# 下一个更大的元素
> 原文: [https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/next-greater-element/](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/next-greater-element/)
给定一个数组,为每个元素打印下一更大元素(NGE)。 元素`x`的下一个更大元素是数组`x`中右侧第一个更大的元素。 对于不存在更大元素的元素,请将下一个更大元素视为 -1。
**示例**:
1. 对于任何数组,最右边的元素始终将下一个更大的元素设为 -1。
2. 对于以降序排列的数组,所有元素的下一个更大元素为 -1。
3. 对于输入数组`[4, 5, 2, 25]`,每个元素的下一个更大元素如下。
```
Element NGE
4 --> 5
5 --> 25
2 --> 25
25 --> -1
```
**d)**对于输入数组`[13, 7, 6, 12]`,每个元素的下一个更大元素如下。
```
Element NGE
13 --> -1
7 --> 12
6 --> 12
12 --> -1
```
**方法 1(简单)**
使用两个循环:外循环一个接一个地选取所有元素。 内循环为外循环选取的元素寻找第一个更大的元素。 如果找到更大的元素,则该元素将作为下一个被打印,否则将打印 -1。
## C++
```cpp
// Simple C++ program to print
// next greater elements in a
// given array
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
/* prints element and NGE pair
for all elements of arr[] of size n */
void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
{
int next, i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
next = -1;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[j])
{
next = arr[j];
break;
}
}
cout << arr[i] << " -- "
<< next << endl;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printNGE(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai(Abby_akku)
```
## C
```
// Simple C program to print next greater elements
// in a given array
#include<stdio.h>
/* prints element and NGE pair for all elements of
arr[] of size n */
void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
{
int next, i, j;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
next = -1;
for (j = i+1; j<n; j++)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[j])
{
next = arr[j];
break;
}
}
printf("%d -- %dn", arr[i], next);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[]= {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printNGE(arr, n);
return 0;
}
```
## Java
```java
// Simple Java program to print next
// greater elements in a given array
class Main
{
/* prints element and NGE pair for
all elements of arr[] of size n */
static void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
{
int next, i, j;
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
{
next = -1;
for (j = i+1; j<n; j++)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[j])
{
next = arr[j];
break;
}
}
System.out.println(arr[i]+" -- "+next);
}
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[]= {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = arr.length;
printNGE(arr, n);
}
}
```
## Python
```
# Function to print element and NGE pair for all elements of list
def printNGE(arr):
for i in range(0, len(arr), 1):
next = -1
for j in range(i+1, len(arr), 1):
if arr[i] < arr[j]:
next = arr[j]
break
print(str(arr[i]) + " -- " + str(next))
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [11,13,21,3]
printNGE(arr)
# This code is contributed by Sunny Karira
```
## C#
```cs
// Simple C# program to print next
