# 10.14 Android GPS初涉
## 本节引言:
说到GPS这个名词,相信大家都不陌生,GPS全球定位技术嘛,嗯,Android中定位的方式 一般有这四种:GPS定位,WIFI定准,基站定位,AGPS定位(基站+GPS);
本系列教程只讲解GPS定位的基本使用!GPS是通过与卫星交互来获取设备当前的经纬度,准确 度较高,但也有一些缺点,最大的缺点就是:**室内几乎无法使用**...需要收到4颗卫星或以上 信号才能保证GPS的准确定位!但是假如你是在室外,无网络的情况,GPS还是可以用的!
本节我们就来探讨下Android中的GPS的基本用法~
## 1.定位相关的一些API
### **1)LocationManager**
官方API文档:[LocationManager](http://androiddoc.qiniudn.com/reference/android/location/LocationManager.html)
这玩意是系统服务来的,不能直接new,需要:
```
LocationManager lm = (LocationManager)getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
```
另外用GPS定位别忘了加权限:
```
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION"/>
```
好的,获得了LocationManager对象后,我们可以调用下面这些常用的方法:
* **addGpsStatusListener**(GpsStatus.Listener listener):添加一个GPS状态监听器
* **addProximityAlert**(double latitude, double longitude, float radius, long expiration, PendingIntent intent): 添加一个临界警告
* **getAllProviders**():获取所有的LocationProvider列表
* **getBestProvider**(Criteria criteria, boolean enabledOnly):根据指定条件返回最优LocationProvider
* **getGpsStatus**(GpsStatus status):获取GPS状态
* **getLastKnownLocation**(String provider):根据LocationProvider获得最近一次已知的Location
* **getProvider**(String name):根据名称来获得LocationProvider
* **getProviders**(boolean enabledOnly):获取所有可用的LocationProvider
* **getProviders**(Criteria criteria, boolean enabledOnly):根据指定条件获取满足条件的所有LocationProvider
* **isProviderEnabled**(String provider):判断指定名称的LocationProvider是否可用
* **removeGpsStatusListener**(GpsStatus.Listener listener):删除GPS状态监听器
* **removeProximityAlert**(PendingIntent intent):删除一个临近警告
* **requestLocationUpdates**(long minTime, float minDistance, Criteria criteria, PendingIntent intent): 通过制定的LocationProvider周期性地获取定位信息,并通过Intent启动相应的组件
* **requestLocationUpdates**(String provider, long minTime, float minDistance, LocationListener listener): 通过制定的LocationProvider周期性地获取定位信息,并触发listener所对应的触发器
### **2)LocationProvider(定位提供者)**
官方API文档:[LocationProvider](http://androiddoc.qiniudn.com/reference/android/location/LocationProvider.html)
这比是GPS定位组件的抽象表示,调用下述方法可以获取该定位组件的相关信息!
常用的方法如下:
* **getAccuracy**():返回LocationProvider精度
* **getName**():返回LocationProvider名称
* **getPowerRequirement**():获取LocationProvider的电源需求
* **hasMonetaryCost**():返回该LocationProvider是收费还是免费的
* **meetsCriteria**(Criteria criteria):判断LocationProvider是否满足Criteria条件
* **requiresCell**():判断LocationProvider是否需要访问网络基站
* **requiresNetwork**():判断LocationProvider是否需要访问网络数据
* **requiresSatellite**():判断LocationProvider是否需要访问基于卫星的定位系统
* **supportsAltitude**():判断LocationProvider是否支持高度信息
* **supportsBearing**():判断LocationProvider是否支持方向信息
* **supportsSpeed**():判断是LocationProvider否支持速度信息
### **3)Location(位置信息)**
官方API文档:[Location](http://androiddoc.qiniudn.com/reference/android/location/Location.html)
位置信息的抽象类,我们可以调用下述方法获取相关的定位信息!
