# C# | 数组
> 原文: [https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-sharp-arrays/](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/c-sharp-arrays/)
数组是一组由普通名称引用的相似类型的变量。 每个数据项都称为数组的元素。 元素的数据类型可以是任何有效的数据类型,例如`char`,`int`,`float`等,并且元素存储在连续的位置。 **数组的长度**指定数组中存在的元素数。 在 [**C#**](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-c-sharp/) 中,数组的内存分配是动态完成的。 而且数组是一种对象,因此使用预定义的函数很容易找到它们的大小。 数组中的变量是有序的,每个变量的索引都从 0 开始。C# 中的数组工作与 C/C++ 中的不同。
有关 C# 中数组的重要注意事项
* 在 C# 中,所有数组都是动态分配的。
* 由于数组是 C# 中的对象,因此我们可以使用成员长度来找到它们的长度。 这与 C/C++ 不同,在 C/C++ 中,我们使用`sizeof`运算符查找长度。
* 像其他变量一样,也可以在数据类型之后使用`[]`声明 C# 数组变量。
* 数组中的变量是有序的,每个变量的索引都从 0 开始。
* C# 数组是基本类型为`System.Array`的对象。
* 数字数组和引用类型元素的默认值分别设置为零和`null`。
* 锯齿状数组元素是引用类型,并且被初始化为`null`。
* 数组元素可以是任何类型,包括数组类型。
* 数组类型是从抽象基本类型`Array`派生的引用类型。 这些类型实现`IEnumerable`,为此,它们在 C# 中的所有数组上使用`foreach`迭代。
根据数组的定义,数组可以包含基本数据类型以及类的对象。 每当使用基元数据类型时,实际值都必须存储在连续的内存位置中。 对于类的对象,实际对象存储在堆段中。
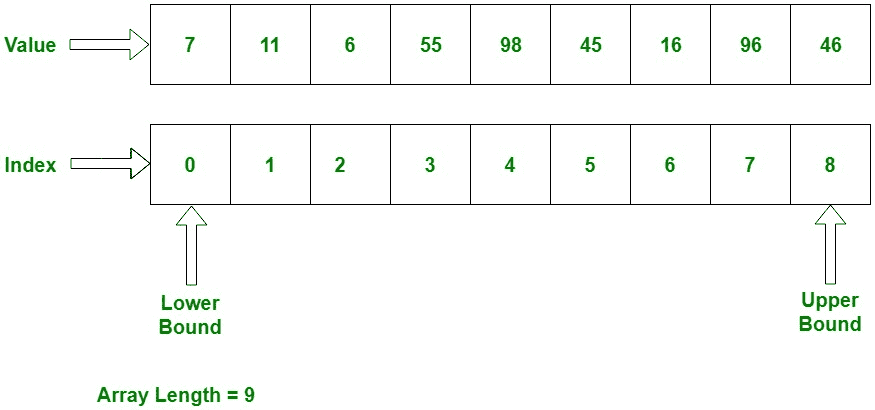
下图显示了数组如何顺序存储值:
[](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/C-Arrays.jpg)
**说明**:
索引从 0 开始,存储值。 我们还可以在数组中存储固定数量的值。 每当数组索引未达到数组大小时,将按顺序将其增加 1。
数组声明
**语法**:
```
< Data Type > [ ] < Name_Array >
```
**此处,**
<数据类型>:它定义数组的元素类型。
[]:它定义数组的大小。
< Name_Array >:这是数组的名称。
**示例**:
```
int[] x; // can store int values
string[] s; // can store string values
double[] d; // can store double values
Student[] stud1; // can store instances of Student class which is custom class
```
**注意**:仅声明数组不会为该数组分配内存。 对于该数组,必须初始化。
数组初始化
如前所述,数组是引用类型,因此**新的**关键字用于创建数组的实例。 我们可以在索引的帮助下分配初始化的单个数组元素。
**Syntax :**
```
type [ ] < Name_Array > = new < datatype > [size];
```
在这里,`type`指定要分配的数据的类型,`size`指定数组中元素的数量,`Name_Array`是数组变量的名称。 并且`new`将根据其大小为数组分配内存。
**示例:展示数组声明和初始化的不同方法**
**示例 1**:
```
// defining array with size 5\.