// greater elements in a given array
using System;
class GFG
{
/* prints element and NGE pair for
all elements of arr[] of size n */
static void printNGE(int []arr, int n)
{
int next, i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
next = -1;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
if (arr[i] < arr[j])
{
next = arr[j];
break;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(arr[i] + " -- " + next);
}
}
// driver code
public static void Main()
{
int []arr= {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = arr.Length;
printNGE(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Sam007
```
## PHP
```php
<?php
// Simple PHP program to print next
// greater elements in a given array
/* prints element and NGE pair for
all elements of arr[] of size n */
function printNGE($arr, $n)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
$next = -1;
for ($j = $i + 1; $j < $n; $j++)
{
if ($arr[$i] < $arr[$j])
{
$next = $arr[$j];
break;
}
}
echo $arr[$i]." -- ". $next."\n";
}
}
// Driver Code
$arr= array(11, 13, 21, 3);
$n = count($arr);
printNGE($arr, $n);
// This code is contributed by Sam007
?>
```
**输出**:
```
11 -- 13
13 -- 21
21 -- -1
3 -- -1
```
**时间复杂度**:`O(n ^ 2)`。 当所有元素以降序排序时,会发生最坏的情况。
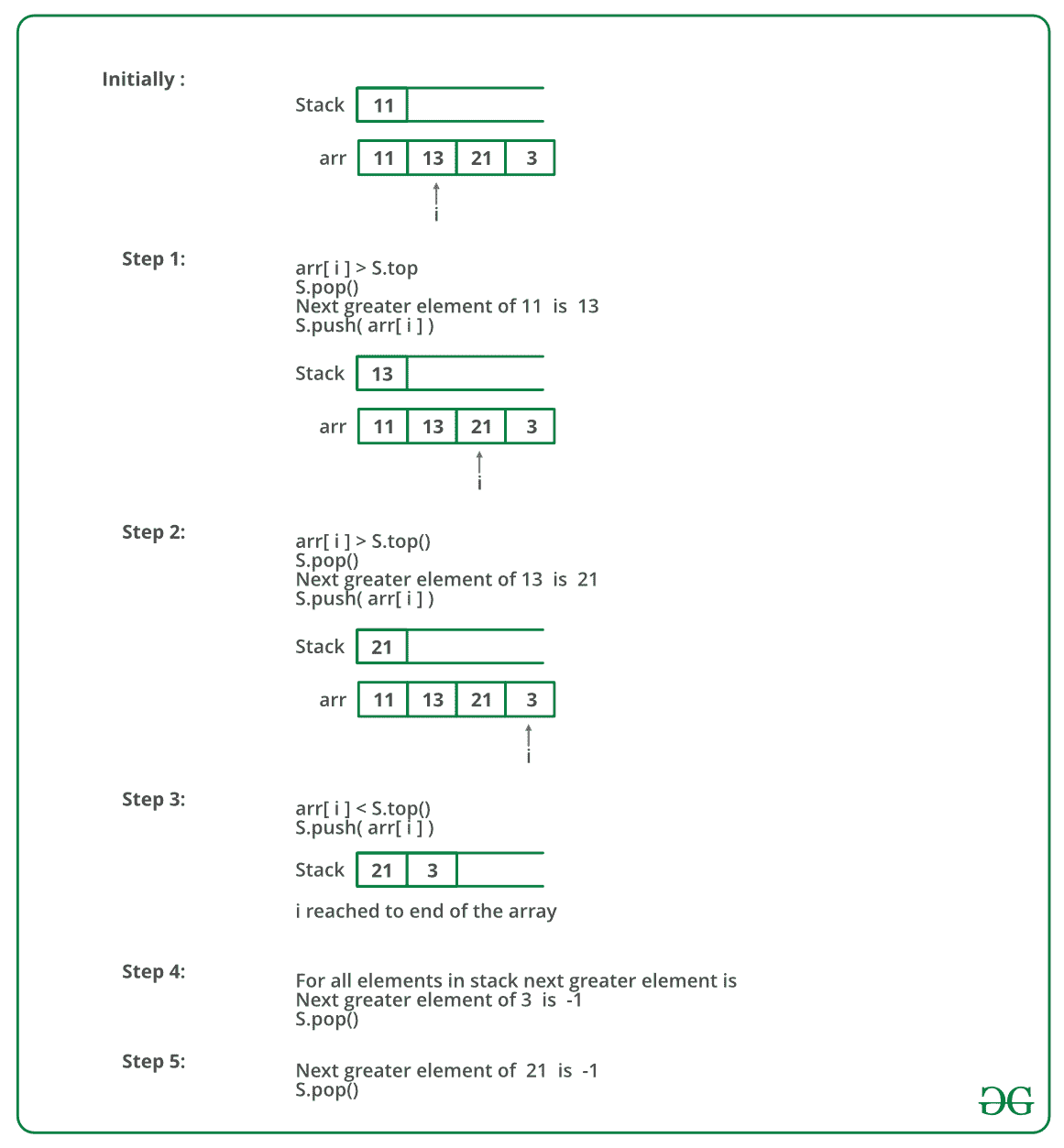
**方法 2(使用堆栈)**
* 将第一个元素推入堆栈。
* 一个接一个地选取其余元素,然后循环执行以下步骤。
1. 在之后标记当前元素为。
2. 如果堆栈不为空,则将堆栈的顶部元素与`next`比较。
3. 如果`next`大于顶部元素,则从堆栈中弹出元素。 `next`是弹出元素的下一个更大元素。
4. 当弹出的元素小于之后的*时,继续从堆栈中弹出。 `next`成为所有此类弹出元素的下一个更大元素
* 最后,将下一个推入堆栈。
* 步骤 2 中的循环结束后,从堆栈中弹出所有元素,并将-1 打印为它们的下一个元素。
下图是上述方法的模拟:
下面是上述方法的实现:
## C++
```
// A Stack based C++ program to find next
// greater element for all array elements.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* prints element and NGE pair for all
elements of arr[] of size n */
void printNGE(int arr[], int n) {
stack < int > s;
/* push the first element to stack */
s.push(arr[0]);
// iterate for rest of the elements
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (s.empty()) {
s.push(arr[i]);
continue;
}
/* if stack is not empty, then
pop an element from stack.
If the popped element is smaller
than next, then
a) print the pair
b) keep popping while elements are
smaller and stack is not empty */
while (s.empty() == false && s.top() < arr[i])
{
cout << s.top() << " --> " << arr[i] << endl;
s.pop();
}
/* push next to stack so that we can find
next greater for it */
s.push(arr[i]);
}
/* After iterating over the loop, the remaining
elements in stack do not have the next greater
element, so print -1 for them */
while (s.empty() == false) {
cout << s.top() << " --> " << -1 << endl;
s.pop();
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main() {
int arr[] = {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printNGE(arr, n);
return 0;
}
```
## C
```
// A Stack based C program to find next greater element
// for all array elements.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#define STACKSIZE 100
