# 定义并训练图以进行异步更新
如前所述,并在此处的图中显示,在异步更新中,所有工作任务在准备就绪时发送参数更新,参数服务器更新参数并发回参数。参数更新没有同步或等待或聚合:
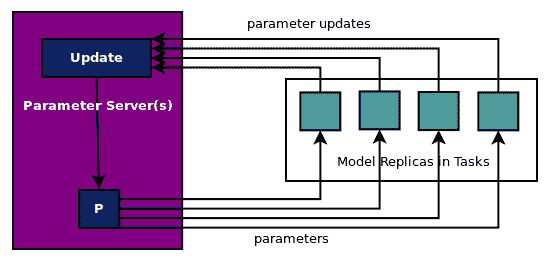The full code for this example is in `ch-15_mnist_dist_async.py`. You are encouraged to modify and explore the code with your own datasets.
对于异步更新,将使用以下步骤创建和训练图:
1. 图的定义在`with`块内完成:
```py
with tf.device(device_func):
```
1. 使用内置的 TensorFlow 函数创建全局步骤变量:
```py
global_step = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
```
1. 此变量也可以定义为:
```py
tf.Variable(0,name='global_step',trainable=False)
```
1. 像往常一样定义数据集,参数和超参数:
```py
x_test = mnist.test.images
y_test = mnist.test.labels
n_outputs = 10 # 0-9 digits
n_inputs = 784 # total pixels
learning_rate = 0.01
n_epochs = 50
batch_size = 100
n_batches = int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
n_epochs_print=10
```
1. 像往常一样定义占位符,权重,偏差,logits,交叉熵,损失操作,训练操作,准确率:
```py
# input images
x_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,
name='x_p',
shape=[None, n_inputs])
# target output
y_p = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32,
name='y_p',
shape=[None, n_outputs])
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_inputs, n_outputs],
name='w'
)
)
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_outputs],
name='b'
)
)
logits = tf.matmul(x_p,w) + b
entropy_op = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_p,
logits=logits
)
loss_op = tf.reduce_mean(entropy_op)
optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss_op,global_step=global_step)
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(logits, 1), tf.argmax(y_p, 1))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
```
当我们学习如何构建同步更新时,这些定义将会改变。
1. TensorFlow 提供了一个主管类,可以帮助创建训练会话,在分布式训练设置中非常有用。创建一个 supervisor 对象,如下所示:
```py
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer
sv = tf.train.Supervisor(is_chief=is_chief,
init_op = init_op(),
global_step=global_step)
```
1. 使用 supervisor 对象创建会话并像往常一样在此会话块下运行训练:
```py
with sv.prepare_or_wait_for_session(server.target) as mts:
lstep = 0
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
for batch in range(n_batches):
x_batch, y_batch = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
feed_dict={x_p:x_batch,y_p:y_batch}
_,loss,gstep=mts.run([train_op,loss_op,global_step],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
lstep +=1
if (epoch+1)%n_epochs_print==0:
print('worker={},epoch={},global_step={}, \
local_step={},loss={}'.
format(FLAGS.task_index,epoch,gstep,lstep,loss))
feed_dict={x_p:x_test,y_p:y_test}
accuracy = mts.run(accuracy_op, feed_dict=feed_dict)
print('worker={}, final accuracy = {}'
.format(FLAGS.task_index,accuracy))
```
在启动参数服务器时,我们得到以下输出:
```py
$ python3 ch-15_mnist_dist_async.py --job_name='ps' --task_index=**0**
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1030] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Quadro P5000 major: 6 minor: 1 memoryClockRate(GHz): 1.506
pciBusID: 0000:01:00.0
totalMemory: 15.89GiB freeMemory: 15.79GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1120] Creating TensorFlow device (/device:GPU:0) -> (device: 0, name: Quadro P5000, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1)
E1213 16:50:14.023235178 27224 ev_epoll1_linux.c:1051] grpc epoll fd: 23
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job ps -> {0 -> localhost:9001}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job worker -> {0 -> localhost:9002, 1 -> localhost:9003, 2 -> localhost:9004}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_server_lib.cc:324] Started server with target: grpc://localhost:9001
```
在启动工作任务时,我们得到以下三个输出:
工作器 1 的输出:
```py
$ python3 ch-15_mnist_dist_async.py --job_name='worker' --task_index=**0**
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1030] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Quadro P5000 major: 6 minor: 1 memoryClockRate(GHz): 1.506
pciBusID: 0000:01:00.0
totalMemory: 15.89GiB freeMemory: 9.16GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1120] Creating TensorFlow device (/device:GPU:0) -> (device: 0, name: Quadro P5000, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1)
E1213 16:50:37.516609689 27507 ev_epoll1_linux.c:1051] grpc epoll fd: 23
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job ps -> {0 -> localhost:9001}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job worker -> {0 -> localhost:9002, 1 -> localhost:9003, 2 -> localhost:9004}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_server_lib.cc:324] Started server with target: grpc://localhost:9002