// But not assigns values
int[] intArray1 = new int[5];
```
上面的语句声明&初始化可以存储五个`int`值的`int`类型数组。 数组大小在方括号(`[]`)中指定。
**示例 2**:
```
// defining array with size 5 and assigning
// values at the same time
int[] intArray2 = new int[5]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
```
上面的语句与之相同,但是它为{}中的每个索引分配值。
**示例 3**:
```
// defining array with 5 elements which
// indicates the size of an array
int[] intArray3 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
```
在上面的语句中,数组的值直接初始化而无需占用其大小。 因此,数组大小将自动为直接获取的值的数量。
声明后初始化数组
声明后可以初始化数组。 不必使用`new`关键字同时声明和初始化。 但是,在声明之后初始化数组,必须使用`new`关键字对其进行初始化。 只能通过分配值来初始化它。
**Example :**
```
// Declaration of the array
string[] str1, str2;
// Initialization of array
str1 = new string[5]{ “Element 1”, “Element 2”, “Element 3”, “Element 4”, “Element 5” };
str2 = new string[5]{ “Element 1”, “Element 2”, “Element 3”, “Element 4”, “Element 5” };
```
**注意**:没有给出大小的初始化在 C# 中无效。 它将给出一个编译时错误。
**示例:初始化数组**的声明错误
```
// compile-time error: must give size of an array
int[] intArray = new int[];
// error : wrong initialization of an array
string[] str1;
str1 = {“Element 1”, “Element 2”, “Element 3”, “Element 4” };
```
访问数组元素
在初始化时,我们可以分配值。 但是,我们也可以在声明和初始化之后使用其索引随机分配数组的值。 我们可以通过索引来访问数组值,将元素的索引放置在方括号内,数组名称为
**示例**:
```
//declares & initializes int type array
int[] intArray = new int[5];
// assign the value 10 in array on its index 0
intArray[0] = 10;
// assign the value 30 in array on its index 2
intArray[2] = 30;
// assign the value 20 in array on its index 1
intArray[1] = 20;
// assign the value 50 in array on its index 4
intArray[4] = 50;
// assign the value 40 in array on its index 3
intArray[3] = 40;
// Accessing array elements using index
intArray[0]; //returns 10
intArray[2]; //returns 30
```
**实现**: **使用不同的循环访问数组元素**
```
// C# program to illustrate creating an array
// of integers, puts some values in the array,
// and prints each value to standard output.
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
// declares an Array of integers.
int[] intArray;
// allocating memory for 5 integers.
intArray = new int[5];
// initialize the first elements
// of the array
intArray[0] = 10;
// initialize the second elements
// of the array
intArray[1] = 20;
// so on...
intArray[2] = 30;
intArray[3] = 40;
intArray[4] = 50;
// accessing the elements
// using for loop
Console.Write("For loop :");
for (int i = 0; i < intArray.Length; i++)
Console.Write(" " + intArray[i]);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("For-each loop :");
// using for-each loop
foreach(int i in intArray)
Console.Write(" " + i);
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("while loop :");
// using while loop
int j = 0;
while (j < intArray.Length) {
Console.Write(" " + intArray[j]);
j++;
}
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.Write("Do-while loop :");
// using do-while loop
int k = 0;
do
{
Console.Write(" " + intArray[k]);
k++;
} while (k < intArray.Length);
}
}
}
```
**输出**:
```
For loop : 10 20 30 40 50
For-each loop : 10 20 30 40 50
while loop : 10 20 30 40 50
Do-while loop : 10 20 30 40 50
```
一维数组
在此数组中仅包含一行用于存储值。 该数组的所有值从 0 到数组大小连续存储。 例如,声明 5 个整数的一维数组:
```
int[] arrayint = new int[5];
```
上面的数组包含从`arrayint[0]`到`arrayint[4]`的元素。 在这里,`new`运算符必须创建数组并通过其默认值初始化其元素。 上面的示例中,所有元素都由零初始化,因为它是`int`类型。
**Example :**
```
// C# program to creating an array
// of the string as week days, store
// day values in the weekdays,
// and prints each value.
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
// declares a 1D Array of string.
string[] weekDays;
// allocating memory for days.
weekDays = new string[] {"Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed",
"Thu", "Fri", "Sat"};
// Displaying Elements of array
foreach(string day in weekDays)
Console.Write(day + " ");
}
}
}
```
**输出**:
```
Sun Mon Tue Wed Thu Fri Sat
```
多维数组
多维数组包含多个行来存储值。 在 [C#](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/introduction-to-c-sharp/)中也称为**矩形数组**,因为它的每行长度都是相同的。 它可以是 **2D 数组**或 **3D 数组**或更多。 为了存储和访问数组的值,需要嵌套循环。 多维数组的声明,初始化和访问如下:
```
// creates a two-dimensional array of
// four rows and two columns.
int[, ] intarray = new int[4, 2];
//creates an array of three dimensions, 4, 2, and 3
int[,, ] intarray1 = new int[4, 2, 3];
```
**Example :**
```
// C# program to illustrate creating
// an multi- dimensional array
// puts some values in the array,
// and print them
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
// Two-dimensional array
int[, ] intarray = new int[, ] { { 1, 2 },
{ 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6 },
{ 7, 8 } };
// The same array with dimensions
// specified 4 row and 2 column.
int[, ] intarray_d = new int[4, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 },
{ 5, 6 }, { 7, 8 } };
// A similar array with string elements.
string[, ] str = new string[4, 2] { { "one", "two" },
{ "three", "four" },
{ "five", "six" },
{ "seven", "eight" } };
// Three-dimensional array.
int[,, ] intarray3D = new int[,, ] { { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 } },
{ { 7, 8, 9 },
{ 10, 11, 12 } } };
// The same array with dimensions
// specified 2, 2 and 3\.
int[,, ] intarray3Dd = new int[2, 2, 3] { { { 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6 } },
{ { 7, 8, 9 },
{ 10, 11, 12 } } };
// Accessing array elements.