// stack structure
struct stack
{
int top;
int items[STACKSIZE];
};
// Stack Functions to be used by printNGE()
void push(struct stack *ps, int x)
{
if (ps->top == STACKSIZE-1)
{
printf("Error: stack overflown");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
else
{
ps->top += 1;
int top = ps->top;
ps->items [top] = x;
}
}
bool isEmpty(struct stack *ps)
{
return (ps->top == -1)? true : false;
}
int pop(struct stack *ps)
{
int temp;
if (ps->top == -1)
{
printf("Error: stack underflow n");
getchar();
exit(0);
}
else
{
int top = ps->top;
temp = ps->items [top];
ps->top -= 1;
return temp;
}
}
/* prints element and NGE pair for all elements of
arr[] of size n */
void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
{
int i = 0;
struct stack s;
s.top = -1;
int element, next;
/* push the first element to stack */
push(&s, arr[0]);
// iterate for rest of the elements
for (i=1; i<n; i++)
{
next = arr[i];
if (isEmpty(&s) == false)
{
// if stack is not empty, then pop an element from stack
element = pop(&s);
/* If the popped element is smaller than next, then
a) print the pair
b) keep popping while elements are smaller and
stack is not empty */
while (element < next)
{
printf("n %d --> %d", element, next);
if(isEmpty(&s) == true)
break;
element = pop(&s);
}
/* If element is greater than next, then push
the element back */
if (element > next)
push(&s, element);
}
/* push next to stack so that we can find
next greater for it */
push(&s, next);
}
/* After iterating over the loop, the remaining
elements in stack do not have the next greater
element, so print -1 for them */
while (isEmpty(&s) == false)
{
element = pop(&s);
next = -1;
printf("n %d --> %d", element, next);
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
int arr[]= {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printNGE(arr, n);
getchar();
return 0;
}
```
## Java
```java
//Java program to print next
//greater element using stack
public class NGE
{
static class stack
{
int top;
int items[] = new int[100];
// Stack functions to be used by printNGE
void push(int x)
{
if (top == 99)
{
System.out.println("Stack full");
}
else
{
items[++top] = x;
}
}
int pop()
{
if (top == -1)
{
System.out.println("Underflow error");
return -1;
}
else
{
int element = items[top];
top--;
return element;
}
}
boolean isEmpty()
{
return (top == -1) ? true : false;
}
}
/* prints element and NGE pair for
all elements of arr[] of size n */
static void printNGE(int arr[], int n)
{
int i = 0;
stack s = new stack();
s.top = -1;
int element, next;
/* push the first element to stack */
s.push(arr[0]);
// iterate for rest of the elements
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
next = arr[i];
if (s.isEmpty() == false)
{
// if stack is not empty, then
// pop an element from stack
element = s.pop();
/* If the popped element is smaller than
next, then a) print the pair b) keep
