# Review Apps
> 原文:[https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/testing_guide/review_apps.html](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/testing_guide/review_apps.html)
* [How does it work?](#how-does-it-work)
* [CI/CD architecture diagram](#cicd-architecture-diagram)
* [Detailed explanation](#detailed-explanation)
* [Auto-stopping of Review Apps](#auto-stopping-of-review-apps)
* [QA runs](#qa-runs)
* [Performance Metrics](#performance-metrics)
* [Cluster configuration](#cluster-configuration)
* [Node pools](#node-pools)
* [Helm](#helm)
* [How to](#how-to)
* [Get access to the GCP Review Apps cluster](#get-access-to-the-gcp-review-apps-cluster)
* [Log into my Review App](#log-into-my-review-app)
* [Enable a feature flag for my Review App](#enable-a-feature-flag-for-my-review-app)
* [Find my Review App slug](#find-my-review-app-slug)
* [Run a Rails console](#run-a-rails-console)
* [Dig into a Pod’s logs](#dig-into-a-pods-logs)
* [Diagnosing unhealthy Review App releases](#diagnosing-unhealthy-review-app-releases)
* [Release failed with `ImagePullBackOff`](#release-failed-with-imagepullbackoff)
* [Node count is always increasing (i.e. never stabilizing or decreasing)](#node-count-is-always-increasing-ie-never-stabilizing-or-decreasing)
* [p99 CPU utilization is at 100% for most of the nodes and/or many components](#p99-cpu-utilization-is-at-100-for-most-of-the-nodes-andor-many-components)
* [The `logging/user/events/FailedMount` chart is going up](#the-loggingusereventsfailedmount-chart-is-going-up)
* [Using K9s](#using-k9s)
* [Troubleshoot a pending `dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns` Deployment](#troubleshoot-a-pending-dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns-deployment)
* [Finding the problem](#finding-the-problem)
* [Solving the problem](#solving-the-problem)
* [Mitigation steps taken to avoid this problem in the future](#mitigation-steps-taken-to-avoid-this-problem-in-the-future)
* [Frequently Asked Questions](#frequently-asked-questions)
* [Other resources](#other-resources)
* [Helpful command line tools](#helpful-command-line-tools)
# Review Apps[](#review-apps "Permalink")
Review Apps 由[管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/merge_requests/6665)自动部署.
## How does it work?[](#how-does-it-work "Permalink")
### CI/CD architecture diagram[](#cicd-architecture-diagram "Permalink")
图 TD A [" build-qa-image,编译生产资产
(仅适用于规范的默认参考)"]; B [review-build-cng]; C [review-deploy]; D [CNG-mirror]; E [review-qa-smoke]; A-> |一旦准备`阶段已完成| BB -.-> |触发 CNG 镜像管道并等待其完成| DD -.-> |轮询直到完成| BB-> |一旦完成`view-build-cng`工作完成| CC-> |完成"审查-部署"工作| E 子图" 1\. gitlab`prepare` stage"结束子图" 2\. gitlab`review-prepare`阶段" B 结束子图" 3\. gitlab`review` stage" C [" review-deploy
Helm 使用云部署 Review App
由 CNG 镜像管道构建的本机映像.
Cloud Native 映像已部署到" review-apps"
Kubernetes(GKE)集群,位于 GCP`gitlab-review-apps`项目中."]结束子图" 4\. gitlab`qa` stage" E [review-qa-smoke
gitlab-qa 对 Review App 运行冒烟套件.]结束子图" CNG 镜像管道" D>构建了 Cloud Native 图像]; 结束
### Detailed explanation[](#detailed-explanation "Permalink")
1. 在`prepare`阶段的每个[管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/pipelines/125315730)上,都会自动启动[`compile-production-assets`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/641770154)作业.
* 完成后, [`review-build-cng`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/467724808)作业开始,因为在后续步骤中触发的[`CNG-mirror`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror)管道依赖[`review-build-cng`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/467724808) .
2. 完成`compile-production-assets`后, [`review-build-cng`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/467724808)作业[将触发](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror/pipelines/44364657) [`CNG-mirror`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror)项目中[的管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror/pipelines/44364657) .
* 仅当您的 MR 包括[CI 或前端更改时](../pipelines.html#changes-patterns) , `review-build-cng`作业才会自动开始. 在其他情况下,该工作是手动的.
* [`CNG-mirror`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror/pipelines/44364657)管道基于[GitLab 管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/pipelines/125315730)的提交创建每个组件(例如`gitlab-rails-ee` , `gitlab-shell` , `gitaly`等)的 Docker 映像,并将它们存储在其[注册表中](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror/container_registry) .
* 我们使用[`CNG-mirror`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror)项目,以便`CNG` (Cloud Native GitLab)项目的注册表不会因大量临时 Docker 映像而过载.
* 请注意,官方的 CNG 图像是由`cloud-native-image`作业构建的,该作业仅针对标签运行,并自身触发[`CNG`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG)管道.
3. 完成`review-build-cng`后, [`review-deploy`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/467724810)作业使用[官方的 GitLab Helm 图表](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/charts/gitlab/)将 Review App 部署到 GCP 上的[`review-apps`](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/clusters/details/us-central1-b/review-apps?project=gitlab-review-apps) Kubernetes 集群.