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[0][0] : " + intarray[0, 0]);
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[0][1] : " + intarray[0, 1]);
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[1][1] : " + intarray[1, 1]);
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[2][0] " + intarray[2, 0]);
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[1][1] (other) : "
+ intarray_d[1, 1]);
Console.WriteLine("2DArray[1][0] (other)"
+ intarray_d[1, 0]);
Console.WriteLine("3DArray[1][0][1] : "
+ intarray3D[1, 0, 1]);
Console.WriteLine("3DArray[1][1][2] : "
+ intarray3D[1, 1, 2]);
Console.WriteLine("3DArray[0][1][1] (other): "
+ intarray3Dd[0, 1, 1]);
Console.WriteLine("3DArray[1][0][2] (other): "
+ intarray3Dd[1, 0, 2]);
// using nested loop show string elements
Console.WriteLine("To String element");
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
Console.Write(str[i, j] + " ");
}
}
}
```
**输出**:
```
2DArray[0][0] : 1
2DArray[0][1] : 2
2DArray[1][1] : 4
2DArray[2][0] 5
2DArray[1][1] (other) : 4
2DArray[1][0] (other)3
3DArray[1][0][1] : 8
3DArray[1][1][2] : 12
3DArray[0][1][1] (other): 5
3DArray[1][0][2] (other): 9
To String element
one two three four five six seven eight
```
锯齿状数组
元素为数组的数组称为锯齿数组,其含义是“ **数组**”。 锯齿状的数组元件可以具有不同的尺寸和大小。 以下示例显示了如何声明,初始化和访问锯齿状数组。
**Example :**
```
// C# program to single-dimensional jagged array
// that contains two single-dimensional array
// elements of different sizes.
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
/*----------2D Array---------------*/
// Declare the array of two elements:
int[][] arr = new int[2][];
// Initialize the elements:
arr[0] = new int[5] { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
arr[1] = new int[4] { 2, 4, 6, 8 };
// Another way of Declare and
// Initialize of elements
int[][] arr1 = { new int[] { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 },
new int[] { 2, 4, 6, 8 } };
// Display the array elements:
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
System.Console.Write("Element [" + i + "] Array: ");
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].Length; j++)
Console.Write(arr[i][j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
Console.WriteLine("Another Array");
// Display the another array elements:
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.Length; i++)
{
System.Console.Write("Element [" + i + "] Array: ");
for (int j = 0; j < arr1[i].Length; j++)
Console.Write(arr1[i][j] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
```
**输出**:
```
Element [0] Array: 1 3 5 7 9
Element [1] Array: 2 4 6 8
Another Array
Element [0] Array: 1 3 5 7 9
Element [1] Array: 2 4 6 8
```
可以混合锯齿状和多维数组。 锯齿状数组是数组的数组,因此其元素是引用类型,并且被初始化为`null`。
**示例**:声明和初始化一维锯齿状数组,该数组包含三个大小不同的二维数组元素。
```
// C# program to single-dimensional jagged array
// that contains three two-dimensional array
// elements of different sizes.
using System;
namespace geeksforgeeks {
class GFG {
// Main Method
public static void Main()
{
int[][, ] arr = new int[3][, ] {new int[, ] {{1, 3}, {5, 7}},
new int[, ] {{0, 2}, {4, 6}, {8, 10}},
new int[, ] {{11, 22}, {99, 88}, {0, 9}}};
// Display the array elements:
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++)
{
int x = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].GetLength(x); j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < arr[j].Rank; k++)
Console.Write(" arr[" + i + "][" + j + ", " + k + "]:"
+ arr[i][j, k] + " ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
x++;
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
}
```
**输出**:
```
arr[0][0, 0]:1 arr[0][0, 1]:3
arr[0][1, 0]:5 arr[0][1, 1]:7
arr[1][0, 0]:0 arr[1][0, 1]:2
arr[1][1, 0]:4 arr[1][1, 1]:6
arr[1][2, 0]:8 arr[1][2, 1]:10
arr[2][0, 0]:11 arr[2][0, 1]:22
arr[2][1, 0]:99 arr[2][1, 1]:88
arr[2][2, 0]:0 arr[2][2, 1]:9
```
**要记住的要点**:
* `GetLength(int)`:返回数组第一维中的元素数。
* 当使用锯齿状数组时,如果索引不存在则是安全的,那么它将抛出`IndexOutOfRange`异常。
- GeeksForGeeks 数组教程
- 介绍
- 数组介绍
- C/C++ 中的数组
- Java 中的数组
- Python 中的数组| 系列 1(简介和功能)
- C# | 数组
- 回转
- 数组旋转程序
- 数组旋转的逆向算法
- 数组旋转的块交换算法
- 程序循环旋转一个数组
- 在经过排序和旋转的数组中搜索元素
- 给定一个经过排序和旋转的数组,查找是否存在一对具有给定总和的数组
- 在只允许旋转给定数组的情况下找到Sum(i * arr[i])的最大值
- 给定数组所有旋转中i * arr [i]的最大和
- 在旋转排序数组中找到旋转计数
- 快速找到数组的多个左旋转| 系列 1
- 在经过排序和旋转的数组中找到最小元素
- 数组右旋转的逆向算法
- 查找具有最大汉明距离的旋转
- 数组左右循环查询
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)空间中打印数组的左旋转
- 旋转几次后,在给定索引处查找元素
- 拆分数组并将第一部分添加到末尾
- 重排
- 重新排列数组,使arr[i] = i
- 编写程序以反转数组或字符串
- 重新排列数组,如果i为偶数则arr[i] >= arr[j],如果i为奇数且j < i则 arr[i] <= arr[j]
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)额外空间中重新排列正数和负数
- 重新排列数组,交替出现&个正数的负数项,多余的空间为O(1) | 系列 1
- 将所有零移动到数组末尾
- 将所有零移动到数组的末尾| 系列 2(使用单遍历)
- 将所有小于或等于 k 的元素组合在一起所需的最小交换
- 使用内置排序功能重新排列正数和负数
- 重新排列数组,使偶数位置大于奇数
- 按顺序重新排列数组-最小,最大,第二个最小,第二个最大..