popping while elements are smaller and
stack is not empty */
while (element < next)
{
System.out.println(element + " --> " + next);
if (s.isEmpty() == true)
break;
element = s.pop();
}
/* If element is greater than next, then
push the element back */
if (element > next)
s.push(element);
}
/* push next to stack so that we can find next
greater for it */
s.push(next);
}
/* After iterating over the loop, the remaining
elements in stack do not have the next greater
element, so print -1 for them */
while (s.isEmpty() == false)
{
element = s.pop();
next = -1;
System.out.println(element + " -- " + next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 11, 13, 21, 3 };
int n = arr.length;
printNGE(arr, n);
}
}
// Thanks to Rishabh Mahrsee for contributing this code
```
## Python
```
# Python program to print next greater element using stack
# Stack Functions to be used by printNGE()
def createStack():
stack = []
return stack
def isEmpty(stack):
return len(stack) == 0
def push(stack, x):
stack.append(x)
def pop(stack):
if isEmpty(stack):
print("Error : stack underflow")
else:
return stack.pop()
'''prints element and NGE pair for all elements of
arr[] '''
def printNGE(arr):
s = createStack()
element = 0
next = 0
# push the first element to stack
push(s, arr[0])
# iterate for rest of the elements
for i in range(1, len(arr), 1):
next = arr[i]
if isEmpty(s) == False:
# if stack is not empty, then pop an element from stack
element = pop(s)
'''If the popped element is smaller than next, then
a) print the pair
b) keep popping while elements are smaller and
stack is not empty '''
while element < next :
print(str(element)+ " -- " + str(next))
if isEmpty(s) == True :
break
element = pop(s)
'''If element is greater than next, then push
the element back '''
if element > next:
push(s, element)
'''push next to stack so that we can find
next greater for it '''
push(s, next)
'''After iterating over the loop, the remaining
elements in stack do not have the next greater
element, so print -1 for them '''
while isEmpty(s) == False:
element = pop(s)
next = -1
print(str(element) + " -- " + str(next))
# Driver program to test above functions
arr = [11, 13, 21, 3]
printNGE(arr)
# This code is contributed by Sunny Karira
```
## C#
```
using System;
// c# program to print next
//greater element using stack
public class NGE
{
public class stack
{
public int top;
public int[] items = new int[100];
// Stack functions to be used by printNGE
public virtual void push(int x)
{
if (top == 99)
{
Console.WriteLine("Stack full");
}
else
{
items[++top] = x;
}
}
public virtual int pop()
{
if (top == -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Underflow error");
return -1;
}
else
{
int element = items[top];
top--;
return element;
}
}
public virtual bool Empty
{
get
{
return (top == -1) ? true : false;
}
}
}
/* prints element and NGE pair for
all elements of arr[] of size n */
public static void printNGE(int[] arr, int n)