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/master_session.cc:1004] Start master session 1421824c3df413b5 with config: gpu_options { per_process_gpu_memory_fraction: 0.2 } allow_soft_placement: true
worker=0,epoch=9,global_step=10896, local_step=5500, loss = 1.2575616836547852
worker=0,epoch=19,global_step=22453, local_step=11000, loss = 0.7158586382865906
worker=0,epoch=29,global_step=39019, local_step=16500, loss = 0.43712112307548523
worker=0,epoch=39,global_step=55513, local_step=22000, loss = 0.3935799300670624
worker=0,epoch=49,global_step=72002, local_step=27500, loss = 0.3877961337566376
worker=0, final accuracy = 0.8865000009536743
```
工作器 2 的输出:
```py
$ python3 ch-15_mnist_dist_async.py --job_name='worker' --task_index=**1**
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1030] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Quadro P5000 major: 6 minor: 1 memoryClockRate(GHz): 1.506
pciBusID: 0000:01:00.0
totalMemory: 15.89GiB freeMemory: 12.43GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1120] Creating TensorFlow device (/device:GPU:0) -> (device: 0, name: Quadro P5000, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1)
E1213 16:50:36.684334877 27461 ev_epoll1_linux.c:1051] grpc epoll fd: 23
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job ps -> {0 -> localhost:9001}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job worker -> {0 -> localhost:9002, 1 -> localhost:9003, 2 -> localhost:9004}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_server_lib.cc:324] Started server with target: grpc://localhost:9003
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/master_session.cc:1004] Start master session 2bd8a136213a1fce with config: gpu_options { per_process_gpu_memory_fraction: 0.2 } allow_soft_placement: true
worker=1,epoch=9,global_step=11085, local_step=5500, loss = 0.6955764889717102
worker=1,epoch=19,global_step=22728, local_step=11000, loss = 0.5891970992088318
worker=1,epoch=29,global_step=39074, local_step=16500, loss = 0.4183048903942108
worker=1,epoch=39,global_step=55599, local_step=22000, loss = 0.32243454456329346
worker=1,epoch=49,global_step=72105, local_step=27500, loss = 0.5384714007377625
worker=1, final accuracy = 0.8866000175476074
```
工作器 3 的输出:
```py
$ python3 ch-15_mnist_dist_async.py --job_name='worker' --task_index=**2**
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1030] Found device 0 with properties:
name: Quadro P5000 major: 6 minor: 1 memoryClockRate(GHz): 1.506
pciBusID: 0000:01:00.0
totalMemory: 15.89GiB freeMemory: 15.70GiB
I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:1120] Creating TensorFlow device (/device:GPU:0) -> (device: 0, name: Quadro P5000, pci bus id: 0000:01:00.0, compute capability: 6.1)
E1213 16:50:35.568349791 27449 ev_epoll1_linux.c:1051] grpc epoll fd: 23
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job ps -> {0 -> localhost:9001}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_channel.cc:215] Initialize GrpcChannelCache for job worker -> {0 -> localhost:9002, 1 -> localhost:9003, 2 -> localhost:9004}
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/rpc/grpc_server_lib.cc:324] Started server with target: grpc://The full code for this example is in ch-15_mnist_dist_sync.py. You are encouraged to modify and explore the code with your own datasets.localhost:9004
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/master_session.cc:1004] Start master session cb0749c9f5fc163e with config: gpu_options { per_process_gpu_memory_fraction: 0.2 } allow_soft_placement: true
I tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime/master_session.cc:1004] Start master session 55bf9a2b9718a571 with config: gpu_options { per_process_gpu_memory_fraction: 0.2 } allow_soft_placement: true
worker=2,epoch=9,global_step=37367, local_step=5500, loss = 0.8077645301818848
worker=2,epoch=19,global_step=53859, local_step=11000, loss = 0.26333487033843994
worker=2,epoch=29,global_step=70299, local_step=16500, loss = 0.6506651043891907
worker=2,epoch=39,global_step=76999, local_step=22000, loss = 0.20321622490882874
worker=2,epoch=49,global_step=82499, local_step=27500, loss = 0.4170967936515808
worker=2, final accuracy = 0.8894000053405762
```
我们打印了全球步骤和本地步骤。全局步骤表示所有工作器任务的步数,而本地步骤是该工作器任务中的计数,这就是为什么本地任务计数高达 27,500 并且每个工作器的每个周期都相同,但是因为工作器正在做按照自己的步伐采取全球性措施,全球步骤的数量在周期或工作器之间没有对称性或模式。此外,我们发现每个工作器的最终准确率是不同的,因为每个工作器在不同的时间执行最终的准确性,当时有不同的参数。
- TensorFlow 101
- 什么是 TensorFlow?