- 将第一个元素加倍,然后将零移动到结尾
- 根据给定的索引对数组重新排序
- 用恒定的额外空间重新排列正数和负数
- 排列给定数字以形成最大数| 系列 1
- 重新排列数组,如果arr[i]为j,则arr[j]变为i | 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列数组| 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列数组| 系列 2(O(1)额外空间)
- 将所有负元素移动到最后,并留出足够的空间
- 重新排列数组,使偶数索引元素较小而奇数索引元素较大
- 正数元素位于偶数位置,负数元素位于奇数位置(不保持相对顺序)
- 用上一个和下一个的乘法替换每个数组元素
- 使用 Fisher-Yates 随机播放算法随机播放给定数组
- 分离偶数和奇数| 系列 3
- 将数组中的 0 和 1 分开
- 最长的双子序列| DP-15
- 在线性时间内找到大小为 3 的排序子序列
- 最大数目等于 0 和 1 的子数组
- 最大产品子数组
- 用右侧的最大元素替换每个元素
- 最大循环子数组总和
- 最长递增子序列的构造(N log N)
- 按频率对元素排序| 系列 2
- 最大化圆形数组中的连续差之和
- 根据另一个数组定义的顺序对数组进行排序
- 查找索引 0 替换为 1,以获得二进制数组中最长的连续序列 1s
- 在给定范围内对数组进行三向分区
- 从两个给定排序数组的备用元素生成所有可能的排序数组
- 安排彼此相邻的线对所需的最小交换次数
- 将数组转换为 Zig-Zag 风格
- 从给定序列中形成最小数
- 将两个连续的相等值替换为一个更大的值
- 重新排列二进制字符串作为 x 和 y 的交替出现
- 数组中不同的相邻元素
- 不使用多余空间将 2n 个整数随机排列为 a1-b1-a2-b2-a3-b3-.bn
- 合并 k 个排序的数组| 系列 1
- 订单统计
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 系列 1
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 系列 2(预期线性时间)
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 组合 3(最坏情况的线性时间)
- 使用 STL 的第 K 个最小/最大元素
- 数组中的 k 个最大(或最小)元素| 添加了最小堆方法
- 按行和按列排序的 2D 数组中的 Kth 个最小元素| 系列 1
- 程序以查找数组中的最大元素
- 查找数组中最大的三个元素
- 查找数组中至少有两个大元素的所有元素
- 未排序数组的均值和中位数的程序
- 使用 STL 的运行整数流的中位数
- 正整数数组中 k 个整数的最小积
- 第 K 个最大和的连续子数组
- 来自两个数组的 K 个最大和组合
- 重叠的连续子数组的 K 个最大和
- 非重叠的连续子数组的 K 个最大和
- 使用O(1)额外空间按相同顺序排列 k 个最小元素
- 在两个数组中找到具有最小和的 k 对
- 数组中两个元素的第 k 个最小绝对差
- 在数组中查找第二大元素
- 查找给定数组中出现次数最多的 k 个数字
- 查找数组中的最小和第二个最小元素
- 寻找最小的遗失号码
- 使得两个元素都不相邻的最大和
- 使用最少数量的比较的数组的最大值和最小值
- 两个元素之间的最大差异,使得较大的元素出现在较小的数字之后
- 给定数组 arr [],找到最大 j – i,使得 arr [j] > arr [i]
- 最大滑动窗口(大小为 k 的所有子数组的最大值)
- 找到两个数字之间的最小距离
- 在先增加然后减少的数组中找到最大元素
- 计算右侧较小的元素
- 最长递增子序列大小(N log N)
- 查找未排序数组中缺失的最小正数| 系列 1
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)多余空间中找到最大重复数
- 给定大小为 n 且数字为 k 的数组,找到出现次数超过 n / k 次的所有元素
- 找出长度为 3 且具有最大乘积的递增子序列
- 两个数组中的最大求和路径
- 从两个排序的数组中找到最接近的对