{
int i = 0;
stack s = new stack();
s.top = -1;
int element, next;
/* push the first element to stack */
s.push(arr[0]);
// iterate for rest of the elements
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
next = arr[i];
if (s.Empty == false)
{
// if stack is not empty, then
// pop an element from stack
element = s.pop();
/* If the popped element is smaller than
next, then a) print the pair b) keep
popping while elements are smaller and
stack is not empty */
while (element < next)
{
Console.WriteLine(element + " --> " + next);
if (s.Empty == true)
{
break;
}
element = s.pop();
}
/* If element is greater than next, then
push the element back */
if (element > next)
{
s.push(element);
}
}
/* push next to stack so that we can find next
greater for it */
s.push(next);
}
/* After iterating over the loop, the remaining
elements in stack do not have the next greater
element, so print -1 for them */
while (s.Empty == false)
{
element = s.pop();
next = -1;
Console.WriteLine(element + " -- " + next);
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] arr = new int[] {11, 13, 21, 3};
int n = arr.Length;
printNGE(arr, n);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
```
**输出**:
```
11 -- 13
13 -- 21
3 -- -1
21 -- -1
```
**时间复杂度**:`O(n)`。
当所有元素以降序排序时,会发生最坏的情况。 如果元素按降序排序,则每个元素最多处理 4 次。
1. 最初被推入堆栈。
2. 处理下一个元素时从堆栈中弹出。
3. 由于下一个元素较小,因此被推回堆栈。
4. 在算法的第 3 步中从堆栈中弹出。
请参见[优化解决方案,以相同顺序进行打印。](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/next-greater-element-in-same-order-as-input/)
如果您发现上述代码/算法有误,请写评论,或者找到其他解决相同问题的方法。
- GeeksForGeeks 数组教程
- 介绍
- 数组介绍
- C/C++ 中的数组
- Java 中的数组
- Python 中的数组| 系列 1(简介和功能)
- C# | 数组
- 回转
- 数组旋转程序
- 数组旋转的逆向算法
- 数组旋转的块交换算法
- 程序循环旋转一个数组
- 在经过排序和旋转的数组中搜索元素
- 给定一个经过排序和旋转的数组,查找是否存在一对具有给定总和的数组
- 在只允许旋转给定数组的情况下找到Sum(i * arr[i])的最大值
- 给定数组所有旋转中i * arr [i]的最大和
- 在旋转排序数组中找到旋转计数
- 快速找到数组的多个左旋转| 系列 1
- 在经过排序和旋转的数组中找到最小元素
- 数组右旋转的逆向算法
- 查找具有最大汉明距离的旋转
- 数组左右循环查询
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)空间中打印数组的左旋转
- 旋转几次后,在给定索引处查找元素
- 拆分数组并将第一部分添加到末尾
- 重排
- 重新排列数组,使arr[i] = i
- 编写程序以反转数组或字符串
- 重新排列数组,如果i为偶数则arr[i] >= arr[j],如果i为奇数且j < i则 arr[i] <= arr[j]
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)额外空间中重新排列正数和负数
- 重新排列数组,交替出现&个正数的负数项,多余的空间为O(1) | 系列 1
- 将所有零移动到数组末尾
- 将所有零移动到数组的末尾| 系列 2(使用单遍历)
- 将所有小于或等于 k 的元素组合在一起所需的最小交换
- 使用内置排序功能重新排列正数和负数
- 重新排列数组,使偶数位置大于奇数
- 按顺序重新排列数组-最小,最大,第二个最小,第二个最大..
- 将第一个元素加倍,然后将零移动到结尾
- 根据给定的索引对数组重新排序
- 用恒定的额外空间重新排列正数和负数
- 排列给定数字以形成最大数| 系列 1
- 重新排列数组,如果arr[i]为j,则arr[j]变为i | 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列数组| 系列 1
- 以最大最小形式重新排列数组| 系列 2(O(1)额外空间)
- 将所有负元素移动到最后,并留出足够的空间
- 重新排列数组,使偶数索引元素较小而奇数索引元素较大
- 正数元素位于偶数位置,负数元素位于奇数位置(不保持相对顺序)
- 用上一个和下一个的乘法替换每个数组元素
- 使用 Fisher-Yates 随机播放算法随机播放给定数组
- 分离偶数和奇数| 系列 3
- 将数组中的 0 和 1 分开
- 最长的双子序列| DP-15
- 在线性时间内找到大小为 3 的排序子序列
- 最大数目等于 0 和 1 的子数组
- 最大产品子数组
- 用右侧的最大元素替换每个元素
- 最大循环子数组总和
- 最长递增子序列的构造(N log N)
- 按频率对元素排序| 系列 2