* 可以在[`scripts/review_apps/review-apps.sh`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/scripts/review_apps/review-apps.sh)找到用于部署 Review App 的实际脚本.
* 这些脚本基本上是[我们的官方 Auto DevOps 脚本](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/lib/gitlab/ci/templates/Auto-DevOps.gitlab-ci.yml) ,其中默认的 CNG 映像会被构建并存储在[`CNG-mirror`项目注册表中](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/CNG-mirror/container_registry)的映像覆盖.
* 由于我们使用的[是官方的 GitLab Helm 图表](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/charts/gitlab/) ,这意味着您将为分支机构获得一个专用的环境,该环境非常接近生产环境.
4. 一旦[`review-deploy`](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/467724810)作业成功,您应该可以使用您的 Review App,这要归功于 MR 小部件与它的直接链接. 要登录 Review App,请参阅"登录我的 Review App?". 下面.
**补充笔记:**
* 如果`review-deploy`工作持续失败(请注意,我们已经试了两次),请在发布消息`#g_qe_engineering_productivity`通道和/或创建`~"Engineering Productivity"` `~"ep::review apps"` `~bug`的问题有链接到您的合并请求. 请注意,部署失败可能会揭示合并请求中引入的实际问题(即,这不一定是暂时性失败)!
* 如果`review-qa-smoke`作业仍然失败(请注意,我们已经重试了两次),请检查该作业的日志:您可能会发现合并请求中引入的实际问题. 您也可以下载工件,以查看发生故障时页面的屏幕截图. 如果您找不到失败的原因,或者看起来与更改无关,请在`#quality`频道中发布一条消息和/或创建`#quality`问题,并带有指向合并请求的链接.
* 手动`review-stop`可用于手动停止复查应用,一旦合并请求的分支在合并后被删除,GitLab 也将启动手动`review-stop` .
* 使用[GitLab 的 Kubernetes 集成](../../user/project/clusters/index.html)将 Kubernetes 集群连接到`gitlab`项目. 这基本上允许直接从合并请求窗口小部件链接到 Review App.
### Auto-stopping of Review Apps[](#auto-stopping-of-review-apps "Permalink")
借助[环境自动停止](../../ci/environments/index.html#environments-auto-stop)功能,Review Apps 在上次部署后 2 天会自动停止.
If you need your Review App to stay up for a longer time, you can [pin its environment](../../ci/environments/index.html#auto-stop-example) or retry the `review-deploy` job to update the “latest deployed at” time.
The `review-cleanup` job that automatically runs in scheduled pipelines (and is manual in merge request) stops stale Review Apps after 5 days, deletes their environment after 6 days, and cleans up any dangling Helm releases and Kubernetes resources after 7 days.
自动在计划的管道中运行的`review-gcp-cleanup`作业(在合并请求中手动执行)将删除所有未与 Kubernetes 资源一起删除的悬空 GCP 网络资源.
## QA runs[](#qa-runs "Permalink")
在`qa`阶段(在`review`阶段之后)的每个[管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/pipelines/125315730)上, `review-qa-smoke`作业都会自动启动,并运行 QA 烟雾套件.
您也可以手动启动`review-qa-all` :它运行完整的质量检查套件.
## Performance Metrics[](#performance-metrics "Permalink")
在每一个[管道](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/pipelines/125315730)在`qa`阶段, `review-performance`作业自动启动:这项工作确实使用基本的浏览器性能测试[Sitespeed.io 集装箱](../../user/project/merge_requests/browser_performance_testing.html) .
## Cluster configuration[](#cluster-configuration "Permalink")
### Node pools[](#node-pools "Permalink")
目前, `review-apps`集群使用以下节点池进行设置:
* 具有自动`e2-highcpu-16` (16 vCPU,16 GB 内存)可抢占节点
### Helm[](#helm "Permalink")
使用的 Helm 版本在[`registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-build-images:gitlab-helm3-kubectl1.14`映像中](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-build-images/-/blob/master/Dockerfile.gitlab-helm3-kubectl1.14#L7)定义,由`review-deploy`和`review-stop`作业使用.
## How to[](#how-to "Permalink")
### Get access to the GCP Review Apps cluster[](#get-access-to-the-gcp-review-apps-cluster "Permalink")
您需要[打开](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-com/access-requests/-/issues/new) `gcp-review-apps-sg` GCP 组[的访问请求(内部链接)](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-com/access-requests/-/issues/new) . 为了加入群组,您必须在访问请求中指定所需的 GCP 角色. 该角色将授予您特定的权限,以便与 Review App 容器进行交互.
Here are some permissions you may want to have, and the roles that grant them:
* `container.pods.getLogs` [检索 pod 日志所](#dig-into-a-pods-logs)必需. 由[查看者( `roles/viewer` )](https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/understanding-roles#kubernetes-engine-roles)授予.
* `container.pods.exec` [运行 Rails 控制台](#run-a-rails-console)所需. 由[Kubernetes Engine 开发人员( `roles/container.developer` )](https://cloud.google.com/iam/docs/understanding-roles#kubernetes-engine-roles)授予.
### Log into my Review App[](#log-into-my-review-app "Permalink")
默认用户名是`root` ,其密码可以在名为`gitlab-{ce,ee} Review App's root password`的 1Password 安全注释中找到.