- 在未排序的数组中找到最大的对和
- 整个数组中最小的较大元素
- 删除小于 next 或变得更小的数组元素
- 在线检查回文的在线算法
- 删除小于 next 或变得更小的数组元素
- 找到要翻转的零,以使连续的 1 的数目最大化
- 计算严格增加的子数组
- 流中的第 K 个最大元素
- 在两个数组中找到具有最小和的 k 对
- k 元素组与数组其余部分之间的最大差值。
- 要使中位数等于 x 的最小元素数量
- 下一个更大的元素
- 范围查询
- MO 的算法(查询平方根分解)| 系列 1(简介)
- Sqrt(或平方根)分解技术 系列 1(简介)
- 稀疏表
- 使用稀疏表进行范围总和查询
- 范围最小查询(平方根分解和稀疏表)
- 数组元素的频率范围查询
- 数组上的恒定时间范围添加操作
- 范围 LCM 查询
- 数组中给定索引范围的 GCD
- 查询给定数组中所有数字的 GCD(给定范围内的元素除外)
- 给定子数组中小于或等于给定数目的元素数
- 给定子数组中小于或等于给定数字的元素数| 第 2 组(包括更新)
- 查询值在给定范围内的数组元素的计数
- 查询二进制数组的子数组的十进制值
- 计算将 L-R 范围内的所有数字相除的元素
- 给定数组范围的 XOR 之和最大的数字
- 在给定范围内出现偶数次的数字的 XOR
- 范围查询中的数组范围查询
- 数组范围查询以搜索元素
- 数组范围查询频率与值相同的元素
- 给定范围内的最大出现次数
- 给定范围内具有相等元素的索引数
- 合并排序树以获取范围顺序统计信息
- 范围内没有重复数字的总数
- 差异数组|O(1)中的范围更新查询
- 对数组的范围查询,其每个元素都是索引值与前一个元素的 XOR
- 查找子数组是否为山脉形式
- 范围总和查询,无更新
- 子数组中的素数(带有更新)
- 在二进制数组中检查子数组表示的数字是奇数还是偶数
- 用于乘法,替换和乘积的数组查询
- 数组范围的平均值
- 执行加减命令后打印修改后的数组
- 在给定范围内对偶数或奇数概率的查询
- 数组中范围的乘积
- 计算范围内的素数
- M 个范围切换操作后的二进制数组
- 合并重叠间隔
- 检查给定间隔中是否有两个间隔重叠
- 间隔之和与除数的更新
- 多次数组范围递增操作后打印修改后的数组
- 范围最大奇数的 XOR 查询
- 查询子数组中不同元素的数量
- 计数和切换二进制数组上的查询
- 数组中的最小-最大范围查询
- 优化问题
- 最大总和连续子数组
- 通过最多买卖两次股份获得最大利润
- 查找平均数最少的子数组
- 找到两个数字之间的最小距离
- 最小化高度之间的最大差异
- 到达终点的最小跳数
- 最大总和增加子序列| DP-14
- 总和大于给定值的最小子数组
- 查找 k 个长度的最大平均子数组
- 计算最小步数以获得给定的所需数组
- 乘积小于 k 的子集数
- 查找使数组回文的最小合并操作数
- 查找不能表示为给定数组的任何子集之和的最小正整数值
- 具有最大总和的子数组的大小
- 找出任何两个元素之间的最小差异
- 使用位操作进行空间优化
- 两个二进制数组中具有相同总和的最长跨度
- 排序
- 替代排序
- 对几乎排序(或 K 排序)的数组进行排序
- 根据给定值的绝对差对数组进行排序
- 以波形形式对数组进行排序
- 将大小为 n 的数组合并为大小为 m + n 的另一个数组
- 对包含 1 到 n 个值的数组进行排序
- 通过交换相邻元素将 1 排序为 N
- 对包含两种类型元素的数组进行排序
- 按频率对元素排序| 系列 1
- 计算数组中的反转 系列 1(使用合并排序)
- 两个元素的和最接近零
- 最短无序子数组
- 排序数组所需的最小交换次数
- 两个排序数组的并集和交集
- 查找两个未排序数组的并集和交集
- 对 0、1 和 2 的数组进行排序
- 找到最小长度未排序子数组,进行排序,使整个数组排序
- 中位数为整数流(运行整数)
- 计算可能的三角形数量
- 查找数组中的对数(x,y),使得 x ^ y > y ^ x
- 计算所有等于 k 的不同对
- 打印给定整数数组的所有不同元素
- 从其对和数组构造一个数组
- 合并两个有O(1)额外空间的排序数组
- 第一个数组中的最大值与第二个数组中的最小值的乘积
- 对数(a [j] > = a [i])的对数,其中 k 个范围在(a [i],a [j])中,可被 x 整除
