>[success] # 语法分析 ( parsing)
~~~
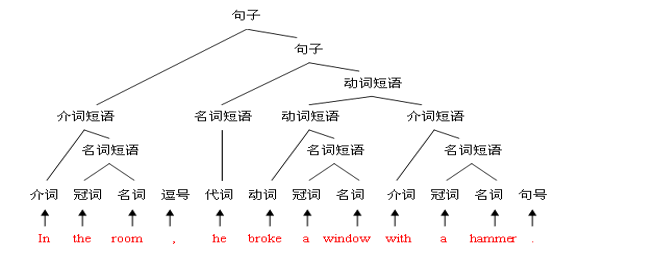
1.语法分析器(parser)从词法分析器输出的token序列中识别出各类短语,并构造语法
分析树(parse tree)
2.如图我们将我们的 tokens 经过语法分析器变成一棵ast 语法树
~~~
>[danger] ##### 图形理解
~~~
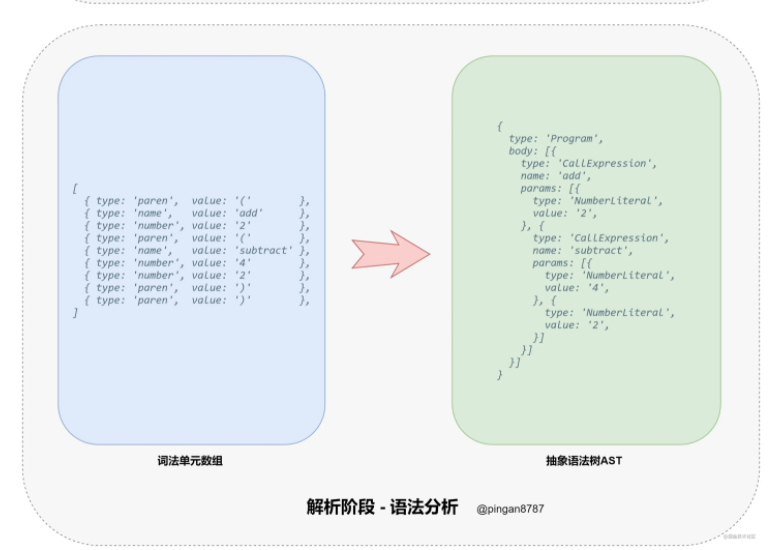
1.将各个token标记成对应 ast 树节点
[
{ type: 'paren', value: '(' },
{ type: 'name', value: 'add' },
{ type: 'number', value: '2' },
{ type: 'paren', value: '(' },
{ type: 'name', value: 'subtract' },
{ type: 'number', value: '4' },
{ type: 'number', value: '2' },
{ type: 'paren', value: ')' }, <<< Closing parenthesis
{ type: 'paren', value: ')' }, <<< Closing parenthesis
]
2.然后根据类型转变生成对应ast 树节点,举个例子type:number
转换对应ast 树节点,类型应为
'NumberLiteral'
{
type: 'NumberLiteral',
value: token.value,
}
想变成这样形式需要循环每一个token 词,代码对照情况
if (token.type === "number") {
current++;
return {
type: "NumberLiteral",
value: token.value,
};
}
当遇到括号时候其实就会形成递归 括号作为'CallExpression' 节点这个节点下又包括新的'NumericLiteral'
~~~
* 代码如下
~~~
// 语法分析器 参数:词法单元数组tokens
function parser(tokens) {
let current = 0; // 设置当前解析的词法单元的索引,作为游标
// 递归遍历(因为函数调用允许嵌套),将词法单元转成 LISP 的 AST 节点
function walk() {
// 获取当前索引下的词法单元 token
let token = tokens[current];
// 数值类型词法单元
if (token.type === 'number') {
current++; // 自增当前 current 值
// 生成一个 AST节点 'NumberLiteral',表示数值字面量
return {
type: 'NumberLiteral',
value: token.value,
};
}
// 字符串类型词法单元
if (token.type === 'string') {
current++;
// 生成一个 AST节点 'StringLiteral',表示字符串字面量
return {
type: 'StringLiteral',
value: token.value,
};
}
// 函数类型词法单元
if (token.type === 'paren' && token.value === '(') {
// 跳过左括号,获取下一个词法单元作为函数名
token = tokens[++current];
let node = {
type: 'CallExpression',
name: token.value,
params: []
};
// 再次自增 current 变量,获取参数词法单元
token = tokens[++current];
// 遍历每个词法单元,获取函数参数,直到出现右括号")"
while ((token.type !== 'paren') || (token.type === 'paren' && token.value !== ')')) {
node.params.push(walk());
token = tokens[current];
}
current++; // 跳过右括号
return node;
}
// 无法识别的字符,抛出错误提示
throw new TypeError(token.type);
}
// 初始化 AST 根节点
let ast = {
type: 'Program',
body: [],
};
// 循环填充 ast.body
while (current < tokens.length) {
ast.body.push(walk());
}
// 最后返回ast
return ast;
}
~~~
[图片来自](https://juejin.cn/post/6844904105937207304#heading-12)
>[danger] ##### 以babel 生成ast语法树 简化了展示
~~~
// const a = 1
const a = {
program: {
type: "Program",
body: [
{
type: "VariableDeclaration",
declarations: [
{
type: "VariableDeclarator",
id: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "a",
},
init: {
type: "NumericLiteral",
value: 1,
},
},
],
kind: "const",
},
],
},
};
// a=1
const b = {
program: {
type: "Program",
body: [
{
type: "ExpressionStatement",
expression: {
type: "AssignmentExpression",
operator: "=",
left: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "a",
},
right: {
type: "NumericLiteral",
value: 1,
},
},
},
],
},
};
/**
* function a(str){
const z = str
console.log(z)
}
*
*/
const c = {
program: {
type: "Program",
body: [
{
type: "FunctionDeclaration",
id: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "a",
},
generator: false,
async: false,
params: [
{
type: "Identifier",
name: "str",
},
],