- TensorFlow 核心
- 代码预热 - Hello TensorFlow
- 张量
- 常量
- 操作
- 占位符
- 从 Python 对象创建张量
- 变量
- 从库函数生成的张量
- 使用相同的值填充张量元素
- 用序列填充张量元素
- 使用随机分布填充张量元素
- 使用tf.get_variable()获取变量
- 数据流图或计算图
- 执行顺序和延迟加载
- 跨计算设备执行图 - CPU 和 GPU
- 将图节点放置在特定的计算设备上
- 简单放置
- 动态展示位置
- 软放置
- GPU 内存处理
- 多个图
- TensorBoard
- TensorBoard 最小的例子
- TensorBoard 详情
- 总结
- TensorFlow 的高级库
- TF Estimator - 以前的 TF 学习
- TF Slim
- TFLearn
- 创建 TFLearn 层
- TFLearn 核心层
- TFLearn 卷积层
- TFLearn 循环层
- TFLearn 正则化层
- TFLearn 嵌入层
- TFLearn 合并层
- TFLearn 估计层
- 创建 TFLearn 模型
- TFLearn 模型的类型
- 训练 TFLearn 模型
- 使用 TFLearn 模型
- PrettyTensor
- Sonnet
- 总结
- Keras 101
- 安装 Keras
- Keras 中的神经网络模型
- 在 Keras 建立模型的工作流程
- 创建 Keras 模型
- 用于创建 Keras 模型的顺序 API
- 用于创建 Keras 模型的函数式 API
- Keras 层
- Keras 核心层
- Keras 卷积层
- Keras 池化层
- Keras 本地连接层
- Keras 循环层
- Keras 嵌入层
- Keras 合并层
- Keras 高级激活层
- Keras 正则化层
- Keras 噪音层
- 将层添加到 Keras 模型
- 用于将层添加到 Keras 模型的顺序 API
- 用于向 Keras 模型添加层的函数式 API
- 编译 Keras 模型
- 训练 Keras 模型
- 使用 Keras 模型进行预测
- Keras 的附加模块
- MNIST 数据集的 Keras 序列模型示例
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 进行经典机器学习
- 简单的线性回归
- 数据准备
- 构建一个简单的回归模型
- 定义输入,参数和其他变量
- 定义模型
- 定义损失函数
- 定义优化器函数
- 训练模型
- 使用训练的模型进行预测
- 多元回归
- 正则化回归
- 套索正则化
- 岭正则化
- ElasticNet 正则化
- 使用逻辑回归进行分类
- 二分类的逻辑回归
- 多类分类的逻辑回归
- 二分类
- 多类分类
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的神经网络和 MLP
- 感知机
- 多层感知机
- 用于图像分类的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 TensorFlow 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 Keras 的 MLP
- 用于 MNIST 分类的基于 TFLearn 的 MLP
- 使用 TensorFlow,Keras 和 TFLearn 的 MLP 总结
- 用于时间序列回归的 MLP
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 RNN
- 简单循环神经网络
- RNN 变种
- LSTM 网络
- GRU 网络
- TensorFlow RNN
- TensorFlow RNN 单元类
- TensorFlow RNN 模型构建类
- TensorFlow RNN 单元包装器类
- 适用于 RNN 的 Keras
- RNN 的应用领域
- 用于 MNIST 数据的 Keras 中的 RNN
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的时间序列数据的 RNN
- 航空公司乘客数据集
- 加载 airpass 数据集
- 可视化 airpass 数据集
- 使用 TensorFlow RNN 模型预处理数据集
- TensorFlow 中的简单 RNN
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM
- TensorFlow 中的 GRU
- 使用 Keras RNN 模型预处理数据集
- 使用 Keras 的简单 RNN
- 使用 Keras 的 LSTM
- 使用 Keras 的 GRU
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的文本数据的 RNN
- 词向量表示
- 为 word2vec 模型准备数据
- 加载和准备 PTB 数据集
- 加载和准备 text8 数据集
- 准备小验证集
- 使用 TensorFlow 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 t-SNE 可视化单词嵌入
- keras 的 skip-gram 模型
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 中的 RNN 模型生成文本
