# Beginner's guide to writing end-to-end tests
> 原文:[https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/testing_guide/end_to_end/beginners_guide.html](https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/development/testing_guide/end_to_end/beginners_guide.html)
* [Before you write a test](#before-you-write-a-test)
* [Determine if end-to-end tests are needed](#determine-if-end-to-end-tests-are-needed)
* [Identify the DevOps stage](#identify-the-devops-stage)
* [Create a skeleton test](#create-a-skeleton-test)
* [The outer `context` block](#the-outer-context-block)
* [The outer `RSpec.describe` block](#the-outer-rspecdescribe-block)
* [The `describe` block](#the-describe-block)
* [The `it` blocks (examples)](#the-it-blocks-examples)
* [Write the test](#write-the-test)
* [De-duplicate your code](#de-duplicate-your-code)
* [Test setup using resources and page objects](#test-setup-using-resources-and-page-objects)
* [Write the page object](#write-the-page-object)
* [Run the spec](#run-the-spec)
# Beginner’s guide to writing end-to-end tests[](#beginners-guide-to-writing-end-to-end-tests "Permalink")
在本教程中,您将学习如何为[GitLab 社区版](https://about.gitlab.com/install/?version=ce)和[GitLab 企业版](https://about.gitlab.com/install/)创建端到端( *e2e* )测试.
在本教程结束时,您将能够:
* 确定是否需要端到端测试.
* Understand the directory structure within `qa/`.
* 编写一个基本的端到端测试,以验证登录功能.
* 开发任何缺少的[页面对象](page_objects.html)库.
## Before you write a test[](#before-you-write-a-test "Permalink")
在编写测试之前,必须将您的[GitLab 开发套件(GDK)](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-development-kit)配置为运行规范. 端到端测试:
* 包含在`qa/`目录中.
* 应该是独立和[幂等的](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Idempotence#Computer_science_meaning) .
* 临时创建[资源](resources.html) (例如项目,问题,用户).
* Test the UI and API interfaces, and use the API to efficiently set up the UI tests.
**提示:**有关更多信息,请参阅[端到端测试最佳实践](best_practices.html) .
## Determine if end-to-end tests are needed[](#determine-if-end-to-end-tests-are-needed "Permalink")
在编写端到端测试之前,请为[GitLab 社区版](https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab-foss/coverage-ruby/#_AllFiles)和[GitLab 企业版](https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab/coverage-ruby/#_AllFiles)项目检查特定功能的代码覆盖率. 在单元,功能或集成级别上是否存在足够的测试范围? 如果回答*是肯定的* ,那么你*就*需要一个终端到终端的测试.
有关 GitLab 中每个级别的测试分布的信息,请参见[测试级别](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/blob/master/doc/development/testing_guide/testing_levels.md) .
* 请参阅[如何以正确的级别进行测试?](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/blob/master/doc/development/testing_guide/testing_levels.md#how-to-test-at-the-correct-level) " [测试级别"](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/blob/master/doc/development/testing_guide/testing_levels.md)文档的"部分".
* 查看功能更改的频率. 如果较低级别的测试中已经包含了稳定的特性,那么这些特性不会经常更改,那么端到端测试可能就不值得考虑.
* 最后,与参与实现功能和较低级别测试的开发人员讨论建议的测试.
**注意:**检查[GitLab 社区版](https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab-foss/coverage-ruby/#_AllFiles)和[GitLab 企业版](https://gitlab-org.gitlab.io/gitlab/coverage-ruby/#_AllFiles)覆盖率项目,以检查是否为此功能编写了以前的测试. 为了分析代码覆盖率,您必须了解哪些应用程序文件实现了特定功能.**注意:**在本教程中,我们将编写一个登录端到端测试,即使它已经被较低级别的测试所覆盖,因为这是大多数端到端流的第一步,并且最容易理解.
## Identify the DevOps stage[](#identify-the-devops-stage "Permalink")
GitLab QA 端到端测试是由[DevOps 生命周期](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/tree/master/qa/qa/specs/features/browser_ui)的不同[阶段](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/tree/master/qa/qa/specs/features/browser_ui)组织的. 确定应按[阶段](https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/product/product-categories/#devops-stages)放置测试的位置,确定该测试属于哪个功能,然后将其放置在该阶段下的子目录中.