body: {
type: "BlockStatement",
body: [
{
type: "VariableDeclaration",
declarations: [
{
type: "VariableDeclarator",
id: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "z",
},
init: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "str",
},
},
],
kind: "const",
},
{
type: "ExpressionStatement",
expression: {
type: "CallExpression",
callee: {
type: "MemberExpression",
object: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "console",
},
computed: false,
property: {
type: "Identifier",
name: "log",
},
},
arguments: [
{
type: "Identifier",
name: "z",
},
],
},
},
],
},
},
],
},
};
~~~
>[danger] ##### 代码
[直接用了 Babel是如何读懂JS代码的中的代码](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27289600)
~~~js
function parse (tokens) {
let i = -1; // 用于标识当前遍历位置
let curToken; // 用于记录当前符号
// 读取下一个语句
function nextStatement () {
// 暂存当前的i,如果无法找到符合条件的情况会需要回到这里
stash();
// 读取下一个符号
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'identifier' && curToken.value === 'if') {
// 解析 if 语句
const statement = {
type: 'IfStatement',
};
// if 后面必须紧跟着 (
nextToken();
if (curToken.type !== 'parens' || curToken.value !== '(') {
throw new Error('Expected ( after if');
}
// 后续的一个表达式是 if 的判断条件
statement.test = nextExpression();
// 判断条件之后必须是 )
nextToken();
if (curToken.type !== 'parens' || curToken.value !== ')') {
throw new Error('Expected ) after if test expression');
}
// 下一个语句是 if 成立时执行的语句
statement.consequent = nextStatement();
// 如果下一个符号是 else 就说明还存在 if 不成立时的逻辑
if (curToken === 'identifier' && curToken.value === 'else') {
statement.alternative = nextStatement();
} else {
statement.alternative = null;
}
commit();
return statement;
}
if (curToken.type === 'brace' && curToken.value === '{') {
// 以 { 开头表示是个代码块,我们暂不考虑JSON语法的存在
const statement = {
type: 'BlockStatement',
body: [],
};
while (i < tokens.length) {
// 检查下一个符号是不是 }
stash();
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'brace' && curToken.value === '}') {
// } 表示代码块的结尾
commit();
break;
}
// 还原到原来的位置,并将解析的下一个语句加到body
rewind();
statement.body.push(nextStatement());
}
// 代码块语句解析完毕,返回结果
commit();
return statement;
}
// 没有找到特别的语句标志,回到语句开头
rewind();
// 尝试解析单表达式语句
const statement = {
type: 'ExpressionStatement',
expression: nextExpression(),
};
if (statement.expression) {
nextToken();
if (curToken.type !== 'EOF' && curToken.type !== 'sep') {
throw new Error('Missing ; at end of expression');
}
return statement;
}
}
// 读取下一个表达式
function nextExpression () {
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'identifier') {
const identifier = {
type: 'Identifier',
name: curToken.value,
};
stash();
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'parens' && curToken.value === '(') {
// 如果一个标识符后面紧跟着 ( ,说明是个函数调用表达式
const expr = {
type: 'CallExpression',
caller: identifier,
arguments: [],
};
stash();
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'parens' && curToken.value === ')') {
// 如果下一个符合直接就是 ) ,说明没有参数
commit();
} else {
// 读取函数调用参数
rewind();
while (i < tokens.length) {
// 将下一个表达式加到arguments当中
expr.arguments.push(nextExpression());
nextToken();
// 遇到 ) 结束
