# TF Estimator - 以前的 TF 学习
TF Estimator 是一个高级 API,通过封装训练,评估,预测和导出函数,可以轻松创建和训练模型。 TensorFlow 最近重新命名并在 TensorFlow 中以新名称 TF Estimator 发布了 TF Learn 软件包,可能是为了避免与 tflearn.org 的 TFLearn 软件包混淆。 TF Estimator API 对原始 TF 学习包进行了重大改进,这些包在 KDD 17 会议上提供的研究论文中有所描述,可以在以下链接中找到: [https://doi.org/10.1145/3097983.3098171](https://doi.org/10.1145/3097983.3098171) 。
TF Estimator 界面设计灵感来自流行的机器学习库 SciKit Learn,允许从不同类型的可用模型创建估计器对象,然后在任何类型的估计器上提供四个主要函数:
* `estimator.fit()`
* `estimator.evaluate()`
* `estimator.predict()`
* `estimator.export()`
函数的名称是不言自明的。估计器对象表示模型,但模型本身是从提供给估计器的模型定义函数创建的。
我们可以在下图中描述估计器对象及其接口:
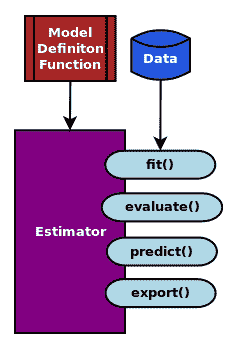
使用 Estimator API 而不是在核心 TensorFlow 中构建所有内容,可以不用担心图,会话,初始化变量或其他低级细节。在撰写本书时,TensorFlow 提供了以下预构建的估计器:
* `tf.contrib.learn.KMeansClustering`
* `tf.contrib.learn.DNNClassifier`
* `tf.contrib.learn.DNNRegressor`
* `tf.contrib.learn.DNNLinearCombinedRegressor`
* `tf.contrib.learn.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier`
* `tf.contrib.learn.LinearClassifier`
* `tf.contrib.learn.LinearRegressor`
* `tf.contrib.learn.LogisticRegressor`
TF Estimator API 中的简单工作流程如下:
1. 找到与您要解决的问题相关的预构建 Estimator。
2. 编写导入数据集的函数。
3. 定义包含特征的数据中的列。
4. 创建在步骤 1 中选择的预构建估计器的实例。
5. 训练估计器。
6. 使用经过训练的估计器进行评估或预测。
下一章讨论的 Keras 库提供了将 Keras 模型转换为 Estimators 的便捷函数:`keras.estimator.model_to_estimator()`。
笔记本`ch-02_TF_High_Level_Libraries`中提供了 MNIST 分类示例的完整代码。 TF Estimator MNIST 示例的输出如下:
```py
INFO:tensorflow:Using default config.
WARNING:tensorflow:Using temporary folder as model directory: /tmp/tmprvcqgu07
INFO:tensorflow:Using config: {'_save_checkpoints_steps': None, '_task_type': 'worker', '_save_checkpoints_secs': 600, '_service': None, '_task_id': 0, '_master': '', '_session_config': None, '_num_worker_replicas': 1, '_keep_checkpoint_max': 5, '_cluster_spec': <tensorflow.python.training.server_lib.ClusterSpec object at 0x7ff9d15f5fd0>, '_keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours': 10000, '_log_step_count_steps': 100, '_is_chief': True, '_save_summary_steps': 100, '_model_dir': '/tmp/tmprvcqgu07', '_num_ps_replicas': 0, '_tf_random_seed': None}
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook.
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into /tmp/tmprvcqgu07/model.ckpt.
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 2.4365, step = 1
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 597.996
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 1.47152, step = 101 (0.168 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 553.29
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.728581, step = 201 (0.182 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 519.498
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.89795, step = 301 (0.193 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 503.414
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.743328, step = 401 (0.202 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 539.251
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.413222, step = 501 (0.181 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 572.327
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.416304, step = 601 (0.174 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 543.99
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.459793, step = 701 (0.184 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 687.748
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.501756, step = 801 (0.146 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:global_step/sec: 654.217
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.666772, step = 901 (0.153 sec)
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1000 into /tmp/tmprvcqgu07/model.ckpt.