常用方法如下:
* float **getAccuracy**():获得定位信息的精度
* double **getAltitude**():获得定位信息的高度
* float **getBearing**():获得定位信息的方向
* double **getLatitude**():获得定位信息的纬度
* double **getLongitude**():获得定位信息的精度
* String **getProvider**():获得提供该定位信息的LocationProvider
* float **getSpeed**():获得定位信息的速度
* boolean **hasAccuracy**():判断该定位信息是否含有精度信息
### **4)Criteria(过滤条件)**
官方API文档:[Criteria](http://androiddoc.qiniudn.com/reference/android/location/Criteria.html)
获取LocationProvider时,可以设置过滤条件,就是通过这个类来设置相关条件的~
常用方法如下:
* **setAccuracy**(int accuracy):设置对的精度要求
* **setAltitudeRequired**(boolean altitudeRequired):设置是否要求LocationProvider能提供高度的信息
* **setBearingRequired**(boolean bearingRequired):设置是否要LocationProvider求能提供方向信息
* **setCostAllowed**(boolean costAllowed):设置是否要求LocationProvider能提供方向信息
* **setPowerRequirement**(int level):设置要求LocationProvider的耗电量
* **setSpeedRequired**(boolean speedRequired):设置是否要求LocationProvider能提供速度信息
## 2.获取LocationProvider的例子
**运行效果图**:

由图可以看到,当前可用的LocationProvider有三个,分别是:
* **passive**:被动提供,由其他程序提供
* **gps**:通过GPS获取定位信息
* **network**:通过网络获取定位信息
**实现代码**:
布局文件:**activity_main.xml**:
```
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_one"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="获得系统所有的LocationProvider" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_two"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="根据条件获取LocationProvider" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_three"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="获取指定的LocationProvider" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_result"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="#81BB4D"
android:padding="5dp"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
</LinearLayout>
```
MainActivity.java:
```
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
private Button btn_one;
private Button btn_two;
private Button btn_three;
private TextView tv_result;
private LocationManager lm;
private List<String> pNames = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存放LocationProvider名称的集合
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
lm = (LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
bindViews();
}
private void bindViews() {
btn_one = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_one);
btn_two = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_two);
btn_three = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_three);
tv_result = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_result);
btn_one.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_two.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_three.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_one:
pNames.clear();
pNames = lm.getAllProviders();
tv_result.setText(getProvider());
break;
case R.id.btn_two:
pNames.clear();
Criteria criteria = new Criteria();
criteria.setCostAllowed(false); //免费
criteria.setAltitudeRequired(true); //能够提供高度信息
criteria.setBearingRequired(true); //能够提供方向信息
pNames = lm.getProviders(criteria, true);
tv_result.setText(getProvider());
break;
case R.id.btn_three:
pNames.clear();
pNames.add(lm.getProvider(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER).getName()); //指定名称
tv_result.setText(getProvider());
break;
}
}
//遍历数组返回字符串的方法
private String getProvider(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (String s : pNames) {
sb.append(s + "\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
```
## 3.判断GPS是否打开以及打开GPS的两种方式
在我们使用GPS定位前的第一件事应该是去判断GPS是否已经打开或可用,没打开的话我们需要去 打开GPS才能完成定位!这里不考虑AGPS的情况~
### **1)判断GPS是否可用**
```
private boolean isGpsAble(LocationManager lm){
return lm.isProviderEnabled(android.location.LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER)?true:false;
}
```
### **2)检测到GPS未打开,打开GPS**
**方法一**:强制打开GPS,Android 5.0后无用....
```
//强制帮用户打开GPS 5.0以前可用
private void openGPS(Context context){
Intent gpsIntent = new Intent();
gpsIntent.setClassName("com.android.settings", "com.android.settings.widget.SettingsAppWidgetProvider");
gpsIntent.addCategory("android.intent.category.ALTERNATIVE");
gpsIntent.setData(Uri.parse("custom:3"));
try {
PendingIntent.getBroadcast(LocationActivity.this, 0, gpsIntent, 0).send();
} catch (PendingIntent.CanceledException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
```
**方法二**:打开GPS位置信息设置页面,让用户自行打开
```
//打开位置信息设置页面让用户自己设置
private void openGPS2(){
Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS);
startActivityForResult(intent,0);
}
```
## 4.动态获取位置信息
这个非常简单,调用requestLocationUpdates方法设置一个LocationListener定时检测位置而已!