if (curToken.type === 'parens' && curToken.value === ')') {
break;
}
// 参数间必须以 , 相间隔
if (curToken.type !== 'comma' && curToken.value !== ',') {
throw new Error('Expected , between arguments');
}
}
}
commit();
return expr;
}
rewind();
return identifier;
}
if (curToken.type === 'number' || curToken.type === 'string') {
// 数字或字符串,说明此处是个常量表达式
const literal = {
type: 'Literal',
value: eval(curToken.value),
};
// 但如果下一个符号是运算符,那么这就是个双元运算表达式
// 此处暂不考虑多个运算衔接,或者有变量存在
stash();
nextToken();
if (curToken.type === 'operator') {
commit();
return {
type: 'BinaryExpression',
left: literal,
right: nextExpression(),
};
}
rewind();
return literal;
}
if (curToken.type !== 'EOF') {
throw new Error('Unexpected token ' + curToken.value);
}
}
// 往后移动读取指针,自动跳过空白
function nextToken () {
do {
i++;
curToken = tokens[i] || { type: 'EOF' };
} while (curToken.type === 'whitespace');
}
// 位置暂存栈,用于支持很多时候需要返回到某个之前的位置
const stashStack = [];
function stash (cb) {
// 暂存当前位置
stashStack.push(i);
}
function rewind () {
// 解析失败,回到上一个暂存的位置
i = stashStack.pop();
curToken = tokens[i];
}
function commit () {
// 解析成功,不需要再返回
stashStack.pop();
}
const ast = {
type: 'Program',
body: [],
};
// 逐条解析顶层语句
while (i < tokens.length) {
const statement = nextStatement();
if (!statement) {
break;
}
ast.body.push(statement);
}
return ast;
}
const ast = parse([
{ type: "whitespace", value: "\n" },
{ type: "identifier", value: "if" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: " " },
{ type: "parens", value: "(" },
{ type: "number", value: "1" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: " " },
{ type: "operator", value: ">" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: " " },
{ type: "number", value: "0" },
{ type: "parens", value: ")" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: " " },
{ type: "brace", value: "{" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: "\n " },
{ type: "identifier", value: "alert" },
{ type: "parens", value: "(" },
{ type: "string", value: "\"if 1 > 0\"" },
{ type: "parens", value: ")" },
{ type: "sep", value: ";" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: "\n" },
{ type: "brace", value: "}" },
{ type: "whitespace", value: "\n" },
]);
~~~
最终得到结果:
~~~js
{
"type": "Program",
"body": [
{
"type": "IfStatement",
"test": {
"type": "BinaryExpression",
"left": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": 1
},
"right": {
"type": "Literal",
"value": 0
}
},
"consequent": {
"type": "BlockStatement",
"body": [
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"caller": {
"type": "Identifier",
"value": "alert"
},
"arguments": [
{
"type": "Literal",
"value": "if 1 > 0"
}
]
}
}
]
},
"alternative": null
}
]
}
~~~
>[info] ## 参考文章
[Building a Debugger: Code Analysis](https://www.nan.fyi/debugger)
https://github1s.com/narendrasss/compiler/blob/main/src/parser.ts#L61
[Babel是如何读懂JS代码的](https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27289600)
[语法上用解析树生根](https://medium.com/basecs/grammatically-rooting-oneself-with-parse-trees-ec9daeda7dad)
[# 【图文详解】200行JS代码,带你实现代码编译器(人人都能学会)](https://juejin.cn/post/6844904105937207304#heading-12)