[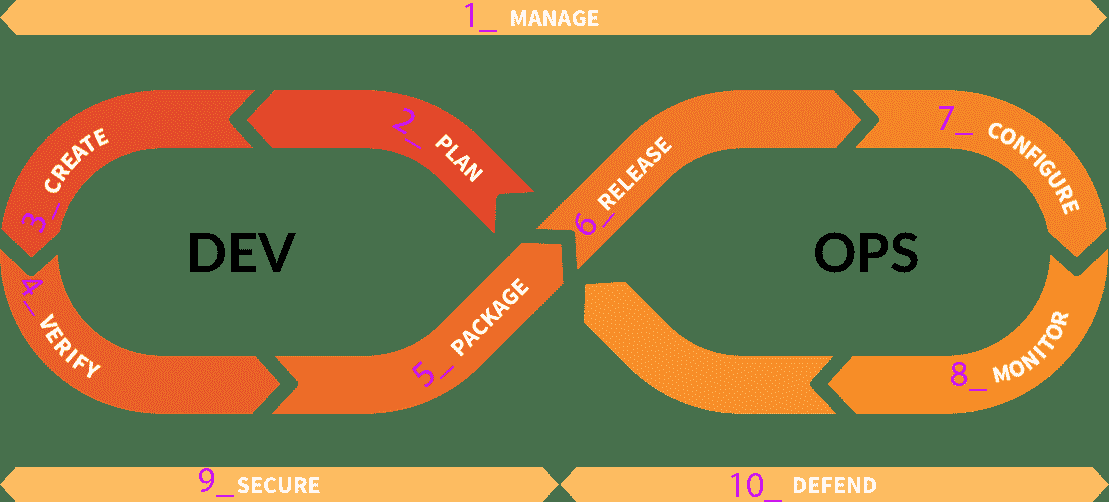](img/gl-devops-lifecycle-by-stage-numbers_V12_10.png)
**注意:**如果该测试仅是企业版,则将在`features/ee`目录中创建该测试,但遵循相同的 DevOps 生命周期格式.
## Create a skeleton test[](#create-a-skeleton-test "Permalink")
在本教程的第一部分中,我们将测试由 Manage 阶段拥有的登录名. 在`qa/specs/features/browser_ui/1_manage/login` ,创建文件`basic_login_spec.rb` .
### The outer `context` block[](#the-outer-context-block "Permalink")
参见[`RSpec.describe`外部块](#the-outer-rspecdescribe-block)
**弃用声明:**遵循 RSpec 4.0 规范在`13.2`中[弃用](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/quality/team-tasks/-/issues/550)了外部`context` . 请改用`RSpec.describe` .
### The outer `RSpec.describe` block[](#the-outer-rspecdescribe-block "Permalink")
规格具有外部`RSpec.describe`指示 DevOps 阶段.
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
end
end
```
### The `describe` block[](#the-describe-block "Permalink")
在我们的外部`RSpec.describe`内部,描述要测试的功能. 在这种情况下,请`Login` .
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
describe 'Login' do
end
end
end
```
### The `it` blocks (examples)[](#the-it-blocks-examples "Permalink")
每个测试套件包含至少一个`it`阻断(实施例). 一个好方法,开始写终端到终端的测试是编写测试用例描述为`it`块:
```
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
describe 'Login' do
it 'can login' do
end
it 'can logout' do
end
end
end
end
```
## Write the test[](#write-the-test "Permalink")
一个重要的问题是"我们要测试什么?" 更重要的是,"我们如何测试?"
首先登录.
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
describe 'Login' do
it 'can login' do
Flow::Login.sign_in
end
it 'can logout' do
Flow::Login.sign_in
end
end
end
end
```
[运行规范后](#run-the-spec) ,我们的测试应登录并结束; 那么我们应该回答"我们要测试什么?"这个问题.
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
describe 'Login' do
it 'can login' do
Flow::Login.sign_in
Page::Main::Menu.perform do |menu|
expect(menu).to be_signed_in
end
end
it 'can logout' do
Flow::Login.sign_in
Page::Main::Menu.perform do |menu|
menu.sign_out
expect(menu).not_to be_signed_in
end
end
end
end
end
```
**我们要测试什么?**
1. 我们可以登录吗?