示例代码如下:
布局:**activity_location.xml**:
```
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_show"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="5dp"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
</LinearLayout>
```
LocationActivity.java:
```
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/11/20 0020.
*/
public class LocationActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private LocationManager lm;
private TextView tv_show;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_location);
tv_show = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_show);
lm = (LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
if (!isGpsAble(lm)) {
Toast.makeText(LocationActivity.this, "请打开GPS~", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
openGPS2();
}
//从GPS获取最近的定位信息
Location lc = lm.getLastKnownLocation(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER);
updateShow(lc);
//设置间隔两秒获得一次GPS定位信息
lm.requestLocationUpdates(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER, 2000, 8, new LocationListener() {
@Override
public void onLocationChanged(Location location) {
// 当GPS定位信息发生改变时,更新定位
updateShow(location);
}
@Override
public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras) {
}
@Override
public void onProviderEnabled(String provider) {
// 当GPS LocationProvider可用时,更新定位
updateShow(lm.getLastKnownLocation(provider));
}
@Override
public void onProviderDisabled(String provider) {
updateShow(null);
}
});
}
//定义一个更新显示的方法
private void updateShow(Location location) {
if (location != null) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("当前的位置信息:\n");
sb.append("精度:" + location.getLongitude() + "\n");
sb.append("纬度:" + location.getLatitude() + "\n");
sb.append("高度:" + location.getAltitude() + "\n");
sb.append("速度:" + location.getSpeed() + "\n");
sb.append("方向:" + location.getBearing() + "\n");
sb.append("定位精度:" + location.getAccuracy() + "\n");
tv_show.setText(sb.toString());
} else tv_show.setText("");
}
private boolean isGpsAble(LocationManager lm) {
return lm.isProviderEnabled(android.location.LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER) ? true : false;
}
//打开设置页面让用户自己设置
private void openGPS2() {
Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS);
startActivityForResult(intent, 0);
}
}
```
好的,非常简单,因为gps需要在室外才能用,于是趁着这个机会小跑出去便利店买了杯奶茶, 顺道截下图~
 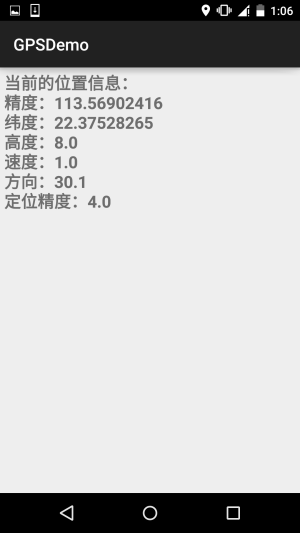 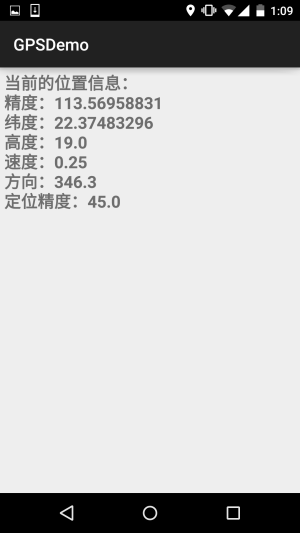
**requestLocationUpdates** (String provider, long minTime, float minDistance, LocationListener listener)
当时间超过minTime(单位:毫秒),或者位置移动超过minDistance(单位:米),就会调用listener中的方法更新GPS信息,建议这个minTime不小于60000,即1分钟,这样会更加高效而且省电,加入你需要尽可能 实时地更新GPS,可以将minTime和minDistance设置为0
对了,别忘了,你还需要一枚权限:
```
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" />
```
## 5.临近警告(地理围栏)
嗯,就是固定一个点,当手机与该点的距离少于指定范围时,可以触发对应的处理! 有点像地理围栏...我们可以调用LocationManager的addProximityAlert方法添加临近警告! 完整方法如下:
**addProximityAlert**(double latitude,double longitude,float radius,long expiration,PendingIntent intent)
属性说明:
* **latitude**:指定固定点的经度
* **longitude**:指定固定点的纬度
* **radius**:指定半径长度
* **expiration**:指定经过多少毫秒后该临近警告就会过期失效,-1表示永不过期
* **intent**:该参数指定临近该固定点时触发该intent对应的组件
**示例代码如下**:
**ProximityActivity.java**:
```
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/11/21 0021.