https://github.com/YongzeYao/the-super-tiny-compiler-CN/blob/master/the-super-tiny-compiler.js
- 工程化 -- Node
- vscode -- 插件
- vscode -- 代码片段
- 前端学会调试
- 谷歌浏览器调试技巧
- 权限验证
- 包管理工具 -- npm
- 常见的 npm ci 指令
- npm -- npm install安装包
- npm -- package.json
- npm -- 查看包版本信息
- npm - package-lock.json
- npm -- node_modules 层级
- npm -- 依赖包规则
- npm -- install 安装流程
- npx
- npm -- 发布自己的包
- 包管理工具 -- pnpm
- 模拟数据 -- Mock
- 页面渲染
- 渲染分析
- core.js && babel
- core.js -- 到底是什么
- 编译器那些术语
- 词法解析 -- tokenize
- 语法解析 -- ast
- 遍历节点 -- traverser
- 转换阶段、生成阶段略
- babel
- babel -- 初步上手之了解
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置(preset-env)
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置@babel/helpers
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置@babel/runtime
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置@babel/plugin-transform-runtime
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置(babel-polyfills )(未来)
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置 polyfill-service
- babel -- 初步上手之各种配置(@babel/polyfill )(过去式)
- babel -- 总结
- 各种工具
- 前端 -- 工程化
- 了解 -- Yeoman
- 使用 -- Yeoman
- 了解 -- Plop
- node cli -- 开发自己的脚手架工具
- 自动化构建工具
- Gulp
- 模块化打包工具为什么出现
- 模块化打包工具(新) -- webpack
- 简单使用 -- webpack
- 了解配置 -- webpack.config.js
- webpack -- loader 浅解
- loader -- 配置css模块解析
- loader -- 图片和字体(4.x)
- loader -- 图片和字体(5.x)
- loader -- 图片优化loader
- loader -- 配置解析js/ts
- webpack -- plugins 浅解
- eslit
- plugins -- CleanWebpackPlugin(4.x)
- plugins -- CleanWebpackPlugin(5.x)
- plugin -- HtmlWebpackPlugin
- plugin -- DefinePlugin 注入全局成员
- webapck -- 模块解析配置
- webpack -- 文件指纹了解
- webpack -- 开发环境运行构建
- webpack -- 项目环境划分
- 模块化打包工具 -- webpack
- webpack -- 打包文件是个啥
- webpack -- 基础配置项用法
- webpack4.x系列学习
- webpack -- 常见loader加载器
- webpack -- 移动端px转rem处理
- 开发一个自己loader
- webpack -- plugin插件
- webpack -- 文件指纹
- webpack -- 压缩css和html构建
- webpack -- 清里构建包
- webpack -- 复制静态文件
- webpack -- 自定义插件
- wepack -- 关于静态资源内联
- webpack -- source map 对照包
- webpack -- 环境划分构建
- webpack -- 项目构建控制台输出
- webpack -- 项目分析
- webpack -- 编译提速优护体积
- 提速 -- 编译阶段
- webpack -- 项目优化
- webpack -- DefinePlugin 注入全局成员
- webpack -- 代码分割
- webpack -- 页面资源提取
- webpack -- import按需引入
- webpack -- 摇树
- webpack -- 多页面打包
- webpack -- eslint
- webpack -- srr打包后续看
- webpack -- 构建一个自己的配置后续看
- webpack -- 打包组件和基础库
- webpack -- 源码
- webpack -- 启动都做了什么
- webpack -- cli做了什么
- webpack - 5
- 模块化打包工具 -- Rollup
- 工程化搭建代码规范
- 规范化标准--Eslint
- eslint -- 扩展配置
- eslint -- 指令
- eslint -- vscode
- eslint -- 原理
- Prettier -- 格式化代码工具
- EditorConfig -- 编辑器编码风格
- 检查提交代码是否符合检查配置
- 整体流程总结
- 微前端
- single-spa
- 简单上手 -- single-spa
- 快速理解systemjs
- single-sap 不使用systemjs
- monorepo -- 工程
- Vue -- 响应式了解
- Vue2.x -- 源码分析
- 发布订阅和观察者模式
- 简单 -- 了解响应式模型(一)
- 简单 -- 了解响应式模型(二)
- 简单 --了解虚拟DOM(一)
- 简单 --了解虚拟DOM(二)
- 简单 --了解diff算法
- 简单 --了解nextick
- Snabbdom -- 理解虚拟dom和diff算法
- Snabbdom -- h函数
- Snabbdom - Vnode 函数
- Snabbdom -- init 函数
- Snabbdom -- patch 函数
- 手写 -- 虚拟dom渲染
- Vue -- minVue
- vue3.x -- 源码分析
- 分析 -- reactivity
- 好文
- grpc -- 浏览器使用gRPC
- grcp-web -- 案例
- 待续