### Enable a feature flag for my Review App[](#enable-a-feature-flag-for-my-review-app "Permalink")
1. 打开您的 Review App 并按照上述说明登录.
2. 创建一个个人访问令牌.
3. 使用[Feature 标志 API](../../api/features.html)启用[功能标志](../../api/features.html) .
### Find my Review App slug[](#find-my-review-app-slug "Permalink")
1. 打开`review-deploy`作业.
2. 查找" `Checking for previous deployment of review-*` .
3. 例如,对于`Checking for previous deployment of review-qa-raise-e-12chm0`在这种情况下,您的 Review App `Checking for previous deployment of review-qa-raise-e-12chm0`将为`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0` .
### Run a Rails console[](#run-a-rails-console "Permalink")
1. 确保首先[具有访问群集](#get-access-to-the-gcp-review-apps-cluster)和`container.pods.exec`权限的权限.
2. [根据您的 Review App](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/workload?project=gitlab-review-apps) `review-qa-raise-e-12chm0` [过滤工作量](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/workload?project=gitlab-review-apps) ,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0` .
3. 查找并打开`task-runner`部署,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-task-runner` .
4. 单击"托管窗格"部分中的 Pod,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-task-runner-d5455cc8-2lsvz` .
5. 点击`KUBECTL`下拉菜单,然后`Exec` - > `task-runner` .
6. 从默认命令`-it -- gitlab-rails console` `-c task-runner -- ls`替换为`-it -- gitlab-rails console` ,或者
* 运行`kubectl exec --namespace review-apps review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-task-runner-d5455cc8-2lsvz -it -- gitlab-rails console`和
* 用您的 Pod 名称替换`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-task-runner-d5455cc8-2lsvz` .
### Dig into a Pod’s logs[](#dig-into-a-pods-logs "Permalink")
1. 确保首先[有权访问集群](#get-access-to-the-gcp-review-apps-cluster)和`container.pods.getLogs`权限.
2. [根据您的 Review App](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/workload?project=gitlab-review-apps) `review-qa-raise-e-12chm0` [过滤工作量](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/workload?project=gitlab-review-apps) ,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0` .
3. 查找并打开`migrations`部署,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-migrations.1` .
4. 单击"托管窗格"部分中的 Pod,例如`review-qa-raise-e-12chm0-migrations.1-nqwtx` .
5. 单击`Container logs`链接.
## Diagnosing unhealthy Review App releases[](#diagnosing-unhealthy-review-app-releases "Permalink")
如果[Review App Stability](https://app.periscopedata.com/app/gitlab/496118/Engineering-Productivity-Sandbox?widget=6690556&udv=785399)下降,则可能表明[Review](https://app.periscopedata.com/app/gitlab/496118/Engineering-Productivity-Sandbox?widget=6690556&udv=785399) `review-apps-ce/ee`集群不健康. 领先的指标可能是导致重新启动的运行状况检查失败或 Review App 部署的多数失败.
[Review Apps Overview 仪表板可](https://console.cloud.google.com/monitoring/classic/dashboards/6798952013815386466?project=gitlab-review-apps&timeDomain=1d)帮助确定群集上的负载峰值,以及节点是否有问题或整个群集是否趋于不正常.
### Release failed with `ImagePullBackOff`[](#release-failed-with-imagepullbackoff "Permalink")
**潜在原因:**
如果看到`ImagePullBackoff`状态,请检查缺少的 Docker 映像.
**在哪里寻找进一步的调试:**
要检查是否已创建 Docker 映像,请运行以下 Docker 命令:
```
`DOCKER_CLI_EXPERIMENTAL=enabled docker manifest repository:tag`
```
此命令的输出指示 Docker 映像是否存在. 例如:
```
DOCKER_CLI_EXPERIMENTAL=enabled docker manifest inspect registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/build/cng-mirror/gitlab-rails-ee:39467-allow-a-release-s-associated-milestones-to-be-edited-thro
```
如果 Docker 映像不存在:
* 验证`helm upgrade --install`命令中的`image.repository`和`image.tag`选项是否与 CNG-mirror 管道使用的存储库名称匹配.
* 在`review-build-cng`作业中进一步查看相应的下游 CNG 镜像管道.
### Node count is always increasing (i.e. never stabilizing or decreasing)[](#node-count-is-always-increasing-ie-never-stabilizing-or-decreasing "Permalink")
**潜在原因:**
这可能表明`review-cleanup`作业未能清除过时的审查应用和 Kubernetes 资源.
**在哪里寻找进一步的调试:**
查看最新的`review-cleanup`作业日志,并确定是否存在任何意外故障.
### p99 CPU utilization is at 100% for most of the nodes and/or many components[](#p99-cpu-utilization-is-at-100-for-most-of-the-nodes-andor-many-components "Permalink")
**潜在原因:**
这可能表明 Helm 无法部署 Review Apps. 当 Helm 有很多`FAILED`版本发布时,CPU 利用率似乎正在增加,这可能是由于 Helm 或 Kubernetes 试图重新创建组件所致.
**在哪里寻找进一步的调试:**
查看最近的`review-deploy`作业日志.
**有用的命令:**
```
# Identify if node spikes are common or load on specific nodes which may get rebalanced by the Kubernetes scheduler
kubectl top nodes | sort --key 3 --numeric
# Identify pods under heavy CPU load
kubectl top pods | sort --key 2 --numeric
```
### The `logging/user/events/FailedMount` chart is going up[](#the-loggingusereventsfailedmount-chart-is-going-up "Permalink")
**潜在原因:**
这可能表明存在太多过时的机密和/或配置图.