*/
public class ProximityActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private LocationManager lm;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_proximity);
lm = (LocationManager) getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
//定义固定点的经纬度
double longitude = 113.56843;
double latitude = 22.374937;
float radius = 10; //定义半径,米
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ProximityReceiver.class);
PendingIntent pi = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(this, -1, intent, 0);
lm.addProximityAlert(latitude, longitude, radius, -1, pi);
}
}
```
还需要注册一个广播接收者:**ProximityReceiver.java**:
```
/**
* Created by Jay on 2015/11/21 0021.
*/
public class ProximityReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
boolean isEnter = intent.getBooleanExtra( LocationManager.KEY_PROXIMITY_ENTERING, false);
if(isEnter) Toast.makeText(context, "你已到达南软B1栋附近", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
else Toast.makeText(context, "你已离开南软B1栋附近", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
```
别忘了注册:
```
<receiver android:name=".ProximityReceiver"/>
```
**运行效果图**:
PS:好吧,设置了10m,结果我从B1走到D1那边,不止10m了吧...还刚好下雨
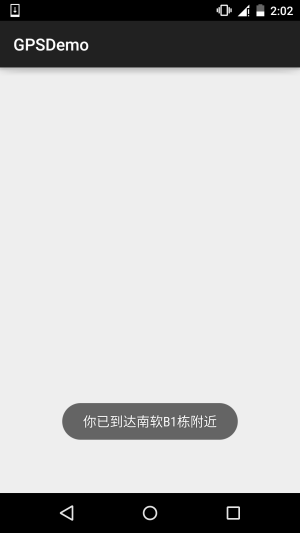 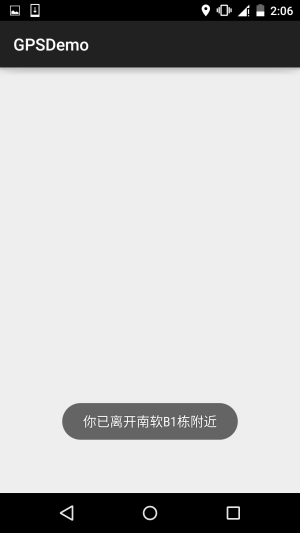
## 6.本节示例代码下载
[GPSDemo.zip](http://static.runoob.com/download/GPSDemo.zip)
## 本节小结:
> 好的,本节给大家介绍了Android中GPS定位的一些基本用法,非常简单,内容部分参考的 李刚老师的《Android疯狂讲义》,只是对例子进行了一些修改以及进行了可用性的测试! 本节就到这里,谢谢~
- 1.0 Android基础入门教程
- 1.0.1 2015年最新Android基础入门教程目录
- 1.1 背景相关与系统架构分析
- 1.2 开发环境搭建
- 1.2.1 使用Eclipse + ADT + SDK开发Android APP
- 1.2.2 使用Android Studio开发Android APP
- 1.3 SDK更新不了问题解决
- 1.4 Genymotion模拟器安装
- 1.5.1 Git使用教程之本地仓库的基本操作
- 1.5.2 Git之使用GitHub搭建远程仓库
- 1.6 .9(九妹)图片怎么玩
- 1.7 界面原型设计
- 1.8 工程相关解析(各种文件,资源访问)
- 1.9 Android程序签名打包
- 1.11 反编译APK获取代码&资源
- 2.1 View与ViewGroup的概念
- 2.2.1 LinearLayout(线性布局)
- 2.2.2 RelativeLayout(相对布局)
- 2.2.3 TableLayout(表格布局)
- 2.2.4 FrameLayout(帧布局)