- 最大化圆形数组中的连续差之和
- 根据另一个数组定义的顺序对数组进行排序
- 查找索引 0 替换为 1,以获得二进制数组中最长的连续序列 1s
- 在给定范围内对数组进行三向分区
- 从两个给定排序数组的备用元素生成所有可能的排序数组
- 安排彼此相邻的线对所需的最小交换次数
- 将数组转换为 Zig-Zag 风格
- 从给定序列中形成最小数
- 将两个连续的相等值替换为一个更大的值
- 重新排列二进制字符串作为 x 和 y 的交替出现
- 数组中不同的相邻元素
- 不使用多余空间将 2n 个整数随机排列为 a1-b1-a2-b2-a3-b3-.bn
- 合并 k 个排序的数组| 系列 1
- 订单统计
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 系列 1
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 系列 2(预期线性时间)
- 未排序数组中第 K 个最小/最大元素| 组合 3(最坏情况的线性时间)
- 使用 STL 的第 K 个最小/最大元素
- 数组中的 k 个最大(或最小)元素| 添加了最小堆方法
- 按行和按列排序的 2D 数组中的 Kth 个最小元素| 系列 1
- 程序以查找数组中的最大元素
- 查找数组中最大的三个元素
- 查找数组中至少有两个大元素的所有元素
- 未排序数组的均值和中位数的程序
- 使用 STL 的运行整数流的中位数
- 正整数数组中 k 个整数的最小积
- 第 K 个最大和的连续子数组
- 来自两个数组的 K 个最大和组合
- 重叠的连续子数组的 K 个最大和
- 非重叠的连续子数组的 K 个最大和
- 使用O(1)额外空间按相同顺序排列 k 个最小元素
- 在两个数组中找到具有最小和的 k 对
- 数组中两个元素的第 k 个最小绝对差
- 在数组中查找第二大元素
- 查找给定数组中出现次数最多的 k 个数字
- 查找数组中的最小和第二个最小元素
- 寻找最小的遗失号码
- 使得两个元素都不相邻的最大和
- 使用最少数量的比较的数组的最大值和最小值
- 两个元素之间的最大差异,使得较大的元素出现在较小的数字之后
- 给定数组 arr [],找到最大 j – i,使得 arr [j] > arr [i]
- 最大滑动窗口(大小为 k 的所有子数组的最大值)
- 找到两个数字之间的最小距离
- 在先增加然后减少的数组中找到最大元素
- 计算右侧较小的元素
- 最长递增子序列大小(N log N)
- 查找未排序数组中缺失的最小正数| 系列 1
- 在O(n)时间和O(1)多余空间中找到最大重复数
- 给定大小为 n 且数字为 k 的数组,找到出现次数超过 n / k 次的所有元素
- 找出长度为 3 且具有最大乘积的递增子序列
- 两个数组中的最大求和路径
- 从两个排序的数组中找到最接近的对
- 在未排序的数组中找到最大的对和
- 整个数组中最小的较大元素
- 删除小于 next 或变得更小的数组元素
- 在线检查回文的在线算法
- 删除小于 next 或变得更小的数组元素
- 找到要翻转的零,以使连续的 1 的数目最大化
- 计算严格增加的子数组
- 流中的第 K 个最大元素
- 在两个数组中找到具有最小和的 k 对
- k 元素组与数组其余部分之间的最大差值。
- 要使中位数等于 x 的最小元素数量
- 下一个更大的元素
- 范围查询
- MO 的算法(查询平方根分解)| 系列 1(简介)
- Sqrt(或平方根)分解技术 系列 1(简介)
- 稀疏表
- 使用稀疏表进行范围总和查询
- 范围最小查询(平方根分解和稀疏表)
- 数组元素的频率范围查询
- 数组上的恒定时间范围添加操作
- 范围 LCM 查询
- 数组中给定索引范围的 GCD
- 查询给定数组中所有数字的 GCD(给定范围内的元素除外)
- 给定子数组中小于或等于给定数目的元素数
- 给定子数组中小于或等于给定数字的元素数| 第 2 组(包括更新)
- 查询值在给定范围内的数组元素的计数
- 查询二进制数组的子数组的十进制值
- 计算将 L-R 范围内的所有数字相除的元素
- 给定数组范围的 XOR 之和最大的数字
- 在给定范围内出现偶数次的数字的 XOR
- 范围查询中的数组范围查询
- 数组范围查询以搜索元素
- 数组范围查询频率与值相同的元素
- 给定范围内的最大出现次数
- 给定范围内具有相等元素的索引数
- 合并排序树以获取范围顺序统计信息
- 范围内没有重复数字的总数
- 差异数组|O(1)中的范围更新查询
- 对数组的范围查询,其每个元素都是索引值与前一个元素的 XOR
- 查找子数组是否为山脉形式
- 范围总和查询,无更新
- 子数组中的素数(带有更新)
- 在二进制数组中检查子数组表示的数字是奇数还是偶数
- 用于乘法,替换和乘积的数组查询
- 数组范围的平均值
- 执行加减命令后打印修改后的数组
- 在给定范围内对偶数或奇数概率的查询
- 数组中范围的乘积
- 计算范围内的素数
- M 个范围切换操作后的二进制数组
- 合并重叠间隔
- 检查给定间隔中是否有两个间隔重叠
- 间隔之和与除数的更新
- 多次数组范围递增操作后打印修改后的数组
- 范围最大奇数的 XOR 查询
- 查询子数组中不同元素的数量
- 计数和切换二进制数组上的查询
- 数组中的最小-最大范围查询
- 优化问题
- 最大总和连续子数组
- 通过最多买卖两次股份获得最大利润
- 查找平均数最少的子数组
- 找到两个数字之间的最小距离
- 最小化高度之间的最大差异
- 到达终点的最小跳数
- 最大总和增加子序列| DP-14
- 总和大于给定值的最小子数组
- 查找 k 个长度的最大平均子数组
- 计算最小步数以获得给定的所需数组
- 乘积小于 k 的子集数
- 查找使数组回文的最小合并操作数
- 查找不能表示为给定数组的任何子集之和的最小正整数值
- 具有最大总和的子数组的大小
- 找出任何两个元素之间的最小差异
- 使用位操作进行空间优化
- 两个二进制数组中具有相同总和的最长跨度
- 排序
- 替代排序
- 对几乎排序(或 K 排序)的数组进行排序
- 根据给定值的绝对差对数组进行排序
- 以波形形式对数组进行排序
- 将大小为 n 的数组合并为大小为 m + n 的另一个数组
- 对包含 1 到 n 个值的数组进行排序
- 通过交换相邻元素将 1 排序为 N
- 对包含两种类型元素的数组进行排序
- 按频率对元素排序| 系列 1
- 计算数组中的反转 系列 1(使用合并排序)
- 两个元素的和最接近零
- 最短无序子数组
- 排序数组所需的最小交换次数
- 两个排序数组的并集和交集
- 查找两个未排序数组的并集和交集
- 对 0、1 和 2 的数组进行排序