- TensorFlow 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- Keras 中的 LSTM 文本生成
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的 CNN
- 理解卷积
- 了解池化
- CNN 架构模式 - LeNet
- 用于 MNIST 数据的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 使用 Keras 的用于 MNIST 的 LeNet CNN
- 用于 CIFAR10 数据的 LeNet
- 使用 TensorFlow 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 使用 Keras 的用于 CIFAR10 的 ConvNets
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的自编码器
- 自编码器类型
- TensorFlow 中的栈式自编码器
- Keras 中的栈式自编码器
- TensorFlow 中的去噪自编码器
- Keras 中的去噪自编码器
- TensorFlow 中的变分自编码器
- Keras 中的变分自编码器
- 总结
- TF 服务:生产中的 TensorFlow 模型
- 在 TensorFlow 中保存和恢复模型
- 使用保护程序类保存和恢复所有图变量
- 使用保护程序类保存和恢复所选变量
- 保存和恢复 Keras 模型
- TensorFlow 服务
- 安装 TF 服务
- 保存 TF 服务的模型
- 提供 TF 服务模型
- 在 Docker 容器中提供 TF 服务
- 安装 Docker
- 为 TF 服务构建 Docker 镜像
- 在 Docker 容器中提供模型
- Kubernetes 中的 TensorFlow 服务
- 安装 Kubernetes
- 将 Docker 镜像上传到 dockerhub
- 在 Kubernetes 部署
- 总结
- 迁移学习和预训练模型
- ImageNet 数据集
- 再训练或微调模型
- COCO 动物数据集和预处理图像
- TensorFlow 中的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中预训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- TensorFlow 中的图像预处理,用于预训练的 VGG16
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- Keras 的 VGG16
- 使用 Keras 中预训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- 使用 Keras 中再训练的 VGG16 进行图像分类
- TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的 Inception v3 进行图像分类
- 使用 TensorFlow 中的再训练的 Inception v3 进行图像分类
- 总结
- 深度强化学习
- OpenAI Gym 101
- 将简单的策略应用于 cartpole 游戏
- 强化学习 101
- Q 函数(在模型不可用时学习优化)
- RL 算法的探索与开发
- V 函数(模型可用时学习优化)
- 强化学习技巧
- 强化学习的朴素神经网络策略
- 实现 Q-Learning
- Q-Learning 的初始化和离散化
- 使用 Q-Table 进行 Q-Learning
- Q-Network 或深 Q 网络(DQN)的 Q-Learning
- 总结
- 生成性对抗网络
- 生成性对抗网络 101
- 建立和训练 GAN 的最佳实践
- 使用 TensorFlow 的简单的 GAN
- 使用 Keras 的简单的 GAN
- 使用 TensorFlow 和 Keras 的深度卷积 GAN
- 总结
- 使用 TensorFlow 集群的分布式模型
- 分布式执行策略
- TensorFlow 集群
- 定义集群规范
- 创建服务器实例
- 定义服务器和设备之间的参数和操作
- 定义并训练图以进行异步更新
- 定义并训练图以进行同步更新
- 总结
- 移动和嵌入式平台上的 TensorFlow 模型
- 移动平台上的 TensorFlow
- Android 应用中的 TF Mobile
- Android 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- iOS 应用中的 TF Mobile
- iOS 上的 TF Mobile 演示
- TensorFlow Lite
- Android 上的 TF Lite 演示
- iOS 上的 TF Lite 演示
- 总结
- R 中的 TensorFlow 和 Keras
- 在 R 中安装 TensorFlow 和 Keras 软件包
- R 中的 TF 核心 API
- R 中的 TF 估计器 API
- R 中的 Keras API
- R 中的 TensorBoard
- R 中的 tfruns 包
- 总结
- 调试 TensorFlow 模型
- 使用tf.Session.run()获取张量值
- 使用tf.Print()打印张量值
- 用tf.Assert()断言条件
- 使用 TensorFlow 调试器(tfdbg)进行调试
- 总结
- 张量处理单元