**在哪里寻找进一步的调试:**
查看[配置列表](https://console.cloud.google.com/kubernetes/config?project=gitlab-review-apps)或`kubectl get secret,cm --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep 'review-'` `kubectl get secret,cm --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep 'review-'` .
怀疑任何超过 5 天的机密或配置图,应将其删除.
**有用的命令:**
```
# List secrets and config maps ordered by created date
kubectl get secret,cm --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep 'review-'
# Delete all secrets that are 5 to 9 days old
kubectl get secret --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep '^review-' | grep '[5-9]d$' | cut -d' ' -f1 | xargs kubectl delete secret
# Delete all secrets that are 10 to 99 days old
kubectl get secret --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep '^review-' | grep '[1-9][0-9]d$' | cut -d' ' -f1 | xargs kubectl delete secret
# Delete all config maps that are 5 to 9 days old
kubectl get cm --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep 'review-' | grep -v 'dns-gitlab-review-app' | grep '[5-9]d$' | cut -d' ' -f1 | xargs kubectl delete cm
# Delete all config maps that are 10 to 99 days old
kubectl get cm --sort-by='{.metadata.creationTimestamp}' | grep 'review-' | grep -v 'dns-gitlab-review-app' | grep '[1-9][0-9]d$' | cut -d' ' -f1 | xargs kubectl delete cm
```
### Using K9s[](#using-k9s "Permalink")
[K9s](https://github.com/derailed/k9s)是功能强大的命令行仪表板,可让您按标签过滤. 这可以帮助确定趋势超过[审阅应用程序资源请求的应用程序](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/scripts/review_apps/base-config.yaml) . Kubernetes 将根据资源请求将 Pod 调度到节点,并允许 CPU 使用量达到上限.
* 在 K9s 中,您可以通过输入`/`字符来排序或添加过滤器
* `-lrelease=<review-app-slug>` -过滤所有发布的 Pod. 这有助于确定单个部署中存在的问题
* `-lapp=<app>` -筛选特定应用程序的所有 pod. 这有助于确定应用程序的资源使用情况.
* 您可以滚动到 Kubernetes 资源并按`d` (描述), `s` (shell), `l` (日志)进行更深入的检查
[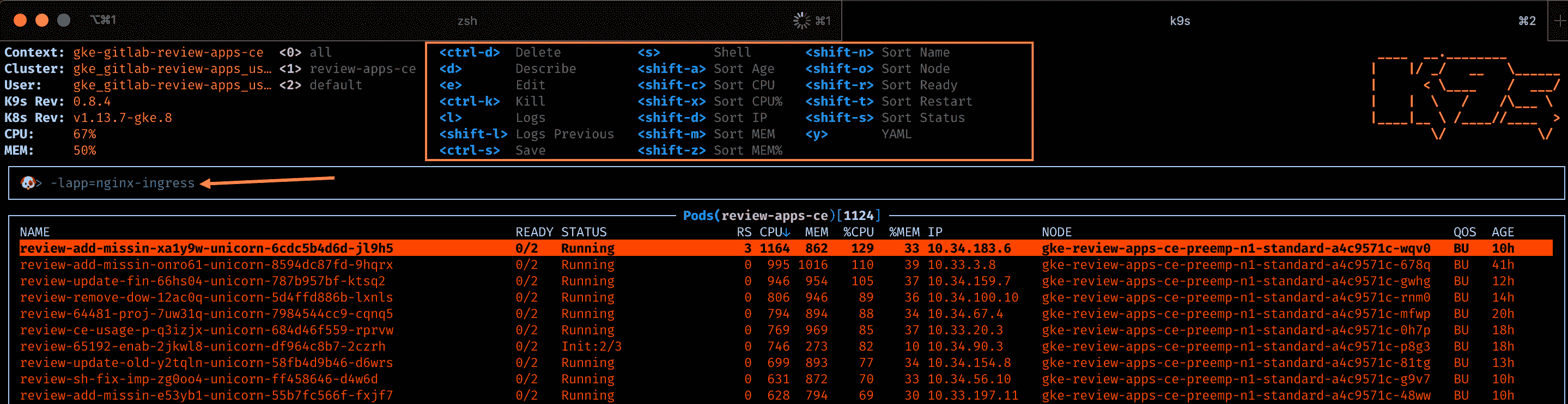](img/k9s.png)
### Troubleshoot a pending `dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns` Deployment[](#troubleshoot-a-pending-dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns-deployment "Permalink")
#### Finding the problem[](#finding-the-problem "Permalink")
[过去](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/-/issues/62834) ,发生了`dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns`部署处于挂起状态的情况,有效地阻止了所有 Review App 分配 DNS 记录,从而使它们无法通过域名访问.
反过来,这阻止了 Review App 的其他组件正常启动(例如`gitlab-runner` ).