- 找到最小长度未排序子数组,进行排序,使整个数组排序
- 中位数为整数流(运行整数)
- 计算可能的三角形数量
- 查找数组中的对数(x,y),使得 x ^ y > y ^ x
- 计算所有等于 k 的不同对
- 打印给定整数数组的所有不同元素
- 从其对和数组构造一个数组
- 合并两个有O(1)额外空间的排序数组
- 第一个数组中的最大值与第二个数组中的最小值的乘积
- 对数(a [j] > = a [i])的对数,其中 k 个范围在(a [i],a [j])中,可被 x 整除
- 随机对为最大加权对的概率
- AP 数组中存在的最小解排列(算术级数)
- 对两个数组的最小乘积之和进行重新排列
- 将数组划分为 k 个片段,以最大化片段最小值的最大值
- 最小乘积对为正整数数组
- 计算形成最小产品三胞胎的方法
- 检查是否反转子数组使数组排序
- 使用另一个数组最大化元素
- 使两个数组的元素相同,最小增减
- 检查是否有任何间隔完全重叠
- 除子数组中的元素外,对数组进行排序
- 对除一个以外的所有数组元素进行排序
- 排序二进制数组所需的最小相邻交换
- 按数组中出现的元素顺序对链接列表进行排序
- 打印数组中排序的不同元素
- 可以单独排序以进行排序的最大分区数
- 使用 STL 根据因素数量进行排序
- 每次取下最小的钢丝绳后剩下的钢丝绳
- 数组中所有元素的排名
- 合并 3 个排序的数组
- 使数组递减的最小减法运算数
- 最大化 arr [i] * i 的总和
- 差异小于 K 的对
- 按排序顺序合并两个未排序的数组
- 从两个数组最大化唯一对
- 应用给定方程后对数组排序
- 每个数组元素的最小绝对差之和
- 查找是否可以使用一个外部数字使数组元素相同
- 两个未排序数组之间的最小差值对
- 程序检查数组是否排序(迭代和递归)
- 查找大于数组中一半元素的元素
- 使两个数组相同的最小交换
- 要添加的元素,以便数组中存在某个范围的所有元素
- 正在搜寻
- 搜索,插入和删除未排序的数组
- 在排序的数组中搜索,插入和删除
- 给定数组 A []和数字 x,请检查 A []中的对,总和为 x
- 在相邻项最多相差 k 的数组中搜索
- 在三个排序的数组中查找共同的元素
- 在无数排序数组中查找元素的位置
- 查找 1 到 n-1 之间的唯一重复元素
- 查找在数组中一次出现的元素,其中每个其他元素出现两次
- 排除某些元素的最大子数组总和
- 数组中的最大平衡和
- 数组的平衡指数
- 领导者数组
- 天花板排列
- 多数元素
- 检查排序数组中的多数元素
- 检查数组是否具有多数元素
- 两指针技术
- 查找峰元素
- 找到给定数组中的两个重复元素
- 在给定的数组中找到一个固定点(等于索引的值)
- 查找给定总和的子数组| 系列 1(负数)
- 数组中的最大三元组和
- 来自三个数组的最小差异三元组
- 查找一个三元组,将其总和成给定值
- 找到所有零和的三元组
- 所有合计给定值的唯一三元组
- 计算总数小于给定值的三元组
- 打印形成 AP 的排序数组中的所有三元组
- XOR 为零的唯一三元组数
- 找到一个三元组,使得两个和等于第三元素
- 查找出现次数的奇数
- 查找丢失的号码
- 计算排序数组中的出现次数(或频率)
- 给定一个已排序的数组和一个数字 x,在数组中找到总和最接近 x 的对
- 在排序的二进制数组中计数 1
- 在整数数组中找到第一个重复元素
- 从重复的数组中查找丢失的元素
- 找到重复的和丢失的| 添加了 3 种新方法
- 在未排序的数组中找到出现奇数的两个数字
- 找到具有给定差异的一对
- 找到四个总和为给定值的元素| 集合 1(n ^ 3 解)
- 找到四个总和为给定值的元素| 系列 2
- 查找是否有一个总和为 0 的子数组
- 在相邻元素之间的差为 1 的数组中搜索元素
- 一系列不同元素中的第三大元素
- 检查数组中是否存在两个元素的总和等于数组其余部分的总和
- 检查给定数组是否包含彼此之间 k 距离内的重复元素
- 使用最少的比较次数搜索未排序数组中的元素
- 连续元素排序数组中仅重复元素的计数
- 在频率大于或等于 n / 2 的排序数组中查找元素。
- 圆形数组中相邻元素的最小绝对差
- 在数组中找到第一个,第二个和第三个最小元素
- 程序来查找数组的最小(或最大)元素
- 每个数组元素中另一个数组中最接近的较大元素
- 计算O(1)额外空间和O(n)时间中数组中所有元素的频率
- 与给定的总和和距末端的最大最短距离配对
- 从数组中删除一个元素(使用两次遍历和一次遍历)
- 计算给定数组中大小为 3 的反转
- 计算给定总和的对
- 对排序向量中的二分搜索
- 困雨水
- 替换元素会使数组元素连续
- 排序数组中的第 k 个缺失元素
- O(log(min(n(n,m)))中具有不同大小的两个排序数组的中位数
- 从两个排序的数组中打印不常见的元素
- 非重复元素
- 数组中最频繁的元素
- 数组中最少的元素
- m 个元素的两个子集之间的最大差
- n 个数组中升序元素的最大和
- 配对使得一个是其他的幂倍
- 查找数组中对的数量,以使它们的 XOR 为 0
- 两次最大出现之间的最小距离
- 如果我们在数组中每次成功搜索后加倍,则找到最终值
- 排序数组中的最后一个重复元素
- 找到一个数组元素,使所有元素都可被它整除
- 以原始顺序查找数组的 k 个最大元素
- 数组中的最大值,至少是其他元素的两倍
- 连续步骤到屋顶
- 两个大小的组之间的最大差异
- 两个大小的组之间的最小差异
- 未排序整数列表中最接近的数字
- 值和索引和的最大绝对差
- 数组中局部极值的数量
- 检查数组是否具有多数元素
- 查找数组中最接近的数字
- 最大和的对数
- 按原始顺序打印给定数组中的 n 个最小元素
- 查找给定数组中缺少的前 k 个自然数
- 数组中的高尚整数(大于等于的元素数等于 value)
- 两个数组对的绝对差的最小和
- 查找数组中非重复(不同)元素的总和
- 检查是否可以从给定数组形成算术级数
- 数组的最小乘积子集
- 计算选择差异最大的对的方法
- 每次成功搜索后通过将元素加倍来重复搜索
- 允许负数的数组中成对乘积的最大和
- 矩阵
- 旋转矩阵元素
- 将方形矩阵旋转 90 度| 系列 1
- 将矩阵旋转 90 度,而无需使用任何额外空间| 系列 2
- 将矩阵旋转 180 度
- 用 K 元素逆时针旋转矩阵的每个环
- 将图像旋转 90 度
- 检查矩阵的所有行是否都是彼此旋转
- 排序给定矩阵
- 查找最大数量为 1 的行
- 在按行排序的矩阵中找到中位数
- 矩阵乘法| 递归的
- 程序将两个矩阵相乘
- 矩阵的标量乘法程序
- 程序打印数组的下三角和上三角矩阵
- 查找矩阵所有行共有的不同元素