- 随机对为最大加权对的概率
- AP 数组中存在的最小解排列(算术级数)
- 对两个数组的最小乘积之和进行重新排列
- 将数组划分为 k 个片段,以最大化片段最小值的最大值
- 最小乘积对为正整数数组
- 计算形成最小产品三胞胎的方法
- 检查是否反转子数组使数组排序
- 使用另一个数组最大化元素
- 使两个数组的元素相同,最小增减
- 检查是否有任何间隔完全重叠
- 除子数组中的元素外,对数组进行排序
- 对除一个以外的所有数组元素进行排序
- 排序二进制数组所需的最小相邻交换
- 按数组中出现的元素顺序对链接列表进行排序
- 打印数组中排序的不同元素
- 可以单独排序以进行排序的最大分区数
- 使用 STL 根据因素数量进行排序
- 每次取下最小的钢丝绳后剩下的钢丝绳
- 数组中所有元素的排名
- 合并 3 个排序的数组
- 使数组递减的最小减法运算数
- 最大化 arr [i] * i 的总和
- 差异小于 K 的对
- 按排序顺序合并两个未排序的数组
- 从两个数组最大化唯一对
- 应用给定方程后对数组排序
- 每个数组元素的最小绝对差之和
- 查找是否可以使用一个外部数字使数组元素相同
- 两个未排序数组之间的最小差值对
- 程序检查数组是否排序(迭代和递归)
- 查找大于数组中一半元素的元素
- 使两个数组相同的最小交换
- 要添加的元素,以便数组中存在某个范围的所有元素
- 正在搜寻
- 搜索,插入和删除未排序的数组
- 在排序的数组中搜索,插入和删除
- 给定数组 A []和数字 x,请检查 A []中的对,总和为 x
- 在相邻项最多相差 k 的数组中搜索
- 在三个排序的数组中查找共同的元素
- 在无数排序数组中查找元素的位置
- 查找 1 到 n-1 之间的唯一重复元素
- 查找在数组中一次出现的元素,其中每个其他元素出现两次
- 排除某些元素的最大子数组总和
- 数组中的最大平衡和
- 数组的平衡指数
- 领导者数组
- 天花板排列
- 多数元素
- 检查排序数组中的多数元素
- 检查数组是否具有多数元素
- 两指针技术
- 查找峰元素
- 找到给定数组中的两个重复元素
- 在给定的数组中找到一个固定点(等于索引的值)
- 查找给定总和的子数组| 系列 1(负数)
- 数组中的最大三元组和
- 来自三个数组的最小差异三元组
- 查找一个三元组,将其总和成给定值
- 找到所有零和的三元组
- 所有合计给定值的唯一三元组
- 计算总数小于给定值的三元组
- 打印形成 AP 的排序数组中的所有三元组
- XOR 为零的唯一三元组数
- 找到一个三元组,使得两个和等于第三元素
- 查找出现次数的奇数
- 查找丢失的号码
- 计算排序数组中的出现次数(或频率)
- 给定一个已排序的数组和一个数字 x,在数组中找到总和最接近 x 的对
- 在排序的二进制数组中计数 1
- 在整数数组中找到第一个重复元素
- 从重复的数组中查找丢失的元素
- 找到重复的和丢失的| 添加了 3 种新方法
- 在未排序的数组中找到出现奇数的两个数字
- 找到具有给定差异的一对
- 找到四个总和为给定值的元素| 集合 1(n ^ 3 解)
- 找到四个总和为给定值的元素| 系列 2
- 查找是否有一个总和为 0 的子数组
- 在相邻元素之间的差为 1 的数组中搜索元素
- 一系列不同元素中的第三大元素
- 检查数组中是否存在两个元素的总和等于数组其余部分的总和
- 检查给定数组是否包含彼此之间 k 距离内的重复元素
- 使用最少的比较次数搜索未排序数组中的元素
- 连续元素排序数组中仅重复元素的计数
- 在频率大于或等于 n / 2 的排序数组中查找元素。
- 圆形数组中相邻元素的最小绝对差
- 在数组中找到第一个,第二个和第三个最小元素
- 程序来查找数组的最小(或最大)元素
- 每个数组元素中另一个数组中最接近的较大元素
- 计算O(1)额外空间和O(n)时间中数组中所有元素的频率
- 与给定的总和和距末端的最大最短距离配对
- 从数组中删除一个元素(使用两次遍历和一次遍历)
- 计算给定数组中大小为 3 的反转
- 计算给定总和的对
- 对排序向量中的二分搜索
- 困雨水
- 替换元素会使数组元素连续
- 排序数组中的第 k 个缺失元素
- O(log(min(n(n,m)))中具有不同大小的两个排序数组的中位数
- 从两个排序的数组中打印不常见的元素