2. 我们可以注销吗?
**我们如何测试?**
1. 检查用户头像是否出现在顶部导航中.
2. 检查用户头像*是否未*出现在顶部导航中.
**注意:**在幕后, `be_signed_in`是一个[谓词匹配器](https://relishapp.com/rspec/rspec-expectations/v/3-8/docs/built-in-matchers/predicate-matchers) ,可[实现对用户头像的检查](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/qa/qa/page/main/menu.rb#L74) .
## De-duplicate your code[](#de-duplicate-your-code "Permalink")
将测试重构为使用`before`块进行测试设置,因为它复制了对`sign_in`的调用.
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Manage' do
describe 'Login' do
before do
Flow::Login.sign_in
end
it 'can login' do
Page::Main::Menu.perform do |menu|
expect(menu).to be_signed_in
end
end
it 'can logout' do
Page::Main::Menu.perform do |menu|
menu.sign_out
expect(menu).not_to be_signed_in
end
end
end
end
end
```
`before`块本质上是一个`before(:each)`并且在每个示例之前运行,确保我们现在在每个测试的开始处登录.
## Test setup using resources and page objects[](#test-setup-using-resources-and-page-objects "Permalink")
接下来,让我们测试登录以外的其他功能. 让我们测试"计划"阶段拥有的"问题",因此在`qa/specs/features/browser_ui/3_create/issues` [创建一个](#identify-the-devops-stage)名为`issues_spec.rb` .
```
# frozen_string_literal: true
module QA
RSpec.describe 'Plan' do
describe 'Issues' do
let(:issue) do
Resource::Issue.fabricate_via_api! do |issue|
issue.title = 'My issue'
issue.description = 'This is an issue specific to this test'
end
end
before do
Flow::Login.sign_in
issue.visit!
end
it 'can close an issue' do
Page::Project::Issue::Show.perform do |show|
show.click_close_issue_button
expect(show).to be_closed
end
end
end
end
end
```
请注意以下要点:
* 在我们的示例开始时,我们将在`page/issue/show.rb` [页面](page_objects.html) .
* 我们的测试仅在需要时制造需要的东西.
* 该问题是通过 API 伪造的,以节省时间.
* GitLab 更喜欢`let()`不是实例变量. 查看[最佳做法](../best_practices.html#let-variables) .
* `be_closed`尚未在`page/project/issue/show.rb`中实现,但将在下一步中实现.
该问题被伪装成[Resource](resources.html) ,它是您可以通过 UI 或 API 创建的 GitLab 实体. 其他示例包括:
* A [Merge Request](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/qa/qa/resource/merge_request.rb).
* A [User](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/qa/qa/resource/user.rb).
* A [Project](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/qa/qa/resource/project.rb).
* A [Group](https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/blob/master/qa/qa/resource/group.rb).
## Write the page object[](#write-the-page-object "Permalink")
[Page Object](page_objects.html)是我们套件中的一个类,代表 GitLab 中的一个页面. **登录**页面就是一个例子. 由于我们的" **问题显示"**页面的页面对象已经存在,请添加`closed?` 方法.
```
module Page::Project::Issue
class Show
view 'app/views/projects/issues/show.html.haml' do
element :closed_status_box
end
def closed?
has_element?(:closed_status_box)
end
end
end
```
接下来,在视图中定义元素`closed_status_box` ,以便页面对象可以看到它.
```
-#=> app/views/projects/issues/show.html.haml .issuable-status-box.status-box.status-box-issue-closed{ ..., data: { qa_selector: 'closed_status_box' } }
```
## Run the spec[](#run-the-spec "Permalink")
在运行规范之前,请确认:
* GDK 已安装.
* GDK 在本地 3000 端口上运行.
* 尚未应用其他[RSpec 元数据标签](rspec_metadata_tests.html) .
* 您的工作目录是 GDK GitLab 安装中的`qa/` .
要运行该规范,请运行以下命令:
```
bundle exec bin/qa Test::Instance::All http://localhost:3000 -- <test_file>
```
Where `<test_file>` is:
* 运行"登录"示例时,请输入`qa/specs/features/browser_ui/1_manage/login/login_spec.rb` .
* 运行"问题"示例时,请执行`qa/specs/features/browser_ui/2_plan/issues/issue_spec.rb` .
- GitLab Docs
- Installation
- Requirements
- GitLab cloud native Helm Chart
- Install GitLab with Docker
- Installation from source
- Install GitLab on Microsoft Azure
- Installing GitLab on Google Cloud Platform
- Installing GitLab on Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Analytics
- Code Review Analytics
- Productivity Analytics
- Value Stream Analytics
- Kubernetes clusters
- Adding and removing Kubernetes clusters
- Adding EKS clusters
- Adding GKE clusters
- Group-level Kubernetes clusters
- Instance-level Kubernetes clusters
- Canary Deployments
- Cluster Environments
- Deploy Boards
- GitLab Managed Apps
- Crossplane configuration
- Cluster management project (alpha)
- Kubernetes Logs
- Runbooks
- Serverless
- Deploying AWS Lambda function using GitLab CI/CD
- Securing your deployed applications
- Groups
- Contribution Analytics
- Custom group-level project templates
- Epics
- Manage epics
- Group Import/Export
- Insights
- Issues Analytics
- Iterations
- Public access
- SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- SCIM provisioning using SAML SSO for GitLab.com groups
- Subgroups
- Roadmap
- Projects
- GitLab Secure
- Security Configuration
- Container Scanning
- Dependency Scanning
- Dependency List
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
- Secret Detection
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- GitLab Security Dashboard
- Offline environments
- Standalone Vulnerability pages
- Security scanner integration
- Badges
- Bulk editing issues and merge requests at the project level
- Code Owners
- Compliance
- License Compliance
- Compliance Dashboard
- Create a project
- Description templates
- Deploy Keys
- Deploy Tokens
- File finder
- Project integrations
- Integrations
- Atlassian Bamboo CI Service
- Bugzilla Service
- Custom Issue Tracker service
- Discord Notifications service
- Enabling emails on push
- GitHub project integration
- Hangouts Chat service
- Atlassian HipChat
- Irker IRC Gateway
- GitLab Jira integration
- Mattermost Notifications Service
- Mattermost slash commands
- Microsoft Teams service
- Mock CI Service
- Prometheus integration
- Redmine Service
- Slack Notifications Service
- Slack slash commands
- GitLab Slack application
- Webhooks
- YouTrack Service
- Insights
- Issues
- Crosslinking Issues
- Design Management
- Confidential issues
- Due dates
- Issue Boards
- Issue Data and Actions
- Labels
- Managing issues
- Milestones
- Multiple Assignees for Issues
- Related issues
- Service Desk
- Sorting and ordering issue lists
- Issue weight
- Associate a Zoom meeting with an issue
- Merge requests
- Allow collaboration on merge requests across forks
- Merge Request Approvals
- Browser Performance Testing
- How to create a merge request
- Cherry-pick changes
- Code Quality
- Load Performance Testing
- Merge Request dependencies
- Fast-forward merge requests
- Merge when pipeline succeeds
- Merge request conflict resolution
- Reverting changes
- Reviewing and managing merge requests
- Squash and merge
- Merge requests versions
- Draft merge requests
- Members of a project
- Migrating projects to a GitLab instance
- Import your project from Bitbucket Cloud to GitLab
- Import your project from Bitbucket Server to GitLab
- Migrating from ClearCase
- Migrating from CVS
- Import your project from FogBugz to GitLab
- Gemnasium
- Import your project from GitHub to GitLab
- Project importing from GitLab.com to your private GitLab instance
- Import your project from Gitea to GitLab
- Import your Jira project issues to GitLab
- Migrating from Perforce Helix
- Import Phabricator tasks into a GitLab project
- Import multiple repositories by uploading a manifest file
- Import project from repo by URL
- Migrating from SVN to GitLab
- Migrating from TFVC to Git
- Push Options
- Releases
- Repository
- Branches
- Git Attributes
- File Locking
- Git file blame
- Git file history
- Repository mirroring
- Protected branches
- Protected tags
- Push Rules
- Reduce repository size
- Signing commits with GPG
- Syntax Highlighting
- GitLab Web Editor
- Web IDE
- Requirements Management
- Project settings
- Project import/export
- Project access tokens (Alpha)
- Share Projects with other Groups
- Snippets
- Static Site Editor
- Wiki
- Project operations
- Monitor metrics for your CI/CD environment
- Set up alerts for Prometheus metrics
- Embedding metric charts within GitLab-flavored Markdown
- Embedding Grafana charts
- Using the Metrics Dashboard
- Dashboard YAML properties
- Metrics dashboard settings
- Panel types for dashboards
- Using Variables
- Templating variables for metrics dashboards
- Prometheus Metrics library
- Monitoring AWS Resources
- Monitoring HAProxy
- Monitoring Kubernetes
- Monitoring NGINX
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller
- Monitoring NGINX Ingress Controller with VTS metrics
- Alert Management
- Error Tracking
- Tracing
- Incident Management
- GitLab Status Page
- Feature Flags
- GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD pipeline configuration reference
- GitLab CI/CD include examples
- Introduction to CI/CD with GitLab
- Getting started with GitLab CI/CD
- How to enable or disable GitLab CI/CD
- Using SSH keys with GitLab CI/CD
- Migrating from CircleCI
- Migrating from Jenkins
- Auto DevOps
- Getting started with Auto DevOps
- Requirements for Auto DevOps
- Customizing Auto DevOps
- Stages of Auto DevOps
- Upgrading PostgreSQL for Auto DevOps
- Cache dependencies in GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab ChatOps
- Cloud deployment
- Docker integration
- Building Docker images with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Docker images
- Building images with kaniko and GitLab CI/CD
- GitLab CI/CD environment variables
- Predefined environment variables reference
- Where variables can be used
- Deprecated GitLab CI/CD variables
- Environments and deployments
- Protected Environments
- GitLab CI/CD Examples
- Test a Clojure application with GitLab CI/CD
- Using Dpl as deployment tool
- Testing a Phoenix application with GitLab CI/CD
- End-to-end testing with GitLab CI/CD and WebdriverIO
- DevOps and Game Dev with GitLab CI/CD
- Deploy a Spring Boot application to Cloud Foundry with GitLab CI/CD
- How to deploy Maven projects to Artifactory with GitLab CI/CD
- Testing PHP projects
- Running Composer and NPM scripts with deployment via SCP in GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy Laravel applications with GitLab CI/CD and Envoy
- Test and deploy a Python application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Ruby application with GitLab CI/CD
- Test and deploy a Scala application to Heroku
- GitLab CI/CD for external repositories
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a Bitbucket Cloud repository
- Using GitLab CI/CD with a GitHub repository
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages
- GitLab Pages domain names, URLs, and baseurls
- Create a GitLab Pages website from scratch
- Custom domains and SSL/TLS Certificates
- GitLab Pages integration with Let's Encrypt
- GitLab Pages Access Control
- Exploring GitLab Pages
- Incremental Rollouts with GitLab CI/CD
- Interactive Web Terminals
- Optimizing GitLab for large repositories
- Metrics Reports
- CI/CD pipelines
- Pipeline Architecture
- Directed Acyclic Graph
- Multi-project pipelines
- Parent-child pipelines
- Pipelines for Merge Requests
- Pipelines for Merged Results
- Merge Trains
- Job artifacts
- Pipeline schedules
- Pipeline settings
- Triggering pipelines through the API
- Review Apps
- Configuring GitLab Runners
- GitLab CI services examples
- Using MySQL
- Using PostgreSQL
- Using Redis
- Troubleshooting CI/CD
- GitLab Package Registry
- GitLab Container Registry
- Dependency Proxy
- GitLab Composer Repository
- GitLab Conan Repository
- GitLab Maven Repository
- GitLab NPM Registry
- GitLab NuGet Repository
- GitLab PyPi Repository
- API Docs
- API resources
- .gitignore API
- GitLab CI YMLs API
- Group and project access requests API
- Appearance API
- Applications API
- Audit Events API
- Avatar API
- Award Emoji API
- Project badges API
- Group badges API
- Branches API
- Broadcast Messages API
- Project clusters API
- Group clusters API
- Instance clusters API
- Commits API
- Container Registry API
- Custom Attributes API
- Dashboard annotations API
- Dependencies API
- Deploy Keys API
- Deployments API
- Discussions API
- Dockerfiles API
- Environments API
- Epics API