- 以螺旋形式打印给定的矩阵
- 查找矩阵中每一行的最大元素
- 在矩阵中查找唯一元素
- 将矩阵元素逐行移动 k
- 矩阵的不同运算
- 以逆时针螺旋形式打印给定矩阵
- 交换方矩阵的主要和次要对角线
- 矩阵中的最大路径总和
- 矩阵对角元素的正方形
- 沿给定方向移动矩阵元素并添加具有相同值的元素
- 按升序对矩阵行进行排序,然后按降序对列进行排序
- 矩阵中间行和列的总和
- 矩阵的按行遍历与按列遍历
- 向右旋转矩阵 K 次
- 检查幂等矩阵的程序
- 程序检查对合矩阵
- 矩阵中第一行和最后一行的交换元素
- zag-zag 方式打印矩阵
- 二维数组中的按行排序
- 马尔可夫矩阵程序
- 检查对角矩阵和标量矩阵的程序
- 按行和列对矩阵进行排序
- 查找岛屿数| 系列 1(使用 DFS)
- 魔术广场| 偶数订单
- 魔术广场
- 检查给定矩阵是否为幻方
- 检查给定矩阵是否为幻方
- 两种矩阵的 Kronecker 积
- 计数总和可分为“ k”的子矩阵
- 对角占优矩阵
- 使矩阵的每一行和每一列相等所需的最少操作
- 计算大小为 n 的矩阵中 k 的频率,其中 matrix(i,j)= i + j
- 给定 1、2、3……k 以之字形打印它们。
- 皇后可以在棋盘上移动的障碍物数量
- 矩阵中 4 个相邻元素的最大积
- 使二进制矩阵对称所需的最小翻转
- 程序检查矩阵是否为下三角
- 程序检查矩阵是否为上三角
- 矩阵中偶数和奇数的频率
- 矩阵的中心元素等于对角线的一半
- 身份矩阵程序
- 程序用矩阵的下对角元素交换上对角元素。
- 稀疏矩阵表示| 系列 3(CSR)
- 填充矩阵以使所有行和所有列的乘积等于 1 的方式
- 矩阵对角线的镜像
- 查找二进制矩阵中是否有一个角为 1 的矩形
- 查找所有填充有 0 的矩形
- 矩阵或网格中两个单元之间的最短距离
- 计算二进制矩阵中 1 和 0 的集合
- 搜索按行和按列排序的矩阵
- 创建具有 O 和 X 的交替矩形的矩阵
- 矩阵的锯齿形(或对角线)遍历
- 原位(固定空间)M x N 大小的矩阵转置| 更新
- 排序从 0 到 n ^ 2 – 1 的数字矩阵的最低成本
- 二进制矩阵中的唯一像元
- 计算特殊矩阵中等于 x 的条目
- 检查给定矩阵是否稀疏
- 方矩阵的两个对角线中的行式公共元素
- 检查矩阵中第 i 行和第 i 列的总和是否相同
- 查找最大数为 1 的二进制矩阵的行号
- 程序检查矩阵是否对称
- 通过遵循单元格值来查找二维数组是否被完全遍历
- 程序以 Z 格式打印矩阵
- 在矩阵中从左上到右下打印所有回文路径
- 骑士的可能举动
- 有效地计算矩阵的对角线总和
- 矩阵的边界元素
- 从点开始以螺旋形式打印矩阵
- 以蛇形图案打印矩阵
- 矩阵对角线互换程序
- 找出两个对角线之和之间的差
- 从给定的二叉树构造祖先矩阵
- 从祖先矩阵构造树
- 圆形矩阵(以螺旋方式构造数字 1 到 m * n 的矩阵)
- Sudoku Generator 程序
- 康威人生游戏计划
- 矩阵中沙漏的最大和
- 方阵中的最大值和最小值。
- 以防螺旋形式打印矩阵
- 查找矩阵的法线和迹线的程序
- 以各种方式对矩阵进行排序
- 设置二进制矩阵的所有元素所需的最少操作
- 以反向螺旋形式打印给定的矩阵
- C 程序检查矩阵是否倾斜对称
- 矩阵元素的总和,其中每个元素是行和列的整数除法
- 稀疏矩阵及其表示| 系列 2(使用列表和键字典)
- 查找使两个矩阵相等的变换数
- 形成矩阵线圈
- 每个元素是其行号和列号的绝对差的矩阵总和
- 检查二进制矩阵中的水平和垂直对称性
- 每个值为 0 或 n 的矩阵的最大行列式
- 螺旋奇数阶方阵的两个对角线之和
- 在二进制矩阵中找到具有最大位差的行对
- 查找矩阵中给定行的所有置换行
- 在二进制矩阵中查找以 1s 形成的形状的周长
- 在矩阵中打印具有相同矩形和的单元格
- 以对角线图案打印矩阵
- 矩阵中两行元素之和的最大差
- 查找具有给定总和的对,以便该对的元素位于不同的行中
- 二进制矩阵中所有零的总覆盖率
- 用行或列的最大 GCD 替换每个矩阵元素
- 计算矩阵中所有排序的行
- 矩阵查询
- 矩阵中的最大 XOR 值
- 可以从下到右传输光线的最大反射镜
- 最后一个方块的方向
- 以矩阵的螺旋形式打印第 K 个元素
- 查找给定的矩阵是否为 Toeplitz
- 在按行和按列排序的矩阵中计数零
- 在列明智和行明智排序矩阵中计算负数
- 在二进制矩阵中查找所有位形成的最大“ +”的大小
- 返回扩展矩阵中的前一个元素
- 使用O(1)额外空间打印 n x n 螺旋矩阵
- 二进制迷宫中的最短路径
- 查找矩阵中图案的方向
- 在矩阵中查找特定对
- 打印给定大小的最大和平方子矩阵
- 给定矩阵的所有行中的公共元素
- 按特定顺序就地转换矩阵
- 布尔矩阵问题
- 给定布尔矩阵,找到 k,使第 k 行中的所有元素均为 0,第 k 列为 1。
- 在给定的布尔矩阵中打印唯一行
- 找到 1 的最大矩形,并允许交换列
- 给定井字棋盘配置的有效性
- 子矩阵总和查询
- 矩阵排名程序
- 全为 1 的最大尺寸矩形二进制子矩阵
- 全为 1 的最大尺寸正方形子矩阵
- 查找矩阵中除给定单元格的行和/或列中的元素以外的所有元素的总和?
- 计算每个岛按行和列分隔的岛数
- 在给定的按行排序的矩阵的所有行中找到一个公共元素
- 给定矩阵“ O”和“ X”,如果被“ X”包围,则将“ O”替换为“ X”
- 给定矩阵“ O”和“ X”,找到被“ X”包围的最大子正方形
- 洪水填充算法–如何在 paint 中实现 fill()?
- 从行和列的排序矩阵中按排序顺序打印所有元素
- 给定一个 n x n 方阵,求出大小为 k x k 的所有子方和
- 查找矩阵转置的程序
- 用于添加两个矩阵的程序
- 矩阵减法程序
- 使用两次遍历收集网格中的最大点
- 在死胡同之前收集最多硬币
- 正好有 k 个硬币的路径数
- 查找从给定起始字符开始的最长连续路径的长度
- 在给定约束条件下找到矩阵中的最长路径
- 到达目的地的最低初始点
- 分而治之| 第 5 组(Strassen 的矩阵乘法)
- 2D 矩阵中的最大和矩形| DP-27
- 杂项
- 子数组/子字符串与子序列以及生成它们的程序
- 产品数组难题
- 具有给定乘积的子数组数
- 链表与数组
- 检查数组元素是否连续 新增方法 3
- 查找一个数组是否是另一个数组的子集 新增方法 3
- 在一个数组中实现两个堆栈
- 查找两个排序数组的相对补码
- 通过 k 次运算的最小增量以使所有元素相等
- 最小化三个不同排序数组的(max(A [i],B [j],C [k])– min(A [i],B [j],C [k]))