- 非重复元素
- 数组中最频繁的元素
- 数组中最少的元素
- m 个元素的两个子集之间的最大差
- n 个数组中升序元素的最大和
- 配对使得一个是其他的幂倍
- 查找数组中对的数量,以使它们的 XOR 为 0
- 两次最大出现之间的最小距离
- 如果我们在数组中每次成功搜索后加倍,则找到最终值
- 排序数组中的最后一个重复元素
- 找到一个数组元素,使所有元素都可被它整除
- 以原始顺序查找数组的 k 个最大元素
- 数组中的最大值,至少是其他元素的两倍
- 连续步骤到屋顶
- 两个大小的组之间的最大差异
- 两个大小的组之间的最小差异
- 未排序整数列表中最接近的数字
- 值和索引和的最大绝对差
- 数组中局部极值的数量
- 检查数组是否具有多数元素
- 查找数组中最接近的数字
- 最大和的对数
- 按原始顺序打印给定数组中的 n 个最小元素
- 查找给定数组中缺少的前 k 个自然数
- 数组中的高尚整数(大于等于的元素数等于 value)
- 两个数组对的绝对差的最小和
- 查找数组中非重复(不同)元素的总和
- 检查是否可以从给定数组形成算术级数
- 数组的最小乘积子集
- 计算选择差异最大的对的方法
- 每次成功搜索后通过将元素加倍来重复搜索
- 允许负数的数组中成对乘积的最大和
- 矩阵
- 旋转矩阵元素
- 将方形矩阵旋转 90 度| 系列 1
- 将矩阵旋转 90 度,而无需使用任何额外空间| 系列 2
- 将矩阵旋转 180 度
- 用 K 元素逆时针旋转矩阵的每个环
- 将图像旋转 90 度
- 检查矩阵的所有行是否都是彼此旋转
- 排序给定矩阵
- 查找最大数量为 1 的行
- 在按行排序的矩阵中找到中位数
- 矩阵乘法| 递归的
- 程序将两个矩阵相乘
- 矩阵的标量乘法程序
- 程序打印数组的下三角和上三角矩阵
- 查找矩阵所有行共有的不同元素
- 以螺旋形式打印给定的矩阵
- 查找矩阵中每一行的最大元素
- 在矩阵中查找唯一元素
- 将矩阵元素逐行移动 k
- 矩阵的不同运算
- 以逆时针螺旋形式打印给定矩阵
- 交换方矩阵的主要和次要对角线
- 矩阵中的最大路径总和
- 矩阵对角元素的正方形
- 沿给定方向移动矩阵元素并添加具有相同值的元素
- 按升序对矩阵行进行排序,然后按降序对列进行排序
- 矩阵中间行和列的总和
- 矩阵的按行遍历与按列遍历
- 向右旋转矩阵 K 次
- 检查幂等矩阵的程序
- 程序检查对合矩阵
- 矩阵中第一行和最后一行的交换元素
- zag-zag 方式打印矩阵
- 二维数组中的按行排序
- 马尔可夫矩阵程序
- 检查对角矩阵和标量矩阵的程序
- 按行和列对矩阵进行排序
- 查找岛屿数| 系列 1(使用 DFS)
- 魔术广场| 偶数订单
- 魔术广场
- 检查给定矩阵是否为幻方
- 检查给定矩阵是否为幻方
- 两种矩阵的 Kronecker 积
- 计数总和可分为“ k”的子矩阵
- 对角占优矩阵
- 使矩阵的每一行和每一列相等所需的最少操作
- 计算大小为 n 的矩阵中 k 的频率,其中 matrix(i,j)= i + j
- 给定 1、2、3……k 以之字形打印它们。
- 皇后可以在棋盘上移动的障碍物数量
- 矩阵中 4 个相邻元素的最大积
- 使二进制矩阵对称所需的最小翻转
- 程序检查矩阵是否为下三角
- 程序检查矩阵是否为上三角
- 矩阵中偶数和奇数的频率
- 矩阵的中心元素等于对角线的一半
- 身份矩阵程序
- 程序用矩阵的下对角元素交换上对角元素。
- 稀疏矩阵表示| 系列 3(CSR)
- 填充矩阵以使所有行和所有列的乘积等于 1 的方式
- 矩阵对角线的镜像
- 查找二进制矩阵中是否有一个角为 1 的矩形
- 查找所有填充有 0 的矩形
- 矩阵或网格中两个单元之间的最短距离
- 计算二进制矩阵中 1 和 0 的集合
- 搜索按行和按列排序的矩阵
- 创建具有 O 和 X 的交替矩形的矩阵
- 矩阵的锯齿形(或对角线)遍历
- 原位(固定空间)M x N 大小的矩阵转置| 更新
- 排序从 0 到 n ^ 2 – 1 的数字矩阵的最低成本
- 二进制矩阵中的唯一像元
- 计算特殊矩阵中等于 x 的条目
- 检查给定矩阵是否稀疏
- 方矩阵的两个对角线中的行式公共元素
- 检查矩阵中第 i 行和第 i 列的总和是否相同
- 查找最大数为 1 的二进制矩阵的行号
- 程序检查矩阵是否对称
