input_fn=p_input_fun))
final_preds = [pred['predictions'][0] for pred in predictions]
# Get accuracy (mean absolute error, MAE)
mae = np.mean([np.abs((actual - predicted) / predicted) for actual, predicted in zip(y_test, final_preds)])
print('Mean Abs Err on test set: {}'.format(acc))
```
1. 其中以`0.71`打印出错误。请注意,由于随机播放的随机性,读者可能会得到略微不同的结果。为了提高准确率,我们可以考虑增加数字周期或引入更低的学习率甚至是某种类型的衰减学习率(指数或线性):
```py
Mean Abs Err on test set: 0.7111111111111111
```
## 工作原理
在本文中,我们将说明如何使用 TensorFlow 估计器和 TensorFlow 提供的数据输入函数。这些函数非常强大,不仅使我们的 TensorFlow 代码更短,更易读,而且还提高了算法的效率,减少了创建和测试算法所需的开发时间。
## 另见
有关决策树,随机森林,梯度提升森林以及可微分性,平滑性和连续性背后的数学的更多参考,我们鼓励读者阅读以下参考文献。
1. 决策树教程。来自伯克利的机器学习速成课程。 [https://ml.berkeley.edu/blog/2017/12/26/tutorial-5/](https://ml.berkeley.edu/blog/2017/12/26/tutorial-5/)
2. 随机森林 python 教程。克里斯阿尔邦。 [https://chrisalbon.com/machine_learning/trees_and_forests/random_forest_classifier_example/](https://chrisalbon.com/machine_learning/trees_and_forests/random_forest_classifier_example/)
3. 关于凸函数的精美 PDF 演示,它们如何用于机器学习,以及平滑度,可微性和连续性之间的差异。由弗朗西斯巴赫。最后还有大约 6 页有用的参考文献,读者可能会觉得有用。 [https://www.di.ens.fr/~fbach/gradsto_allerton.pdf](https://www.di.ens.fr/~fbach/gradsto_allerton.pdf)
4. 关于软决策树的文章:将神经网络提炼为软决策树。 Frosst 和 Hinton。 2017\. [https://cex.inf.unibz.it/resources/Frosst+Hinton-CExAIIA_2017.pdf](https://cex.inf.unibz.it/resources/Frosst+Hinton-CExAIIA_2017.pdf)
5. TensorFlow 实现了一个神经树。作者:Benoit Deschamps。 [https://github.com/benoitdescamps/Neural-Tree](https://github.com/benoitdescamps/Neural-Tree)
- TensorFlow 入门
- 介绍
- TensorFlow 如何工作
- 声明变量和张量
- 使用占位符和变量
- 使用矩阵
- 声明操作符
- 实现激活函数
- 使用数据源
- 其他资源
- TensorFlow 的方式
- 介绍
- 计算图中的操作
- 对嵌套操作分层
- 使用多个层
- 实现损失函数
- 实现反向传播
- 使用批量和随机训练
- 把所有东西结合在一起
- 评估模型
- 线性回归
- 介绍
- 使用矩阵逆方法
- 实现分解方法
- 学习 TensorFlow 线性回归方法
- 理解线性回归中的损失函数
- 实现 deming 回归
- 实现套索和岭回归
- 实现弹性网络回归
- 实现逻辑回归
- 支持向量机
- 介绍
- 使用线性 SVM
- 简化为线性回归
- 在 TensorFlow 中使用内核
- 实现非线性 SVM
- 实现多类 SVM
- 最近邻方法
- 介绍
- 使用最近邻
- 使用基于文本的距离
- 使用混合距离函数的计算
- 使用地址匹配的示例
- 使用最近邻进行图像识别
- 神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现操作门
- 使用门和激活函数
- 实现单层神经网络
- 实现不同的层
- 使用多层神经网络
- 改进线性模型的预测
- 学习玩井字棋
- 自然语言处理
- 介绍
- 使用词袋嵌入
- 实现 TF-IDF
- 使用 Skip-Gram 嵌入
- 使用 CBOW 嵌入
- 使用 word2vec 进行预测
- 使用 doc2vec 进行情绪分析
- 卷积神经网络
- 介绍
- 实现简单的 CNN
- 实现先进的 CNN
- 重新训练现有的 CNN 模型
- 应用 StyleNet 和 NeuralStyle 项目
- 实现 DeepDream
- 循环神经网络
- 介绍
- 为垃圾邮件预测实现 RNN
- 实现 LSTM 模型
- 堆叠多个 LSTM 层
- 创建序列到序列模型
- 训练 Siamese RNN 相似性度量
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 介绍
- 实现单元测试
- 使用多个执行程序
- 并行化 TensorFlow
- 将 TensorFlow 投入生产
- 生产环境 TensorFlow 的一个例子
- 使用 TensorFlow 服务
- 更多 TensorFlow
- 介绍
- 可视化 TensorBoard 中的图
- 使用遗传算法
- 使用 k 均值聚类
- 求解常微分方程组
- 使用随机森林
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras