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 0.426257.
INFO:tensorflow:Starting evaluation at 2017-12-15-02:27:45
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from /tmp/tmprvcqgu07/model.ckpt-1000
INFO:tensorflow:Finished evaluation at 2017-12-15-02:27:45
INFO:tensorflow:Saving dict for global step 1000: accuracy = 0.8856, global_step = 1000, loss = 0.40996
{'accuracy': 0.88559997, 'global_step': 1000, 'loss': 0.40995964}
```
您将在第 5 章中看到如何使用核心 TensorFlow 创建此类模型。
- TensorFlow 101
- 什么是 TensorFlow?
- TensorFlow 核心
- 代码预热 - Hello TensorFlow
- 张量
- 常量
- 操作
- 占位符
- 从 Python 对象创建张量
- 变量
- 从库函数生成的张量
- 使用相同的值填充张量元素
- 用序列填充张量元素
- 使用随机分布填充张量元素
- 使用tf.get_variable()获取变量
- 数据流图或计算图
- 执行顺序和延迟加载
- 跨计算设备执行图 - CPU 和 GPU
- 将图节点放置在特定的计算设备上
- 简单放置
- 动态展示位置
- 软放置
- GPU 内存处理
- 多个图
- TensorBoard
- TensorBoard 最小的例子
- TensorBoard 详情
- 总结
- TensorFlow 的高级库
- TF Estimator - 以前的 TF 学习
- TF Slim
- TFLearn
- 创建 TFLearn 层
- TFLearn 核心层
- TFLearn 卷积层
- TFLearn 循环层
- TFLearn 正则化层
- TFLearn 嵌入层
- TFLearn 合并层
- TFLearn 估计层
- 创建 TFLearn 模型
- TFLearn 模型的类型
- 训练 TFLearn 模型
- 使用 TFLearn 模型
- PrettyTensor
- Sonnet
- 总结
- Keras 101
- 安装 Keras
- Keras 中的神经网络模型
- 在 Keras 建立模型的工作流程
- 创建 Keras 模型
- 用于创建 Keras 模型的顺序 API
- 用于创建 Keras 模型的函数式 API
- Keras 层
- Keras 核心层
- Keras 卷积层
- Keras 池化层
- Keras 本地连接层
- Keras 循环层
- Keras 嵌入层
- Keras 合并层
- Keras 高级激活层
- Keras 正则化层
- Keras 噪音层
- 将层添加到 Keras 模型
- 用于将层添加到 Keras 模型的顺序 API
- 用于向 Keras 模型添加层的函数式 API
- 编译 Keras 模型
- 训练 Keras 模型
- 使用 Keras 模型进行预测
- Keras 的附加模块
- MNIST 数据集的 Keras 序列模型示例
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 进行经典机器学习
- 简单的线性回归
- 数据准备
- 构建一个简单的回归模型
- 定义输入,参数和其他变量
- 定义模型
- 定义损失函数
- 定义优化器函数
- 训练模型
- 使用训练的模型进行预测
- 多元回归
- 正则化回归
- 套索正则化
- 岭正则化
- ElasticNet 正则化
- 使用逻辑回归进行分类
- 二分类的逻辑回归
- 多类分类的逻辑回归
- 二分类
- 多类分类
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的神经网络和 MLP
- 感知机
- 多层感知机
- 用于图像分类的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 TensorFlow 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 Keras 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 TFLearn 的 MLP
- 使用 TensorFlow,Keras 和 TFLearn 的 MLP 总结
- 用于时间序列回归的 MLP
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 RNN
- 简单循环神经网络
- RNN 变种
- LSTM 网络
- GRU 网络
- TensorFlow RNN
- TensorFlow RNN 单元类
- TensorFlow RNN 模型构建类
- TensorFlow RNN 单元包装器类
- 适用于 RNN 的 Keras
- RNN 的应用领域
- 用于 MNIST 数据的 Keras 中的 RNN
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的时间序列数据的 RNN
- 航空公司乘客数据集
- 加载 airpass 数据集
- 可视化 airpass 数据集
- 使用 TensorFlow RNN 模型预处理数据集
- TensorFlow 中的简单 RNN
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM
- TensorFlow 中的 GRU
- 使用 Keras RNN 模型预处理数据集
- 使用 Keras 的简单 RNN
- 使用 Keras 的 LSTM
- 使用 Keras 的 GRU
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的文本数据的 RNN