经过一番挖掘后,我们发现在使用`systemd-mount`瞬时作用域(例如 pod)执行新安装时,新安装失败:
```
MountVolume.SetUp failed for volume "dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns-token-sj5jm" : mount failed: exit status 1
Mounting command: systemd-run
Mounting arguments: --description=Kubernetes transient mount for /var/lib/kubelet/pods/06add1c3-87b4-11e9-80a9-42010a800107/volumes/kubernetes.io~secret/dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns-token-sj5jm --scope -- mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /var/lib/kubelet/pods/06add1c3-87b4-11e9-80a9-42010a800107/volumes/kubernetes.io~secret/dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns-token-sj5jm
Output: Failed to start transient scope unit: Connection timed out
```
这可能是因为 GitLab 图表创建了 67 个资源,导致在基础 GCP 节点上创建了许多安装点.
在[根本的问题似乎是一个`systemd`错误](https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/57345#issuecomment-359068048)是固定在`systemd` `v237` . 不幸的是,我们的 GCP 节点当前正在使用`v232` .
记录下来,找出此问题的调试步骤是:
1. 将 kubectl 上下文切换到 review-apps-ce(我们建议使用[kubectx](https://github.com/ahmetb/kubectx/) )
2. `kubectl get pods | grep dns`
3. `kubectl describe pod <pod name>`并确认确切的错误消息
4. 在兔子洞中找到[相关的 Kubernetes 错误报告后](https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/57345) ,在网上搜索确切的错误消息
5. 通过 GCP 控制台通过 SSH 访问节点( **计算机引擎> VM 实例,**然后单击`dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns` pod 运行的节点的" SSH"按钮)
6. In the node: `systemctl --version` => `systemd 232`
7. 收集更多信息:
* `mount | grep kube | wc -l` `mount | grep kube | wc -l` =>例如 290
* `systemctl list-units --all | grep -i var-lib-kube | wc -l` `systemctl list-units --all | grep -i var-lib-kube | wc -l` =>例如 142
8. 检查多少个 Pod 处于不良状态:
* 获取运行给定节点的所有 Pod: `kubectl get pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME`
* 获取给定节点上的所有`Running` pods: `kubectl get pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME | grep Running` `kubectl get pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME | grep Running`
* 在给定节点上获取所有处于不良状态的 Pod: `kubectl get pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME | grep -v 'Running' | grep -v 'Completed'` `kubectl get pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME | grep -v 'Running' | grep -v 'Completed'`
#### Solving the problem[](#solving-the-problem "Permalink")
为了解决该问题,我们需要(强制)耗尽一些节点:
1. 在运行`dns-gitlab-review-app-external-dns` pod 的节点上尝试正常排水,以使 Kubernetes 自动将其移动到另一个节点: `kubectl drain NODE_NAME`
2. 如果那不起作用,您还可以通过删除所有吊舱来强制"排水"节点: `kubectl delete pods --field-selector=spec.nodeName=NODE_NAME`
3. 在节点中:
* 执行`systemctl daemon-reload`以删除无效/无效的单元
* 如果那不能解决问题,请执行硬重启: `sudo systemctl reboot`
4. 取消封锁所有封锁的节点: `kubectl uncordon NODE_NAME`封锁`kubectl uncordon NODE_NAME`
同时,由于大多数 Review App 处于损坏状态,因此我们将其删除以清理非`Running` Pod 列表. 以下是一个命令,用于根据其上次部署日期(当前日期为当时的 6 月 6 日)删除 Review Apps,
```
helm ls -d | grep "Jun 4" | cut -f1 | xargs helm delete --purge
```
#### Mitigation steps taken to avoid this problem in the future[](#mitigation-steps-taken-to-avoid-this-problem-in-the-future "Permalink")
我们用较小的计算机创建了一个新的节点池,这样一来,将来计算机就不太可能遇到"装载点过多"的问题.
## Frequently Asked Questions[](#frequently-asked-questions "Permalink")
**在每次测试运行时触发 CNG 映像生成是否过多? 这将创建数千个未使用的 Docker 映像.**
> 我们必须从某个地方开始,以后再改进. 另外,我们正在使用 CNG-mirror 项目来存储这些 Docker 映像,以便我们可以在某个时候清除注册表,并使用一个新的,空的注册表.
**我们如何确保它免受滥用? 应用程序向世界开放,因此我们需要找到一种方法将其限制为仅限我们自己.**
> This isn’t enabled for forks.