- 通过遵循单元格值来查找二维数组是否被完全遍历
- 程序以 Z 格式打印矩阵
- 在矩阵中从左上到右下打印所有回文路径
- 骑士的可能举动
- 有效地计算矩阵的对角线总和
- 矩阵的边界元素
- 从点开始以螺旋形式打印矩阵
- 以蛇形图案打印矩阵
- 矩阵对角线互换程序
- 找出两个对角线之和之间的差
- 从给定的二叉树构造祖先矩阵
- 从祖先矩阵构造树
- 圆形矩阵(以螺旋方式构造数字 1 到 m * n 的矩阵)
- Sudoku Generator 程序
- 康威人生游戏计划
- 矩阵中沙漏的最大和
- 方阵中的最大值和最小值。
- 以防螺旋形式打印矩阵
- 查找矩阵的法线和迹线的程序
- 以各种方式对矩阵进行排序
- 设置二进制矩阵的所有元素所需的最少操作
- 以反向螺旋形式打印给定的矩阵
- C 程序检查矩阵是否倾斜对称
- 矩阵元素的总和,其中每个元素是行和列的整数除法
- 稀疏矩阵及其表示| 系列 2(使用列表和键字典)
- 查找使两个矩阵相等的变换数
- 形成矩阵线圈
- 每个元素是其行号和列号的绝对差的矩阵总和
- 检查二进制矩阵中的水平和垂直对称性
- 每个值为 0 或 n 的矩阵的最大行列式
- 螺旋奇数阶方阵的两个对角线之和
- 在二进制矩阵中找到具有最大位差的行对
- 查找矩阵中给定行的所有置换行
- 在二进制矩阵中查找以 1s 形成的形状的周长
- 在矩阵中打印具有相同矩形和的单元格
- 以对角线图案打印矩阵
- 矩阵中两行元素之和的最大差
- 查找具有给定总和的对,以便该对的元素位于不同的行中
- 二进制矩阵中所有零的总覆盖率
- 用行或列的最大 GCD 替换每个矩阵元素
- 计算矩阵中所有排序的行
- 矩阵查询
- 矩阵中的最大 XOR 值
- 可以从下到右传输光线的最大反射镜
- 最后一个方块的方向
- 以矩阵的螺旋形式打印第 K 个元素
- 查找给定的矩阵是否为 Toeplitz
- 在按行和按列排序的矩阵中计数零
- 在列明智和行明智排序矩阵中计算负数
- 在二进制矩阵中查找所有位形成的最大“ +”的大小
- 返回扩展矩阵中的前一个元素
- 使用O(1)额外空间打印 n x n 螺旋矩阵
- 二进制迷宫中的最短路径
- 查找矩阵中图案的方向
- 在矩阵中查找特定对
- 打印给定大小的最大和平方子矩阵
- 给定矩阵的所有行中的公共元素
- 按特定顺序就地转换矩阵
- 布尔矩阵问题
- 给定布尔矩阵,找到 k,使第 k 行中的所有元素均为 0,第 k 列为 1。
- 在给定的布尔矩阵中打印唯一行
- 找到 1 的最大矩形,并允许交换列
- 给定井字棋盘配置的有效性
- 子矩阵总和查询
- 矩阵排名程序
- 全为 1 的最大尺寸矩形二进制子矩阵
- 全为 1 的最大尺寸正方形子矩阵
- 查找矩阵中除给定单元格的行和/或列中的元素以外的所有元素的总和?
- 计算每个岛按行和列分隔的岛数
- 在给定的按行排序的矩阵的所有行中找到一个公共元素
- 给定矩阵“ O”和“ X”,如果被“ X”包围,则将“ O”替换为“ X”
- 给定矩阵“ O”和“ X”,找到被“ X”包围的最大子正方形
- 洪水填充算法–如何在 paint 中实现 fill()?
- 从行和列的排序矩阵中按排序顺序打印所有元素
- 给定一个 n x n 方阵,求出大小为 k x k 的所有子方和
- 查找矩阵转置的程序
- 用于添加两个矩阵的程序
- 矩阵减法程序
- 使用两次遍历收集网格中的最大点
- 在死胡同之前收集最多硬币
- 正好有 k 个硬币的路径数
- 查找从给定起始字符开始的最长连续路径的长度
- 在给定约束条件下找到矩阵中的最长路径
- 到达目的地的最低初始点
- 分而治之| 第 5 组(Strassen 的矩阵乘法)
- 2D 矩阵中的最大和矩形| DP-27
- 杂项
- 子数组/子字符串与子序列以及生成它们的程序
- 产品数组难题
- 具有给定乘积的子数组数
- 链表与数组
- 检查数组元素是否连续 新增方法 3
- 查找一个数组是否是另一个数组的子集 新增方法 3
- 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈
- 查找两个排序数组的相对补码
- 通过 k 次运算的最小增量以使所有元素相等
- 最小化三个不同排序数组的(max(A [i],B [j],C [k])– min(A [i],B [j],C [k]))