- 词向量表示
- 为 word2vec 模型准备数据
- 加载和准备 PTB 数据集
- 加载和准备 text8 数据集
- 准备小验证集
- 使用 TensorFlow 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 t-SNE 可视化单词嵌入
- keras 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的 RNN 模型生成文本
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- Keras 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 CNN
- 理解卷积
- 了解池化
- CNN 架构模式 - LeNet
- 用于 MNIST 数据的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 使用 Keras 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 用于 CIFAR10 数据的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 使用 Keras 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的自编码器
- 自编码器类型
- TensorFlow 中的栈式自编码器
- Keras 中的栈式自编码器
- TensorFlow 中的去噪自编码器
- Keras 中的去噪自编码器
- TensorFlow 中的变分自编码器
- Keras 中的变分自编码器
- 总结
- TF 服务:生产中的 TensorFlow 模型
- 在 TensorFlow 中保存和恢复模型
- 使用保护程序类保存和恢复所有图变量
- 使用保护程序类保存和恢复所选变量
- 保存和恢复 Keras 模型
- TensorFlow 服务
- 安装 TF 服务
- 保存 TF 服务的模型
- 提供 TF 服务模型
- 在 Docker 容器中提供 TF 服务
- 安装 Docker
- 为 TF 服务构建 Docker 镜像
- 在 Docker 容器中提供模型
- Kubernetes 中的 TensorFlow 服务
- 安装 Kubernetes
- 将 Docker 镜像上传到 dockerhub
- 在 Kubernetes 部署
- 总结
- 迁移学习和预训练模型
- ImageNet 数据集
- 再训练或微调模型
- COCO 动物数据集和预处理图像
- TensorFlow 中的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中预训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- TensorFlow 中的图像预处理,用于预训练的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- Keras 的 VGG16
- 使用 Keras 中预训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- 使用 Keras 中再训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3 进行图像分类
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再训练的 Inception v3 进行图像分类
- 总结
- 深度强化学习
- OpenAI Gym 101
- 将简单的策略应用于 cartpole 游戏
- 强化学习 101
- Q 函数(在模型不可用时学习优化)
- RL 算法的探索与开发
- V 函数(模型可用时学习优化)
- 强化学习技巧
- 强化学习的朴素神经网络策略
- 实现 Q-Learning
- Q-Learning 的初始化和离散化
- 使用 Q-Table 进行 Q-Learning
- Q-Network 或深 Q 网络(DQN)的 Q-Learning
- 总结
- 生成性对抗网络
- 生成性对抗网络 101
- 建立和训练 GAN 的最佳实践
- 使用 TensorFlow 的简单的 GAN
- 使用 Keras 的简单的 GAN
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的深度卷积 GAN
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 集群的分布式模型
- 分布式执行策略
- TensorFlow 集群
- 定义集群规范
- 创建服务器实例
- 定义服务器和设备之间的参数和操作
- 定义并训练图以进行异步更新
- 定义并训练图以进行同步更新
- 总结
- 移动和嵌入式平台上的 TensorFlow 模型
- 移动平台上的 TensorFlow
- Android 应用中的 TF Mobile
- Android 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- iOS 应用中的 TF Mobile
- iOS 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- TensorFlow Lite
- Android 上的 TF Lite 演示
- iOS 上的 TF Lite 演示
- 总结
- R 中的 TensorFlow 和 Keras
- 在 R 中安装 TensorFlow 和 Keras 软件包
- R 中的 TF 核心 API
- R 中的 TF 估计器 API
- R 中的 Keras API
- R 中的 TensorBoard
- R 中的 tfruns 包
- 总结
- 调试 TensorFlow 模型
- 使用tf.Session.run()获取张量值
- 使用tf.Print()打印张量值
- 用tf.Assert()断言条件
- 使用 TensorFlow 调试器(tfdbg)进行调试
- 总结
- 张量处理单元