- 2.2.5 GridLayout(网格布局)
- 2.2.6 AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)
- 2.3.1 TextView(文本框)详解
- 2.3.2 EditText(输入框)详解
- 2.3.3 Button(按钮)与ImageButton(图像按钮)
- 2.3.4 ImageView(图像视图)
- 2.3.5.RadioButton(单选按钮)&Checkbox(复选框)
- 2.3.6 开关按钮ToggleButton和开关Switch
- 2.3.7 ProgressBar(进度条)
- 2.3.8 SeekBar(拖动条)
- 2.3.9 RatingBar(星级评分条)
- 2.4.1 ScrollView(滚动条)
- 2.4.2 Date & Time组件(上)
- 2.4.3 Date & Time组件(下)
- 2.4.4 Adapter基础讲解
- 2.4.5 ListView简单实用
- 2.4.6 BaseAdapter优化
- 2.4.7ListView的焦点问题
- 2.4.8 ListView之checkbox错位问题解决
- 2.4.9 ListView的数据更新问题
- 2.5.0 构建一个可复用的自定义BaseAdapter
- 2.5.1 ListView Item多布局的实现
- 2.5.2 GridView(网格视图)的基本使用
- 2.5.3 Spinner(列表选项框)的基本使用
- 2.5.4 AutoCompleteTextView(自动完成文本框)的基本使用
- 2.5.5 ExpandableListView(可折叠列表)的基本使用
- 2.5.6 ViewFlipper(翻转视图)的基本使用
- 2.5.7 Toast(吐司)的基本使用
- 2.5.8 Notification(状态栏通知)详解
- 2.5.9 AlertDialog(对话框)详解
- 2.6.0 其他几种常用对话框基本使用
- 2.6.1 PopupWindow(悬浮框)的基本使用
- 2.6.2 菜单(Menu)
- 2.6.3 ViewPager的简单使用
- 2.6.4 DrawerLayout(官方侧滑菜单)的简单使用
- 3.1.1 基于监听的事件处理机制
- 3.2 基于回调的事件处理机制
- 3.3 Handler消息传递机制浅析
- 3.4 TouchListener PK OnTouchEvent + 多点触碰
- 3.5 监听EditText的内容变化
- 3.6 响应系统设置的事件(Configuration类)
- 3.7 AnsyncTask异步任务
- 3.8 Gestures(手势)
- 4.1.1 Activity初学乍练
- 4.1.2 Activity初窥门径
- 4.1.3 Activity登堂入室
- 4.2.1 Service初涉
- 4.2.2 Service进阶
- 4.2.3 Service精通
- 4.3.1 BroadcastReceiver牛刀小试
- 4.3.2 BroadcastReceiver庖丁解牛
- 4.4.2 ContentProvider再探——Document Provider
- 4.5.1 Intent的基本使用
- 4.5.2 Intent之复杂数据的传递
- 5.1 Fragment基本概述
- 5.2.1 Fragment实例精讲——底部导航栏的实现(方法1)
- 5.2.2 Fragment实例精讲——底部导航栏的实现(方法2)
- 5.2.3 Fragment实例精讲——底部导航栏的实现(方法3)
- 5.2.4 Fragment实例精讲——底部导航栏+ViewPager滑动切换页面
- 5.2.5 Fragment实例精讲——新闻(购物)类App列表Fragment的简单实现
- 6.1 数据存储与访问之——文件存储读写
- 6.2 数据存储与访问之——SharedPreferences保存用户偏好参数
- 6.3.1 数据存储与访问之——初见SQLite数据库
- 6.3.2 数据存储与访问之——又见SQLite数据库
- 7.1.1 Android网络编程要学的东西与Http协议学习
- 7.1.2 Android Http请求头与响应头的学习
- 7.1.3 Android HTTP请求方式:HttpURLConnection
- 7.1.4 Android HTTP请求方式:HttpClient