- Events
- Feature Flags API
- Feature flag user lists API
- Freeze Periods API
- Geo Nodes API
- Group Activity Analytics API
- Groups API
- Import API
- Issue Boards API
- Group Issue Boards API
- Issues API
- Epic Issues API
- Issues Statistics API
- Jobs API
- Keys API
- Labels API
- Group Labels API
- License
- Licenses API
- Issue links API
- Epic Links API
- Managed Licenses API
- Markdown API
- Group and project members API
- Merge request approvals API
- Merge requests API
- Project milestones API
- Group milestones API
- Namespaces API
- Notes API
- Notification settings API
- Packages API
- Pages domains API
- Pipeline schedules API
- Pipeline triggers API
- Pipelines API
- Project Aliases API
- Project import/export API
- Project repository storage moves API
- Project statistics API
- Project templates API
- Projects API
- Protected branches API
- Protected tags API
- Releases API
- Release links API
- Repositories API
- Repository files API
- Repository submodules API
- Resource label events API
- Resource milestone events API
- Resource weight events API
- Runners API
- SCIM API
- Search API
- Services API
- Application settings API
- Sidekiq Metrics API
- Snippets API
- Project snippets
- Application statistics API
- Suggest Changes API
- System hooks API
- Tags API
- Todos API
- Users API
- Project-level Variables API
- Group-level Variables API
- Version API
- Vulnerabilities API
- Vulnerability Findings API
- Wikis API
- GraphQL API
- Getting started with GitLab GraphQL API
- GraphQL API Resources
- API V3 to API V4
- Validate the .gitlab-ci.yml (API)
- User Docs
- Abuse reports
- User account
- Active sessions
- Deleting a User account
- Permissions
- Personal access tokens
- Profile preferences
- Threads
- GitLab and SSH keys
- GitLab integrations
- Git
- GitLab.com settings
- Infrastructure as code with Terraform and GitLab
- GitLab keyboard shortcuts
- GitLab Markdown
- AsciiDoc
- GitLab Notification Emails
- GitLab Quick Actions
- Autocomplete characters
- Reserved project and group names
- Search through GitLab
- Advanced Global Search
- Advanced Syntax Search
- Time Tracking
- GitLab To-Do List
- Administrator Docs
- Reference architectures
- Reference architecture: up to 1,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 2,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 3,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 5,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 10,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 25,000 users
- Reference architecture: up to 50,000 users
- Troubleshooting a reference architecture set up
- Working with the bundled Consul service
- Configuring PostgreSQL for scaling
- Configuring GitLab application (Rails)
- Load Balancer for multi-node GitLab
- Configuring a Monitoring node for Scaling and High Availability
- NFS
- Working with the bundled PgBouncer service
- Configuring Redis for scaling
- Configuring Sidekiq
- Admin Area settings
- Continuous Integration and Deployment Admin settings
- Custom instance-level project templates
- Diff limits administration
- Enable and disable GitLab features deployed behind feature flags
- Geo nodes Admin Area
- GitLab Pages administration
- Health Check
- Job logs
- Labels administration
- Log system
- PlantUML & GitLab
- Repository checks
- Repository storage paths
- Repository storage types
- Account and limit settings
- Service templates
- System hooks
- Changing your time zone
- Uploads administration
- Abuse reports
- Activating and deactivating users
- Audit Events
- Blocking and unblocking users
- Broadcast Messages
- Elasticsearch integration
- Gitaly
- Gitaly Cluster
- Gitaly reference
- Monitoring GitLab
- Monitoring GitLab with Prometheus
- Performance Bar
- Usage statistics
- Object Storage
- Performing Operations in GitLab
- Cleaning up stale Redis sessions
- Fast lookup of authorized SSH keys in the database
- Filesystem Performance Benchmarking
- Moving repositories managed by GitLab
- Run multiple Sidekiq processes
- Sidekiq MemoryKiller
- Switching to Puma
- Understanding Unicorn and unicorn-worker-killer
- User lookup via OpenSSH's AuthorizedPrincipalsCommand
- GitLab Package Registry administration
- GitLab Container Registry administration
- Replication (Geo)