## Other resources[](#other-resources "Permalink")
* [Review Apps integration for CE/EE (presentation)](https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1QPLr6FO4LduROU8pQIPkX1yfGvD13GEJIBOenqoKxR8/edit?usp=sharing)
* [Stability issues](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/quality/team-tasks/-/issues/212)
### Helpful command line tools[](#helpful-command-line-tools "Permalink")
* [K9s-](https://github.com/derailed/k9s)启用跨 Pod 的 CLI 仪表板并启用按标签过滤
* [船尾](https://github.com/wercker/stern) -基于标签/字段选择器启用跨 Pod 日志拖尾
* * *
[Return to Testing documentation](index.html)
- GitLab Docs
- Installation
- Requirements
- GitLab cloud native Helm Chart
- Install GitLab with Docker
- Installation from source
- Install GitLab on Microsoft Azure
- Installing GitLab on Google Cloud Platform
- Installing GitLab on Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Analytics
- Code Review Analytics
- Productivity Analytics
- Value Stream Analytics
- Kubernetes clusters
- Adding and removing Kubernetes clusters
- Adding EKS clusters
- Adding GKE clusters
- Group-level Kubernetes clusters
- Instance-level Kubernetes clusters
- Canary Deployments
- Cluster Environments
- Deploy Boards
- GitLab Managed Apps
- Crossplane configuration
- Cluster management project (alpha)
- Kubernetes Logs
- Runbooks
- Serverless
- Deploying AWS Lambda function using GitLab CI/CD
- Securing your deployed applications
- Groups
- Contribution Analytics
- Custom group-level project templates
- Epics
- Manage epics
- Group Import/Export
- Insights
- Issues Analytics
- Iterations
- Public access
- SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- SCIM provisioning using SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- Subgroups
- Roadmap
- Projects
- GitLab Secure
- Security Configuration
- Container Scanning
- Dependency Scanning
- Dependency List
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Secret Detection
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- GitLab Security Dashboard
- Offline environments
- Standalone Vulnerability pages
- Security scanner integration
- Badges
- Bulk editing issues and merge requests at the project level
- Code Owners
- Compliance
- License Compliance
- Compliance Dashboard
- Create a project
- Description templates
- Deploy Keys
- Deploy Tokens
- File finder
- Project integrations
- Integrations
- Atlassian Bamboo CI Service
- Bugzilla Service
- Custom Issue Tracker service
- Discord Notifications service
- Enabling emails on push
- GitHub project integration
- Hangouts Chat service
- Atlassian HipChat
- Irker IRC Gateway
- GitLab Jira integration
- Mattermost Notifications Service
- Mattermost slash commands
- Microsoft Teams service
- Mock CI Service
- Prometheus integration
- Redmine Service
- Slack Notifications Service
- Slack slash commands
- GitLab Slack application
- Webhooks
- YouTrack Service
- Insights
- Issues
- Crosslinking Issues
- Design Management
- Confidential issues
- Due dates
- Issue Boards
- Issue Data and Actions
- Labels
- Managing issues
- Milestones
- Multiple Assignees for Issues
- Related issues
- Service Desk
- Sorting and ordering issue lists
- Issue weight
- Associate a Zoom meeting with an issue
- Merge requests
- Allow collaboration on merge requests across forks
- Merge Request Approvals
- Browser Performance Testing
- How to create a merge request
- Cherry-pick changes
- Code Quality
- Load Performance Testing
- Merge Request dependencies
- Fast-forward merge requests
- Merge when pipeline succeeds
- Merge request conflict resolution
- Reverting changes
- Reviewing and managing merge requests
- Squash and merge
- Merge requests versions
- Draft merge requests
- Members of a project
- Migrating projects to a GitLab instance
- Import your project from Bitbucket Cloud to GitLab
- Import your project from Bitbucket Server to GitLab
- Migrating from ClearCase
- Migrating from CVS
- Import your project from FogBugz to GitLab
- Gemnasium
- Import your project from GitHub to GitLab
- Project importing from GitLab.com to your private GitLab instance
- Import your project from Gitea to GitLab
- Import your Jira project issues to GitLab
- Migrating from Perforce Helix
- Import Phabricator tasks into a GitLab project
- Import multiple repositories by uploading a manifest file
- Import project from repo by URL
- Migrating from SVN to GitLab
- Migrating from TFVC to Git
- Push Options
- Releases
- Repository
- Branches
- Git Attributes
- File Locking
- Git file blame
- Git file history
- Repository mirroring
- Protected branches
- Protected tags
- Push Rules
- Reduce repository size
- Signing commits with GPG
- Syntax Highlighting
- GitLab Web Editor
- Web IDE
- Requirements Management
- Project settings
- Project import/export
- Project access tokens (Alpha)
- Share Projects with other Groups
- Snippets
- Static Site Editor
- Wiki
- Project operations
- Monitor metrics for your CI/CD environment
- Set up alerts for Prometheus metrics
- Embedding metric charts within GitLab-flavored Markdown
- Embedding Grafana charts
- Using the Metrics Dashboard
- Dashboard YAML properties
- Metrics dashboard settings
- Panel types for dashboards
- Using Variables
- Templating variables for metrics dashboards
- Prometheus Metrics library
- Monitoring AWS Resources
- Monitoring HAProxy
- Monitoring Kubernetes
- Monitoring NGINX
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller with VTS metrics
- Alert Management
- Error Tracking
- Tracing
- Incident Management
- GitLab Status Page
- Feature Flags
- GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD pipeline configuration reference
- GitLab CI/CD include examples
- Introduction to CI/CD with GitLab
- Getting started with GitLab CI/CD
- How to enable or disable GitLab CI/CD
- Using SSH keys with GitLab CI/CD
- Migrating from CircleCI
- Migrating from Jenkins
- Auto DevOps
- Getting started with Auto DevOps