- 7.2.1 Android XML数据解析
- 7.2.2 Android JSON数据解析
- 7.3.1 Android 文件上传
- 7.3.2 Android 文件下载(1)
- 7.3.3 Android 文件下载(2)
- 7.4 Android 调用 WebService
- 7.5.1 WebView(网页视图)基本用法
- 7.5.2 WebView和JavaScrip交互基础
- 7.5.3 Android 4.4后WebView的一些注意事项
- 7.5.4 WebView文件下载
- 7.5.5 WebView缓存问题
- 7.5.6 WebView处理网页返回的错误码信息
- 7.6.1 Socket学习网络基础准备
- 7.6.2 基于TCP协议的Socket通信(1)
- 7.6.3 基于TCP协议的Socket通信(2)
- 7.6.4 基于UDP协议的Socket通信
- 8.1.1 Android中的13种Drawable小结 Part 1
- 8.1.2 Android中的13种Drawable小结 Part 2
- 8.1.3 Android中的13种Drawable小结 Part 3
- 8.2.1 Bitmap(位图)全解析 Part 1
- 8.2.2 Bitmap引起的OOM问题
- 8.3.1 三个绘图工具类详解
- 8.3.2 绘图类实战示例
- 8.3.3 Paint API之—— MaskFilter(面具)
- 8.3.4 Paint API之—— Xfermode与PorterDuff详解(一)
- 8.3.5 Paint API之—— Xfermode与PorterDuff详解(二)
- 8.3.6 Paint API之—— Xfermode与PorterDuff详解(三)
- 8.3.7 Paint API之—— Xfermode与PorterDuff详解(四)
- 8.3.8 Paint API之—— Xfermode与PorterDuff详解(五)
- 8.3.9 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(颜色过滤器)(1/3)
- 8.3.10 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(颜色过滤器)(2-3)
- 8.3.11 Paint API之—— ColorFilter(颜色过滤器)(3-3)
- 8.3.12 Paint API之—— PathEffect(路径效果)
- 8.3.13 Paint API之—— Shader(图像渲染)
- 8.3.14 Paint几个枚举/常量值以及ShadowLayer阴影效果
- 8.3.15 Paint API之——Typeface(字型)
- 8.3.16 Canvas API详解(Part 1)
- 8.3.17 Canvas API详解(Part 2)剪切方法合集
- 8.3.18 Canvas API详解(Part 3)Matrix和drawBitmapMash
- 8.4.1 Android动画合集之帧动画
- 8.4.2 Android动画合集之补间动画
- 8.4.3 Android动画合集之属性动画-初见
- 8.4.4 Android动画合集之属性动画-又见
- 9.1 使用SoundPool播放音效(Duang~)
- 9.2 MediaPlayer播放音频与视频
- 9.3 使用Camera拍照
- 9.4 使用MediaRecord录音
- 10.1 TelephonyManager(电话管理器)
- 10.2 SmsManager(短信管理器)
- 10.3 AudioManager(音频管理器)
- 10.4 Vibrator(振动器)
- 10.5 AlarmManager(闹钟服务)
- 10.6 PowerManager(电源服务)
- 10.7 WindowManager(窗口管理服务)
- 10.8 LayoutInflater(布局服务)
- 10.9 WallpaperManager(壁纸管理器)
- 10.10 传感器专题(1)——相关介绍
- 10.11 传感器专题(2)——方向传感器
- 10.12 传感器专题(3)——加速度/陀螺仪传感器
- 10.12 传感器专题(4)——其他传感器了解
- 10.14 Android GPS初涉
- 11.0《2015最新Android基础入门教程》完结散花~