- Geo database replication
- Geo with external PostgreSQL instances
- Geo configuration
- Using a Geo Server
- Updating the Geo nodes
- Geo with Object storage
- Docker Registry for a secondary node
- Geo for multiple nodes
- Geo security review (Q&A)
- Location-aware Git remote URL with AWS Route53
- Tuning Geo
- Removing secondary Geo nodes
- Geo data types support
- Geo Frequently Asked Questions
- Geo Troubleshooting
- Geo validation tests
- Disaster Recovery (Geo)
- Disaster recovery for planned failover
- Bring a demoted primary node back online
- Automatic background verification
- Rake tasks
- Back up and restore GitLab
- Clean up
- Namespaces
- Maintenance Rake tasks
- Geo Rake Tasks
- GitHub import
- Import bare repositories
- Integrity check Rake task
- LDAP Rake tasks
- Listing repository directories
- Praefect Rake tasks
- Project import/export administration
- Repository storage Rake tasks
- Generate sample Prometheus data
- Uploads migrate Rake tasks
- Uploads sanitize Rake tasks
- User management
- Webhooks administration
- X.509 signatures
- Server hooks
- Static objects external storage
- Updating GitLab
- GitLab release and maintenance policy
- Security
- Password Storage
- Custom password length limits
- Restrict allowed SSH key technologies and minimum length
- Rate limits
- Webhooks and insecure internal web services
- Information exclusivity
- How to reset your root password
- How to unlock a locked user from the command line
- User File Uploads
- How we manage the TLS protocol CRIME vulnerability
- User email confirmation at sign-up
- Security of running jobs
- Proxying assets
- CI/CD Environment Variables
- Contributor and Development Docs
- Contribute to GitLab
- Community members & roles
- Implement design & UI elements
- Issues workflow
- Merge requests workflow
- Code Review Guidelines
- Style guides
- GitLab Architecture Overview
- CI/CD development documentation
- Database guides
- Database Review Guidelines
- Database Review Guidelines
- Migration Style Guide
- What requires downtime?
- Understanding EXPLAIN plans
- Rake tasks for developers
- Mass inserting Rails models
- GitLab Documentation guidelines
- Documentation Style Guide
- Documentation structure and template
- Documentation process
- Documentation site architecture
- Global navigation
- GitLab Docs monthly release process
- Telemetry Guide
- Usage Ping Guide
- Snowplow Guide
- Experiment Guide
- Feature flags in development of GitLab
- Feature flags process
- Developing with feature flags
- Feature flag controls
- Document features deployed behind feature flags
- Frontend Development Guidelines
- Accessibility & Readability
- Ajax
- Architecture
- Axios
- Design Patterns
- Frontend Development Process
- DropLab
- Emojis
- Filter
- Frontend FAQ
- GraphQL
- Icons and SVG Illustrations
- InputSetter
- Performance
- Principles
- Security
- Tooling
- Vuex
- Vue
- Geo (development)
- Geo self-service framework (alpha)
- Gitaly developers guide
- GitLab development style guides
- API style guide
- Go standards and style guidelines
- GraphQL API style guide
- Guidelines for shell commands in the GitLab codebase
- HTML style guide
- JavaScript style guide
- Migration Style Guide
- Newlines style guide
- Python Development Guidelines
- SCSS style guide
- Shell scripting standards and style guidelines
- Sidekiq debugging
- Sidekiq Style Guide
- SQL Query Guidelines
- Vue.js style guide
- Instrumenting Ruby code
- Testing standards and style guidelines
- Flaky tests
- Frontend testing standards and style guidelines
- GitLab tests in the Continuous Integration (CI) context
- Review Apps
- Smoke Tests
- Testing best practices
- Testing levels
- Testing Rails migrations at GitLab
- Testing Rake tasks
- End-to-end Testing
- Beginner's guide to writing end-to-end tests
- End-to-end testing Best Practices
- Dynamic Element Validation
- Flows in GitLab QA
- Page objects in GitLab QA
- Resource class in GitLab QA
- Style guide for writing end-to-end tests
- Testing with feature flags
- Translate GitLab to your language
- Internationalization for GitLab
- Translating GitLab
- Proofread Translations
- Merging translations from CrowdIn
- Value Stream Analytics development guide
- GitLab subscription
- Activate GitLab EE with a license