- Requirements for Auto DevOps
- Customizing Auto DevOps
- Stages of Auto DevOps
- Upgrading PostgreSQL for Auto DevOps
- Cache dependencies in GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab ChatOps
- Cloud deployment
- Docker integration
- Building Docker images with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Docker images
- Building images with kaniko and GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD environment variables
- Predefined environment variables reference
- Where variables can be used
- Deprecated GitLab CI/CD variables
- Environments and deployments
- Protected Environments
- GitLab CI/CD Examples
- Test a Clojure application with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Dpl as deployment tool
- Testing a Phoenix application with GitLab CI/CD
- End-to-end testing with GitLab CI/CD and WebdriverIO
- DevOps and Game Dev with GitLab CI/CD
- Deploy a Spring Boot application to Cloud Foundry with GitLab CI/CD
- How to deploy Maven projects to Artifactory with GitLab CI/CD
- Testing PHP projects
- Running Composer and NPM scripts with deployment via SCP in GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy Laravel applications with GitLab CI/CD and Envoy
- Test and deploy a Python application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Ruby application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Scala application to Heroku
- GitLab CI/CD for external repositories
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a Bitbucket Cloud repository
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a GitHub repository
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages domain names, URLs, and baseurls
- Create a GitLab Pages website from scratch
- Custom domains and SSL/TLS Certificates
- GitLab Pages integration with Let's Encrypt
- GitLab Pages Access Control
- Exploring GitLab Pages
- Incremental Rollouts with GitLab CI/CD
- Interactive Web Terminals
- Optimizing GitLab for large repositories
- Metrics Reports
- CI/CD pipelines
- Pipeline Architecture
- Directed Acyclic Graph
- Multi-project pipelines
- Parent-child pipelines
- Pipelines for Merge Requests
- Pipelines for Merged Results
- Merge Trains
- Job artifacts
- Pipeline schedules
- Pipeline settings
- Triggering pipelines through the API
- Review Apps
- Configuring GitLab Runners
- GitLab CI services examples
- Using MySQL
- Using PostgreSQL
- Using Redis
- Troubleshooting CI/CD
- GitLab Package Registry
- GitLab Container Registry
- Dependency Proxy
- GitLab Composer Repository
- GitLab Conan Repository
- GitLab Maven Repository
- GitLab NPM Registry
- GitLab NuGet Repository
- GitLab PyPi Repository
- API Docs
- API resources
- .gitignore API
- GitLab CI YMLs API
- Group and project access requests API
- Appearance API
- Applications API
- Audit Events API
- Avatar API
- Award Emoji API
- Project badges API
- Group badges API
- Branches API
- Broadcast Messages API
- Project clusters API
- Group clusters API
- Instance clusters API
- Commits API
- Container Registry API
- Custom Attributes API
- Dashboard annotations API
- Dependencies API
- Deploy Keys API
- Deployments API
- Discussions API
- Dockerfiles API
- Environments API
- Epics API
- Events
- Feature Flags API
- Feature flag user lists API
- Freeze Periods API
- Geo Nodes API
- Group Activity Analytics API
- Groups API
- Import API
- Issue Boards API
- Group Issue Boards API
- Issues API
- Epic Issues API
- Issues Statistics API
- Jobs API
- Keys API
- Labels API
- Group Labels API
- License
- Licenses API
- Issue links API
- Epic Links API
- Managed Licenses API
- Markdown API
- Group and project members API
- Merge request approvals API
- Merge requests API
- Project milestones API
- Group milestones API
- Namespaces API
- Notes API
- Notification settings API
- Packages API
- Pages domains API
- Pipeline schedules API
- Pipeline triggers API
- Pipelines API
- Project Aliases API
- Project import/export API
- Project repository storage moves API
- Project statistics API
- Project templates API
- Projects API
- Protected branches API
- Protected tags API
- Releases API
- Release links API
- Repositories API
- Repository files API
- Repository submodules API
- Resource label events API
- Resource milestone events API
- Resource weight events API
- Runners API
- SCIM API
- Search API
- Services API
- Application settings API
- Sidekiq Metrics API
- Snippets API
- Project snippets
- Application statistics API
- Suggest Changes API
- System hooks API
- Tags API
- Todos API
- Users API
- Project-level Variables API
- Group-level Variables API
- Version API
- Vulnerabilities API
- Vulnerability Findings API
- Wikis API
- GraphQL API
- Getting started with GitLab GraphQL API
- GraphQL API Resources
- API V3 to API V4
- Validate the .gitlab-ci.yml (API)
- User Docs
- Abuse reports
- User account
- Active sessions
- Deleting a User account
- Permissions
- Personal access tokens
- Profile preferences
- Threads
- GitLab and SSH keys
- GitLab integrations
- Git
- GitLab.com settings
- Infrastructure as code with Terraform and GitLab
- GitLab keyboard shortcuts
- GitLab Markdown
- AsciiDoc
- GitLab Notification Emails
- GitLab Quick Actions
- Autocomplete characters
- Reserved project and group names
- Search through GitLab
- Advanced Global Search
- Advanced Syntax Search
- Time Tracking
- GitLab To-Do List
- Administrator Docs
- Reference architectures
- Reference architecture: up to 1,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 2,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 3,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 5,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 10,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 25,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 50,000 users
- Troubleshooting a reference architecture set up
- Working with the bundled Consul service
- Configuring PostgreSQL for scaling
- Configuring GitLab application (Rails)
- Load Balancer for multi-node GitLab
- Configuring a Monitoring node for Scaling and High Availability
- NFS
- Working with the bundled PgBouncer service
- Configuring Redis for scaling
- Configuring Sidekiq
- Admin Area settings
- Continuous Integration and Deployment Admin settings
- Custom instance-level project templates
- Diff limits administration
- Enable and disable GitLab features deployed behind feature flags
- Geo nodes Admin Area
- GitLab Pages administration
- Health Check
- Job logs
- Labels administration
- Log system
- PlantUML & GitLab
- Repository checks
- Repository storage paths
- Repository storage types
- Account and limit settings
- Service templates
- System hooks
- Changing your time zone
- Uploads administration
- Abuse reports
- Activating and deactivating users
- Audit Events
- Blocking and unblocking users
- Broadcast Messages
- Elasticsearch integration
- Gitaly
- Gitaly Cluster
- Gitaly reference
- Monitoring GitLab
- Monitoring GitLab with Prometheus
- Performance Bar
- Usage statistics
- Object Storage
- Performing Operations in GitLab
- Cleaning up stale Redis sessions
- Fast lookup of authorized SSH keys in the database
- Filesystem Performance Benchmarking
- Moving repositories managed by GitLab
- Run multiple Sidekiq processes
- Sidekiq MemoryKiller
- Switching to Puma
- Understanding Unicorn and unicorn-worker-killer
- User lookup via OpenSSH's AuthorizedPrincipalsCommand
- GitLab Package Registry administration
- GitLab Container Registry administration
- Replication (Geo)
- Geo database replication
- Geo with external PostgreSQL instances
- Geo configuration
- Using a Geo Server
- Updating the Geo nodes
- Geo with Object storage
- Docker Registry for a secondary node
- Geo for multiple nodes
- Geo security review (Q&A)
- Location-aware Git remote URL with AWS Route53
- Tuning Geo
- Removing secondary Geo nodes
- Geo data types support
- Geo Frequently Asked Questions
- Geo Troubleshooting
- Geo validation tests
- Disaster Recovery (Geo)
- Disaster recovery for planned failover
- Bring a demoted primary node back online
- Automatic background verification
- Rake tasks
- Back up and restore GitLab
- Clean up
- Namespaces
- Maintenance Rake tasks
- Geo Rake Tasks
- GitHub import
- Import bare repositories
- Integrity check Rake task
- LDAP Rake tasks
- Listing repository directories
- Praefect Rake tasks
- Project import/export administration
- Repository storage Rake tasks
- Generate sample Prometheus data
- Uploads migrate Rake tasks
- Uploads sanitize Rake tasks
- User management
- Webhooks administration
- X.509 signatures
- Server hooks
- Static objects external storage
- Updating GitLab
- GitLab release and maintenance policy
- Security
- Password Storage
- Custom password length limits
- Restrict allowed SSH key technologies and minimum length
- Rate limits
- Webhooks and insecure internal web services
- Information exclusivity
- How to reset your root password
- How to unlock a locked user from the command line
- User File Uploads
- How we manage the TLS protocol CRIME vulnerability
- User email confirmation at sign-up
- Security of running jobs
- Proxying assets
- CI/CD Environment Variables
- Contributor and Development Docs
- Contribute to GitLab
- Community members & roles
- Implement design & UI elements
- Issues workflow
- Merge requests workflow
- Code Review Guidelines
- Style guides
- GitLab Architecture Overview
- CI/CD development documentation
- Database guides
- Database Review Guidelines
- Database Review Guidelines
- Migration Style Guide
- What requires downtime?
- Understanding EXPLAIN plans
- Rake tasks for developers
- Mass inserting Rails models
- GitLab Documentation guidelines
- Documentation Style Guide
- Documentation structure and template
- Documentation process
- Documentation site architecture
- Global navigation
- GitLab Docs monthly release process
- Telemetry Guide
- Usage Ping Guide
- Snowplow Guide
- Experiment Guide
- Feature flags in development of GitLab
- Feature flags process
- Developing with feature flags
- Feature flag controls
- Document features deployed behind feature flags
- Frontend Development Guidelines
- Accessibility & Readability
- Ajax
- Architecture
- Axios
- Design Patterns
- Frontend Development Process
- DropLab
- Emojis
- Filter
- Frontend FAQ
- GraphQL
- Icons and SVG Illustrations
- InputSetter
- Performance
- Principles
- Security
- Tooling
- Vuex
- Vue
- Geo (development)
- Geo self-service framework (alpha)
- Gitaly developers guide
- GitLab development style guides
- API style guide
- Go standards and style guidelines
- GraphQL API style guide
- Guidelines for shell commands in the GitLab codebase
- HTML style guide
- JavaScript style guide
- Migration Style Guide
- Newlines style guide
- Python Development Guidelines
- SCSS style guide
- Shell scripting standards and style guidelines
- Sidekiq debugging
- Sidekiq Style Guide
- SQL Query Guidelines
- Vue.js style guide
- Instrumenting Ruby code
- Testing standards and style guidelines
- Flaky tests
- Frontend testing standards and style guidelines
- GitLab tests in the Continuous Integration (CI) context
- Review Apps
- Smoke Tests
- Testing best practices
- Testing levels
- Testing Rails migrations at GitLab
- Testing Rake tasks
- End-to-end Testing
- Beginner's guide to writing end-to-end tests
- End-to-end testing Best Practices
- Dynamic Element Validation
- Flows in GitLab QA
- Page objects in GitLab QA
- Resource class in GitLab QA
- Style guide for writing end-to-end tests
- Testing with feature flags
- Translate GitLab to your language
- Internationalization for GitLab
- Translating GitLab
- Proofread Translations
- Merging translations from CrowdIn
- Value Stream Analytics development guide
- GitLab subscription
- Activate GitLab EE with a license
